
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The type of the following organic reaction should be identified.
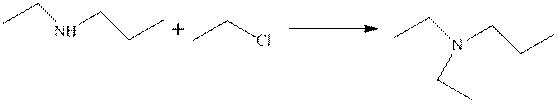
Concept introduction:
Nucleophilic substitution reaction is an organic reaction that includes the attack of a nucleophile on electrophilic center along with the removal of the leaving group.
(b)
Interpretation:
The type of the following organic reaction should be identified.
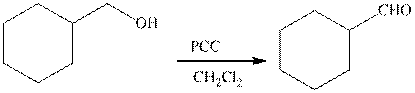
Concept introduction:
Oxidation reaction is defined as the addition of oxygen atom to the reactant molecule that causes the increase of the oxidation state of the reactant molecule.
Pyridinium chlorochromate(PCC) is a derivative of chromic acid but it is milder in nature. It is employed in the oxidation reaction of primary and secondary alcohol. The primary alcohol is oxidized to form
(c)
Interpretation:
The type of the following organic reaction should be identified.
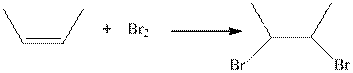
Concept introduction:
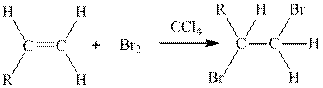
Where, R is an alkyl group.
(d)
Interpretation:
The type of following organic reaction should be identified.
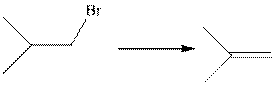
Concept introduction:
Elimination reaction is the type of reaction in which two substituents are removed from the reactant molecule to form the product Elimination reaction is of two types:
1.
2.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 27 Solutions
General Chemistry: Principles and Modern Applications (11th Edition)
- Synthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- If possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forward
- We mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
