
Concept explainers
1. be a point on the graph of .
(a) Express the distance d from P to the origin as a function of x.
(b) What is d if ?
(c) What is d if ?
(d) Use a graphing utility to graph .
(e) For what values of x is d smallest?
To find:
a. To express the distance from to the origin as a function of .
Answer to Problem 1AYU
Solution:
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
a. To express the distance from to the origin as a function of :
Since is a point on the graph . Substitute for . Then
To find:
b. To find if .
Answer to Problem 1AYU
Solution:
b. 8
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
b. To find if :
To find:
c. To find if .
Answer to Problem 1AYU
Solution:
c.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
c. To find if :
To find:
d. To graph .
Answer to Problem 1AYU
Solution:
d.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
d. To graph :
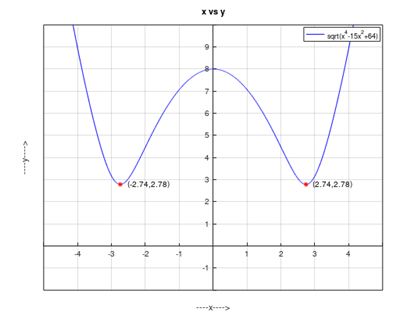
To find:
e. To find values of is smallest.
Answer to Problem 1AYU
Solution:
e.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
e. To find values of is smallest:
From the graph it can be seen that when attains its minimum.
Therefore, is smallest when .
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





