The crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) can be defined as CFSE = 31 number of electrons the dxy, dxx, and dyzorbitals are stabilized (lower energy) with respect to the average energy of thed orbitals and that the deand dr, orbitals are destabilized. As described in Are You Wondering 24-3, the stabilization is -0.4
a. Plot the hydration energies as a function of the
b. Assuming that all the hexaaqua complexes are high spin, which ions have zero CFSE?
c. If lines are drawn between those ions with CFSE = 0, a line of negative slope is obtained. Can you explain this finding?
d. The ions that do not have CFSE = 0 have heats of hydration that are more negative than the lines drawn in part (c). What is the explanation for this?
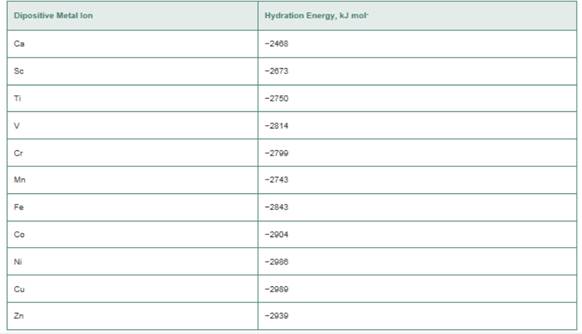
e. Estimate the value of L. for the Fe(ll) ion in an octahedral field of water molecules. What
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 24 Solutions
EP GENERAL CHEMISTRY-MOD.MASTERINGCHEM.
- Which of the following molecules are NOT typical carbohydrates? For the molecules that are carbohydrates, label them as an aldose or ketose. HO Он ОН ОН Он ОН но ΤΗ HO ОН HO eve Он он ОН ОН ОН If polyethylene has an average molecular weight of 25,000 g/mol, how many repeat units are present?arrow_forwardDraw the a-anomer cyclized pyranose Haworth projection of the below hexose. Circle the anomeric carbons. Number the carbons on the Fischer and Haworth projections. Assign R and S for each chiral center. HO CHO -H HO -H H- -OH H -OH CH₂OH Draw the ẞ-anomer cyclized furanose Haworth projection for the below hexose. Circle the anomeric carbons. Number the carbons on the Fischer and Haworth projections. HO CHO -H H -OH HO -H H -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardName the below disaccharide. Circle any hemiacetals. Identify the numbering of glycosidic linkage, and identify it as a or ẞ. OH HO HO OH HO HO HO OHarrow_forward
- What are the monomers used to make the following polymers? F. а. b. с. d. Вецер хочому なarrow_forward1. Propose a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I'm looking for curved mechanistic arrows and appropriate formal charges on intermediates. OMe MeO OMe Me2N NMe2 OTBS OH xylenes OMe 'OTBSarrow_forwardWhat is the polymer made from the following monomers? What type of polymerization is used for each? а. ОН H2N но b. ن -NH2 d. H₂N NH2 довarrow_forward
- Condensation polymers are produced when monomers containing two different functional groups link together with the loss of a small molecule such as H2O. The difunctional monomer H2N(CH2)6COOH forms a condensation polymer. Draw the carbon-skeleton structure of the dimer that forms from this monomer.arrow_forwardWhat is the structure of the monomer?arrow_forward→ BINDERIYA GANBO... BINDERIYA GANBO. AP Biology Notes Gamino acid chart - G... 36:22 司 10 ☐ Mark for Review Q 1 Hide 80 8 2 =HA O=A¯ = H₂O Acid HIO HBrO HCIO Question 10 of 35 ^ Σ DELL □ 3 % Λ & 6 7 * ∞ 8 do 5 $ 4 # m 3 ° ( 9 Highlights & Notes AXC Sign out Carrow_forward
- Which representation(s) show polymer structures that are likely to result in rigid, hard materials and those that are likely to result in flexible, stretchable, soft materials?arrow_forward3. Enter the molecular weight of the product obtained from the Williamson Ether Synthesis? OH OH & OH excess CH3l Ag₂Oarrow_forwardPlease answer 1, 2 and 3 on the endarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





