
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
Electrophilic
- 1) Generation of an electrophile
- 2) Attack of the electrophile on the aromatic ring, creating a resonance-stabilized carbocation called an arenium ion. It loses aromaticity in this step, so the energy of activation is high. Furthermore, this is the rate-determining step of the reaction because of the disruption of aromaticity. The arenium ion is a hybrid resonance structure. There are three general resonance contributors of an arenium ion.
- 3) Deprotonation of the arenium ion by a weak base to regain aromaticity.
Grignard reaction: The Grignard reaction is an organic reaction used to create a variety of products through the reaction of an organomagnesium compound, also known as a "Grignard reagent" with an electrophile, followed by acid work-up.
Reductive amination: Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions.
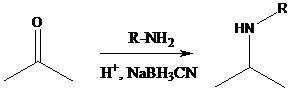
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (a) starting from benzene
Apply retrosynthetic analysis
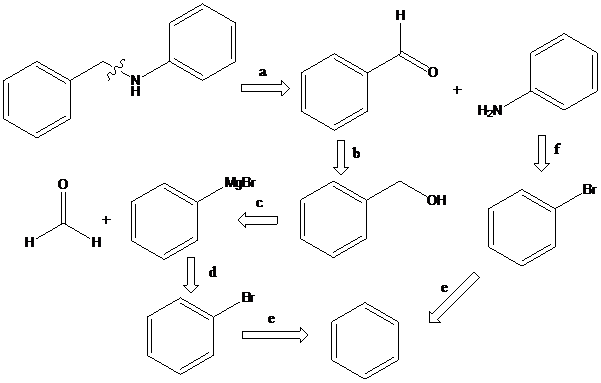
(b)
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution: Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as a result of an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. Here are three general steps to an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
- 1) Generation of an electrophile
- 2) Attack of the electrophile on the aromatic ring, creating a resonance-stabilized carbocation called an arenium ion. It loses aromaticity in this step, so the energy of activation is high. Furthermore, this is the rate-determining step of the reaction because of the disruption of aromaticity. The arenium ion is a hybrid resonance structure. There are three general resonance contributors of an arenium ion.
- 3) Deprotonation of the arenium ion by a weak base to regain aromaticity.
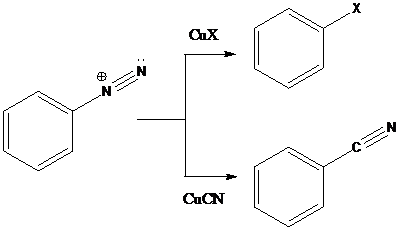
Sandmeyer reaction: Sandmeyer reactions use copper salts as the reagents. Here, aryldiazonium salt is converted into aryl halides or aryl cyanides by using copper halides or copper cyanides.
A compound containing an amino group is treated with sodium nitrite and HCl leading to the formation of diazonium salt.
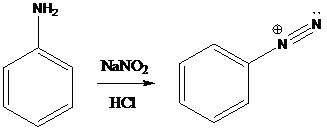
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (b) starting from benzene
Apply a retrosynthetic analysis

(c)
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution: Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a reaction in which the hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced as a result of an electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring. Here are three general steps to an electrophilic aromatic substitution.
- 1) Generation of an electrophile
- 2) Attack of the electrophile on the aromatic ring, creating a resonance-stabilized carbocation called an arenium ion. It loses aromaticity in this step, so the energy of activation is high. Furthermore, this is the rate-determining step of the reaction because of the disruption of aromaticity. The arenium ion is a hybrid resonance structure. There are three general resonance contributors of an arenium ion.
- 3) Deprotonation of the arenium ion by a weak base to regain aromaticity.
Grignard reaction: The Grignard reaction is an organic reaction used to create a variety of products through the reaction of an organomagnesium compound, also known as a "Grignard reagent" with an electrophile, followed by acid work-up.
Nucleophilic substitution reaction: It is the reaction of an electron pair donor (the nucleophile, Nu) with an electron pair acceptor (the electrophile). A sp3-hybridized electrophile must have a leaving group (X) in order for the reaction to take place. The term SN2 means that two molecules are involved in the actual transition state.
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (c) starting from benzene
Apply a retrosynthetic analysis
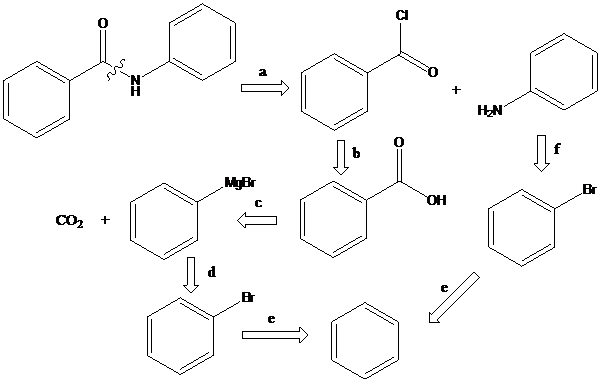
(d)
Interpretation: The synthetic routes for the given compounds starting from benzene have to be proposed
Concept Introduction:
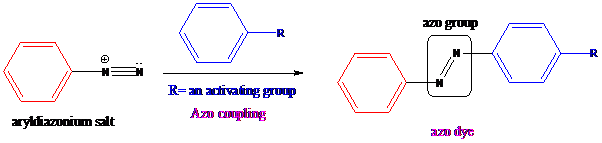
Azo coupling: Aryldiazonium salts on coupling with an activated aromatic ring give an azo dye which produces a deep color in the final product. This color is due to the extended conjugation in it. This reaction occurs by electrophilic substitution reaction. This method is called an azo coupling. The obtained final compound is known as azo dyes.
Friedel–Crafts acylation: The Friedel–Crafts acylation is the reaction of an arene with acyl chlorides or anhydrides using a strong Lewis acid catalyst. This reaction proceeds via electrophilic aromatic substitution to form monoacylated products.
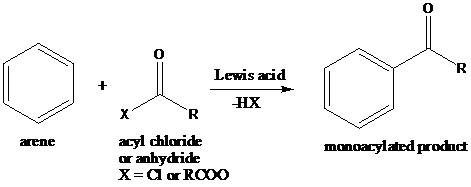
To find: Propose the synthetic routes for the given compound (d) starting from benzene
Apply a retrosynthetic analysis for the given azo dye

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Binder Ready Version
- + C8H16O2 (Fatty acid) + 11 02 → 8 CO2 a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? H2o CO₂ c. Which reactant is the electron donor? Futty acid d. Which reactant is the electron acceptor? e. Which of the product is now reduced? f. Which of the products is now oxidized? 02 #20 102 8 H₂O g. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? 2 h. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forward→ Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + 1FAD + 1ADP 2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1ATP a. Which of the above are the reactants? b. Which of the above are the products? c. Which reactant is the electron donor? d. Which reactants are the electron acceptors? e. Which of the products are now reduced? f. Which product is now oxidized? g. Which process was used to produce the ATP? h. Where was the energy initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? i. Where was the carbon initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished? j. Where were the electrons initially in this chemical reaction and where is it now that it is finished?arrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. OCH 3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) Br (Choose one) Explanation Check NO2 (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Aarrow_forward
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





