
(a)
Interpretation: Using a different type of reactions, 1-hexanol is to be prepared from hexyl amine, heptyl amine and pentyl amine
Concept Introduction: A number of transformations are used to prepare 1-hexanol. Some of them are listed as follows:
- a) Alcohol on treatment with phosphorous tribromide gives alkyl bromide
- b) Alkyl bromide in azide synthesis produces primary amine
- c) Alkyl halide on treatment with sodium cyanide gives alkyl cyanide
- d) Cyanide on reduction gives alkyl amine with an increment of one carbon atom skeleton
- e)
Alkene on ozonolysis produces carbonyl compounds - f)
Alkyl halides with strong base gives alkene - g) Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions.
Aldehyde orketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primaryamines .
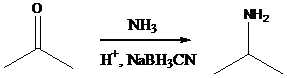
Using these concepts, we can transfer 1-hexanol into the given compounds.
(b)
Interpretation: Using a different type of reactions, 1-hexanol is to be prepared from hexyl amine, heptyl amine and pentyl amine
Concept Introduction: A number of transformations are used to prepare 1-hexanol. Some of them are listed as follows:
- a) Alcohol on treatment with phosphorous tribromide gives alkyl bromide
- b) Alkyl bromide in azide synthesis produces primary amine
- c) Alkyl halide on treatment with sodium cyanide gives alkyl cyanide
- d) Cyanide on reduction gives alkyl amine with an increment of one carbon atom skeleton
- e) Alkene on ozonolysis produces carbonyl compounds
- f) Alkyl halides with strong base gives alkene
- g) Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions. Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primary amines.
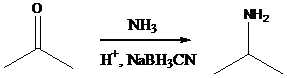
Using these concepts, we can transfer 1-hexanol into the given compounds.
(c)
Interpretation: Using a different type of reactions, 1-hexanol is to be prepared from hexyl amine, heptyl amine and pentyl amine
Concept Introduction: A number of transformations are used to prepare 1-hexanol. Some of them are listed as follows:
- a) Alcohol on treatment with phosphorous tribromide gives alkyl bromide
- b) Alkyl bromide in azide synthesis produces primary amine
- c) Alkyl halide on treatment with sodium cyanide gives alkyl cyanide
- d) Cyanide on reduction gives alkyl amine with an increment of one carbon atom skeleton
- e) Alkene on ozonolysis produces carbonyl compounds
- f) Alkyl halides with strong base gives alkene
- g) Sodium cyanoborohydride is a strong reducing agent than sodium borohydride. It reduces the carbonyl group into amine group in a rapid way. So, it is called as reductive amination reactions. Aldehyde or ketone group is reacted with ammonia in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent and a proton source in the reaction medium to produce primary amines.
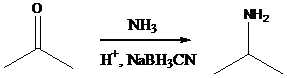
Using these concepts, we can transfer 1-hexanol into the given compounds.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Binder Ready Version
- Draw the mechanism to make the alcohol 2-hexanol. Draw the Mechanism to make the alcohol 1-hexanol.arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with 1-pentanal in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forwardIdentify each chiral carbon as either R or S. Identify the overall carbohydrates as L or Darrow_forward
- Ethers can be formed via acid-catalyzed acetal formation. Draw the mechanism for the molecule below and ethanol.arrow_forwardHOCH, H HO CH-OH OH H OH 11 CH₂OH F II OH H H 0 + H OHarrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the formation of diol by starting with one pen and all in... basic conditions then acidic conditions then draw the mechanism for the formation of a carboxylic acid from your product.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





