
(a)
Interpretation:
Starch should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Starch is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is starch.
Starch consists of many units of monosaccharide as it is a
Thus, starch is classified as polysaccharide.
(b)
Interpretation:
Glucose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Glucose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is glucose.
Glucose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule. Glucose is obtained by the photosynthesis process and also found in plants.
The structure is:
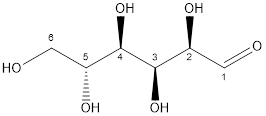
Thus, glucose is classified as monosaccharide.
(c)
Interpretation:
Sucrose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Sucrose is classified as disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is sucrose.
Sucrose consists of two units of monosaccharide. One fructose unit and glucose unit combined with each other by glycosidic bond to form sucrose.
The structure is:
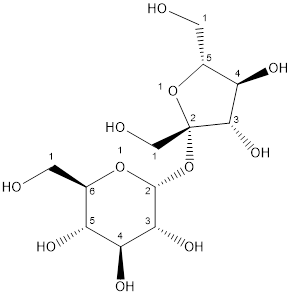
Thus, sucrose is classified as disaccharide.
(d)
Interpretation:
Ribose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Ribose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is ribose.
Ribose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule. Ribose consists of an
The structure is:
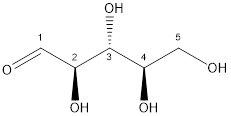
Thus, ribose is classified as monosaccharide.
(e)
Interpretation:
Cellulose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Cellulose is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is cellulose.
Cellulose consists of many units of monosaccharide or sugar as it is a polymeric carbohydrate which consists of various sugar units linked with glycosidic bonds.
Thus, cellulose is classified as polysaccharide.
(f)
Interpretation:
Glycogen should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds
Answer to Problem 52A
Glycogen is classified as polysaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is glycogen.
Glycogen consists of many units of monosaccharide or sugar as it is a polymeric carbohydrate which consists of various sugar units linked with glycosidic bonds.
Thus, glycogen is classified as polysaccharide.
(g)
Interpretation:
Fructose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Fructose is classified as monosaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is fructose.
Fructose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolysed into simpler molecule.
The structure is:
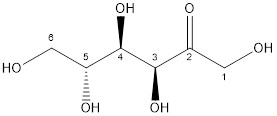
Thus, fructose is classified as monosaccharide.
(h)
Interpretation:
Lactose should be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides or polysaccharides.
Concept introduction:
A biological molecule which consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen is known as saccharide or carbohydrate. The general formula of saccharide is
Saccharides are classified as: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are defined as a simpler carbohydrate which contains one sugar molecule and can’t ne hydrolysed into smaller carbohydrate.
Disaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains two sugar molecules that is when two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds. It is a double ring structure.
Polysaccharides are defined as a saccharide which contains many units of sugar molecules that is more than two monosaccharides are linked by glycosidic bonds.
Answer to Problem 52A
Lactose is classified as disaccharide.
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is lactose.
Lactose consists of two units of monosaccharide or sugar. One galactose unit and glucose unit combined with each other by glycosidic bond to form sucrose.
The structure is:
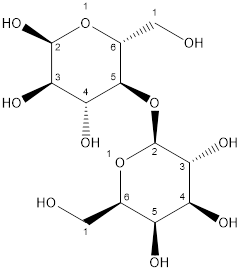
Thus, lactose is classified as disaccharide.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. 'N' 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forwardSubmit Problem 3 of 10 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the amine side product. O 'N' NH 1. NaOH, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Select to Drawarrow_forwardb) Certain cyclic compounds are known to be conformationally similar to carbohydrates, although they are not themselves carbohydrates. One example is Compound C shown below, which could be imagined as adopting four possible conformations. In reality, however, only one of these is particularly stable. Circle the conformation you expect to be the most stable, and provide an explanation to justify your choice. For your explanation to be both convincing and correct, it must contain not only words, but also "cartoon" orbital drawings contrasting the four structures. Compound C Possible conformations (circle one): Детarrow_forward
- Lab Data The distance entered is out of the expected range. Check your calculations and conversion factors. Verify your distance. Will the gas cloud be closer to the cotton ball with HCI or NH3? Did you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? - X Experimental Set-up HCI-NH3 NH3-HCI Longer Tube Time elapsed (min) 5 (exact) 5 (exact) Distance between cotton balls (cm) 24.30 24.40 Distance to cloud (cm) 9.70 14.16 Distance traveled by HCI (cm) 9.70 9.80 Distance traveled by NH3 (cm) 14.60 14.50 Diffusion rate of HCI (cm/hr) 116 118 Diffusion rate of NH3 (cm/hr) 175.2 175.2 How to measure distance and calculate ratearrow_forwardFor the titration of a divalent metal ion (M2+) with EDTA, the stoichiometry of the reaction is typically: 1:1 (one mole of EDTA per mole of metal ion) 2:1 (two moles of EDTA per mole of metal ion) 1:2 (one mole of EDTA per two moles of metal ion) None of the abovearrow_forwardPlease help me solve this reaction.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2,2-dimethylpropanal with acetaldehyde and sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





