
(a)
Interpretation:
Important functions of triglycerides should be listed.
Concept introduction:
The molecules which contain hydrocarbons and not soluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents is known as a lipid.
Lipids are classified as:
Triglycerides, Phospholipids and, Steroids and Waxes
The type of lipid found in our blood is known as triglycerides. Triglyceride is obtained by the three glycerol molecules and three fatty acids.
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids consist of carboxylic acids with a long aliphatic chain which can be saturated or unsaturated. Generally, fatty acids exist as phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesteryl esters. These are important structural components for cells.
In the structure of triglyceride, three glycerol molecules and three fatty acids are linked with each other by ester bonds.
The structure of triglyceride is:
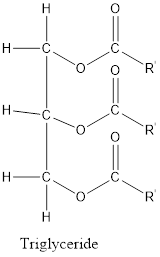
Where, R’ = alkyl group, etc.
The important functions of triglycerides are:
- Triglycerides provide energy to the body.
- Triglycerides are known to be the primary form of energy storage in the body.
- Triglycerides provide insulation that is thermal insulation. and protection to the body acting as fluid cushions.
- Triglycerides provide energy to the body.
- Triglycerides also act as transport for fat-soluble vitamins.
Thus, an important function of triglycerides is to be the primary form of energy storage in the body. They store the energy which is obtained by the breakdown of food and the energy is further used for various processes,
(b)
Interpretation:
Important functions of phospholipids should be listed.
Concept introduction:
The molecules which contain hydrocarbons and not soluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents is known as a lipid.
Lipids are classified as:
Triglycerides, Phospholipids and, Steroids and Waxes
The type of lipid found in our blood is known as triglycerides. Triglyceride is obtained by the three glycerol molecules and three fatty acids.
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids consist of a
The general structure of phospholipids contains a glycerol molecule(s), phosphate group and two fatty acids. These are known as complex lipids.
The important functions of phospholipids are:
- Phospholipids help in the formation of structural components of membranes and regulation of membrane permeability in association with proteins implies phospholipids help in the formation of cell membranes.
- Phospholipids maintain conformation in mitochondria of components of the electron transport chain.
- Phospholipids act as a transporter which helps in the transport of lipids in the blood.
- Phospholipids plays important role in the synthesis of different lipoproteins.
Thus, an important function of Phospholipids is formation of cell membrane
(c)
Interpretation:
Important functions of waxes should be listed.
Concept introduction:
The molecules which contain hydrocarbons and not soluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents is known as a lipid.
Lipids are classified as:
Triglycerides, Phospholipids and, Steroids and Waxes
The type of lipid found in our blood is known as triglycerides. Triglyceride is obtained by the three glycerol molecules and three fatty acids.
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids consist of a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain which can be saturated or unsaturated. Generally, fatty acids exist as phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesteryl esters. These are important structural components for cells.
A simple lipid consists of an ester of long-chain alcohol and fatty acid is known as wax. The alcohol present in a wax consists of 12-32 carbon atoms. The reaction between an alcohol and fatty acid results in the formation of wax having an ester bond.
An important function of wax is:
Wax provides a protective coating to the plants to control hydration, evaporation or to prevent them from drying. It is known as a water repellent. Waxes maintain animal skin and plants by forming a protective covering. In the case of plants, it prevents the loss of water.
(d)
Interpretation:
Important functions of steroids should be listed.
Concept introduction:
The molecules which contain hydrocarbons and not soluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents is known as a lipid.
Lipids are classified as:
Triglycerides, Phospholipids and, Steroids and Waxes
The type of lipid found in our blood is known as triglycerides. Triglyceride is obtained by the three glycerol molecules and three fatty acids.
Explanation of Solution
Fatty acids consist of carboxylic acids with a long aliphatic chain which can be saturated or unsaturated. Generally, fatty acids exist as phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesteryl esters. These are important structural components for cells.
The general structure of steroid contains 17 carbon atoms which are linked with each other in four fused rings, three rings contains six carbon atoms that are cyclohexane rings and one is a five-membered ring that is cyclopentane.
Important functions of steroids are:
- Steroids are the components of cell membranes that maintain the fluidity in the cell membrane. For example, Cholesterol decreases the fluidity of the membrane.
- Steroids also store energy like lipids.
- Steroids act as a hormone in the body.
An important function of Steroids is to maintain or control the activity of cell.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
- Indicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forwardA unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





