
Interpretation:
The number of possible isomers for galactose, glucose and fructose should be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The compounds having similar chemical formula but different structures are known as isomers.
The compounds having similar chemical or molecular formula but different connectivity is known as constitutional isomers.
Number of stereoisomers is calculated by below expression:
Where, n = number of chiral carbons
Answer to Problem 10SSC
Number of isomers of glucose = 16
Number of isomers of galactose = 16
Number of isomers of fructose = 8
Explanation of Solution
Glucose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolyzed into simpler molecule.
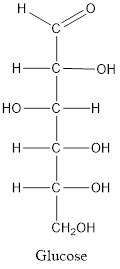
When a carbon atom is linked with different groups is known as chiral carbon and center is known as chiral center. Chiral center is represented by a symbol *.
The structure is drawn as with symbol *:
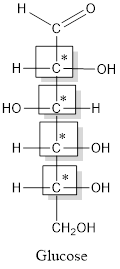
Thus, four chiral centers are present in the above structure as first four carbon atoms are linked with four different groups.
Number of isomers is calculated as:
Here, n = 4 (3 chiral carbon atoms are present)
Number of isomers =
= 16
Therefore, sixteen isomers are present for the structure of glucose.
Galactose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolyzed into simpler molecule.
In galactose, the hydroxyl group linked with forth carbon atom of the chain is present on left side whereas in glucose, the hydroxyl group linked with forth carbon atom of the chain is present on right side.
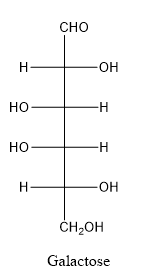
When a carbon atom is linked with different groups is known as chiral carbon and center is known as chiral center. Chiral center is represented by a symbol *.
The structure is drawn as with symbol *:
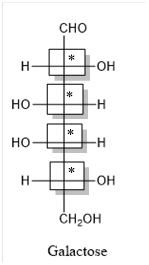
Thus, four chiral centers are present in the above structure as first four carbon atoms are linked with four different groups.
Number of isomers is calculated as:
Here, n = 4 (3 chiral carbon atoms are present)
Number of isomers =
= 16
Therefore, sixteen isomers are present for the structure of galactose.
Fructose consists of single unit of sugar which can’t be hydrolyzed into simpler molecule.
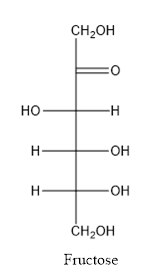
When a carbon atom is linked with different groups is known as chiral carbon and center is known as chiral center. Chiral center is represented by a symbol *.
The structure is drawn as with symbol *:
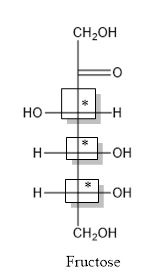
Thus, three chiral centers are present in the above structure as first three carbon atoms are linked with four different groups.
Number of isomers is calculated as:
Here, n = 3 (3 chiral carbon atoms are present)
Number of isomers =
= 8
Therefore, eight isomers are present for the structure of fructose.
Chapter 23 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





