
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780321948915
Author: William S. Klug, Michael R. Cummings, Charlotte A. Spencer, Michael A. Palladino
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 23, Problem 11PDQ
Corn plants from a test plot are measured, and the distribution of heights at 10-cm intervals is recorded in the following table:
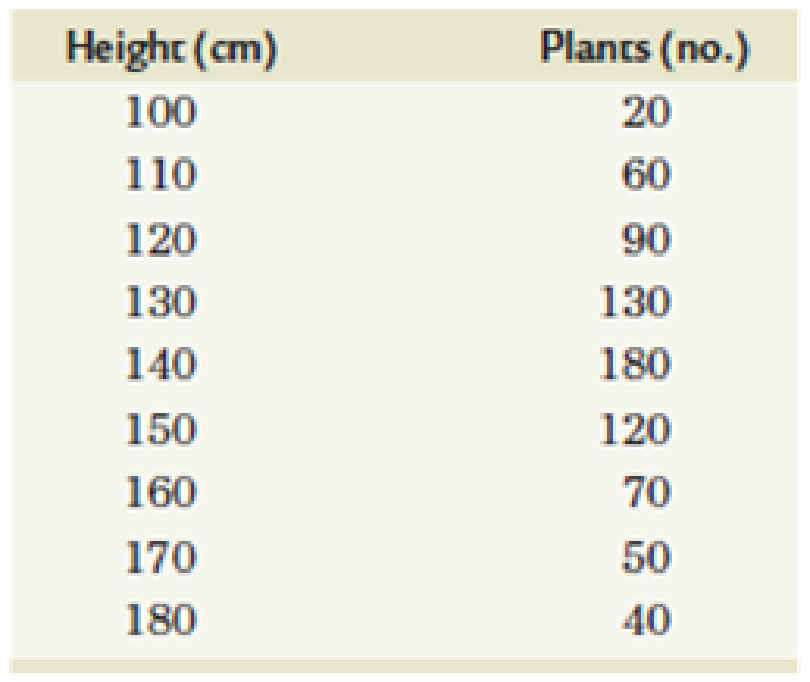
Calculate (a) the mean height, (b) the variance, (c) the standard deviation, and (d) the standard error of the mean. Plot a rough graph of plant height against frequency. Do the values represent a normal distribution? Based on your calculations, how would you assess the variation within this population?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Case Study—Ella
Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch.
Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen)
Breads
Spreads
Cheeses
Vegetables
Proteins
Specific food items to select
White Bread 6-inches
Honey Mustard
Provolone
LettuceTomatoBell Peppers
Turkey
Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories
How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich exactl ______kcal ?
Part B - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for…
C
MasteringHealth MasteringNu ×
session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17465255&attemptNo=1&offset=prev
Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Instant Absorption Questions
SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q
a) B1,
b) B2,
c) hybrid rate constant (1)
d) hybrid rate constant (2)
e) t1/2,dist
f) t1/2,elim
g) k10
h) k12
i) k21
j) initial concentration (C0)
k) central compartment volume (V1)
l) steady-state volume (Vss)
m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule
n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule
o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞)
p) total AUC (using short cut method)
q) volume from AUC (VAUC)
Chapter 23 Solutions
Concepts of Genetics (11th Edition)
Ch. 23 - A homozygous plant with 20-cm-diameter flowers is...Ch. 23 - The following table shows measurements for fiber...Ch. 23 - The following cable gives the percentage of twin...Ch. 23 - Prob. 1CSCh. 23 - Prob. 2CSCh. 23 - Prob. 3CSCh. 23 - HOW DO WE KNOW? In this chapter, we focused on a...Ch. 23 - CONCEPT QUESTION Review the Chapter Concepts list...Ch. 23 - Define the following: (a) polygenic, (b) additive...Ch. 23 - A dark-red strain and a white strain of wheat are...
Ch. 23 - Height in humans depends on the additive action of...Ch. 23 - An inbred strain of plants has a mean height of 24...Ch. 23 - Erma and Harvey were a compatible barnyard pair,...Ch. 23 - In the following table, average differences of...Ch. 23 - What kind of heritability estimates (broad sense...Ch. 23 - List as many human traits as you can that are...Ch. 23 - Corn plants from a test plot are measured, and the...Ch. 23 - The following variances were calculated for two...Ch. 23 - The mean and variance of plant height of two...Ch. 23 - Prob. 14PDQCh. 23 - Prob. 15PDQCh. 23 - In an assessment of learning in Drosophila, flies...Ch. 23 - Prob. 17PDQCh. 23 - Prob. 18PDQCh. 23 - In a population of 100 inbred, genotypically...Ch. 23 - Many traits of economic or medical significance...Ch. 23 - A 3-inch plant was crossed with a 15-inch plant,...Ch. 23 - In a cross between a strain of large guinea pigs...Ch. 23 - Type A1B brachydactyly (short middle phalanges) is...Ch. 23 - In a series of crosses between two true-breeding...Ch. 23 - Students in a genetics laboratory began an...Ch. 23 - Prob. 26ESPCh. 23 - Canine hip dysplasia is a quantitative trait that...Ch. 23 - Floral traits in plants often play key roles in...Ch. 23 - In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Glitazones reduce insulin resistance by binding to a transcription factor in adipocytes, thereby reducing thesecretion of fatty acids. Glitazones are taken orally (in pill form). Using pharmacokinetic modeling, deriveequations to describe how the concentration of glitazones varies in the plasma as a function of time. Yourequations should be of the form: dCglitazone /dt = something, or dMglitazone /dt = something. Your model shouldinclude three compartments: the gut, the plasma, and the fatty tissues. Make sure to include a diagram thatillustrates your thinking, state all assumptions, and define your variables. Do not solve the equations.arrow_forwardCase Study—Ella Review the case study and then answer Parts A through F. Ella has a family history of diabetes. She wants to follow a healthful eating pattern that can lower her risk for developing this condition. Her dietitian recommends a goal of 450 to 600 kcal per meal and advises Ella to follow the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for carbohydrates and the Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015-2020, which recommend limiting added sugar. She also recommends that Ella choose whole grains rather than processed grains. Ella decides to pack a lunch to take to work every day. This morning she’s making a sandwich for her lunch. Categories of Sandwich Options (Top of the screen) Breads Spreads Cheeses Vegetables Proteins Specific food items to select White Bread 6-inches Honey Mustard Provolone LettuceTomatoBell Peppers Turkey Part A - Reading Nutrition Facts Panels for Total Kilocalories How many total kilocalories are in Ella’s sandwich? _____…arrow_forward, if one of the archaeological specimens lacked the celiac disease-causing epitope, how could PCR be used to identify the allele in a contemporary germplasm collection of wild wheats, and to assist in transferring the allele to modern wheat varieties?arrow_forward
- Now you will consider the composition of lipoproteins, including where they are synthesized, how they circulate, and where the various lipid and protein components are located within the lipoprotein molecule. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.arrow_forwardThe Oregon Wolfe Barley mapping population is unique in having 12 easily-scored morphological markers, each showing monogenic inheritance. Do you consider these markers useful? Briefly defend your answer, pointing out advantages and disadvantages of morphological vs. molecular markers.arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Instant Absorption Questions Calculate these : a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
- In a population of Jackalopes (pictured below), horn length will vary between 0.5 and 2 feet, with the mean length somewhere around 1.05 feet. You pick Jackalopes that have horn lengths around 1.75 feet to breed as this appears to be the optimal length for battling other Jackalopes for food. After a round of breeding, you measure the offsprings' mean horn length is 1.67. What is the heritability of horns length (h2)? Is Jackalope horn length a heritable trait? (4 pts)? 12pt v R Paragraph V BIU A श्र > Barrow_forwardThere are many differences between DNA replication happening during mitosis in a Douglas fir tree growing in the Oregon Cascade Mountains and DNA replication happening during a PCR reaction in a forestry research lab at Oregon State University where the laboratory is amplifying a Simple Sequence Repeat. Complete the following table that compares the two DNA replication events in terms of the primers, the nucleotides, the polymerase, and the target sequence. Additionally, give a general value for the number of copies of the template DNA after one S phase in one cell and after the lab has completed the PCR reaction. Tree SSR Type your answer here: Primers Nucleotides Polymerase Target sequence Number of copiesarrow_forwardDescribe how insulin binding to its receptor induces glucose uptake in healthy individuals. Please specifyeach step in the cascade and use a diagram to illustrate the answer.arrow_forward
- There is a patient with breast cancer, after staining the breast tissue with H&E, state the molecular subtype of the tumour extracted. Results of H&E staining are down belowarrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Instant Absorption Questions Calculate these : a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardUse the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for a propanoic acid solution (CH₂CH₂CO₂H, pK₁ = 4.874) to calculate the quotient [A-]/[HA] at three different pH values. pH = 4.479 [A-] [HA] [A-] pH = 4.874 [HA] = pH = 5.220 [A-] = [HA]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning



Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Case Studies In Health Information Management
Biology
ISBN:9781337676908
Author:SCHNERING
Publisher:Cengage


Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to the NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods Fifth edition; Author: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B5rUrKLMoas;License: Standard Youtube License