
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 2P
In Fig. 22-34 the electric field lines on the left have twice the separation of those on the right. (a) If the magnitude of the field at A is 40 N/C, what is the magnitude of the force on a proton at A? (b) What is the magnitude of the magnitude of the field at B?
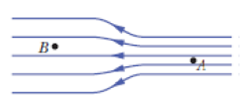
Figure 22-34 Problem 2.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
l
No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer
Chapter 22 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 22 - Figure 22-22 shows three arrangements of electric...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-23 shows two square arrays of charged...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-24, two particles of charge q are...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-25 shows four situations in which four...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-26 shows two charged particles fixed in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-27, two identical circular...Ch. 22 - The potential energies associated with four...Ch. 22 - a In Checkpoint 4, if the dipole rotates from...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-28 shows two disks and a flat ring, each...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-29, an electron e travels through a...
Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-30a, a circular plastic rod with...Ch. 22 - When three electric dipoles ire near each other,...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-32 shows three rods, each with the same...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-33 shows five protons that are launched...Ch. 22 - Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines both...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-34 the electric field lines on the left...Ch. 22 - SSM The nucleus of a plutonium-239 atom contains...Ch. 22 - Two charged particles are attached to an x axis:...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged particle produces an electric Held...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of a point charge that would...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-35, the four particles form...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-36, the four particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-37 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-38a shows two charged particles fixed...Ch. 22 - SSM Two charged particles are fixed to x axis:...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-39 shows an uneven arrangement of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-40 shows a proton on the central...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-41, particle 1 of charge q1 = 5.00q and...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-42, the three particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-43 shows a plastic ring of radius R =...Ch. 22 - Two charged beads are on the plastic ring in Fig....Ch. 22 - The electric field of an electric dipole along the...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-45 shows an electric dipole. What are...Ch. 22 - Equations 22-8 and 22-9 are approximations of the...Ch. 22 - SSM Electric quadrupole. Figure 22-46 shows a...Ch. 22 - Density, density, density. a A charge 300e is...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-47 shows two parallel nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-49 shows three circular arcs centered on...Ch. 22 - GO ILW In Fig. 22-50, a thin glass rod forms a...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig, 22-51, two curved plastic rods, one of...Ch. 22 - Charge is uniformly distributed around a ring of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-52a shows a nonconducting rod with a...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-53 shows two concentric rings, of...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-54, a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-56, a semi-infinite nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A disk of radius 2.5 cm has a surface charge...Ch. 22 - SSM WWW At what distance along the central...Ch. 22 - A circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm...Ch. 22 - Suppose you design an apparatus in which a...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-58a shows a circular disk that is...Ch. 22 - In Millikans experiment, an oil drop of radius...Ch. 22 - GO An electron with a speed of 5.00 108 cm/s...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged cloud system produces an electric...Ch. 22 - Humid air breaks down its molecules become ionized...Ch. 22 - SSM An electron is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 22 - An alpha particle the nucleus of a helium atom has...Ch. 22 - ILW An electron on the axis of an electric dipole...Ch. 22 - An electron is accelerated eastward at 1.80 ...Ch. 22 - SSM Beams of high-speed protons can be produced in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-59, an electron e is to be released...Ch. 22 - A 10.0 g block with a charge of 8.00 10-5 C is...Ch. 22 - At some instant the velocity components of an...Ch. 22 - Assume that a honeybee is a sphere of diameter...Ch. 22 - An electron eaters a region of uniform electric...Ch. 22 - GO Two large parallel copper plates are 5.0 cm...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-61, an electron is shot at an...Ch. 22 - ILW A uniform electric field exists in a region...Ch. 22 - An electric dipole consists of charges 2e and -2e...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole consisting of charges of...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - How much work is required to turn an electric...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - Find an expression for the oscillation frequency...Ch. 22 - a What is the magnitude of an electrons...Ch. 22 - A spherical water drop 1.20 m in diameter is...Ch. 22 - Three particles, each with positive charge Q, form...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-64a, a particle of charge Q produces an...Ch. 22 - A proton and an electron form two comers of an...Ch. 22 - A charge uniform linear density = 9.0 nC/m lies on...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-65, eight particles form a square in...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each with a charge of magnitude 12...Ch. 22 - The following table gives the charge seen by...Ch. 22 - A charge of 20 nC is uniformly distributed along a...Ch. 22 - An electron is constrained to the central axis of...Ch. 22 - SSM The electric field in an xy plane produced by...Ch. 22 - a What total excess charge q must the disk in Fig....Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 1.00 C,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-67, an electric dipole swings from an...Ch. 22 - A particle of charge q1 is at the origin of an x...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each of positive charge q, are...Ch. 22 - A clock face has negative point charges q, 2q,...Ch. 22 - Calculate the electric dipole moment of an...Ch. 22 - An electric field E with an average magnitude of...Ch. 22 - A circular rod has a radius of curvature R = 9.00...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole with dipole moment p= 3.00 ...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-68, a uniform, upward electric field E...Ch. 22 - For the data of Problem 70, assume that the charge...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 2.00 pC,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-69, particle 1 of charge q1 = 1.00pC...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why is turbidity not an accurate measurement of viable bacteria in a culture?
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
MAKE CONNECTIONS In Concept 20.2, you learned about genome-wide association studies. Explain how these studies...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
7. An earthquake 45 km from a city produces P and S waves that travel outward at 5000 and 3000 m/s, respectivel...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Match the following cell types with their correct definition. _________Macrophage _________NK cell _________Eos...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Complete the description of the environment which fine-grained igneous rocks form by choosing the appropriate t...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardhelp me with the experimental set up for the excel i did. the grapharrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes how to calculate the average acceleration of any object? Average acceleration is always halfway between the initial acceleration of an object and its final acceleration. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in velocity of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the displacement of an object divided by the time interval. Average acceleration is always equal to the change in speed of an object divided by the time interval.arrow_forward
- The figure shows the velocity versus time graph for a car driving on a straight road. Which of the following best describes the acceleration of the car? v (m/s) t(s) The acceleration of the car is negative and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is constant. The acceleration of the car is positive and increasing. The acceleration of the car is positive and decreasing. The acceleration of the car is negative and increasing.arrow_forwardWhich figure could represent the velocity versus time graph of a motorcycle whose speed is increasing? v (m/s) v (m/s) t(s) t(s)arrow_forwardUnlike speed, velocity is a the statement? Poisition. Direction. Vector. Scalar. quantity. Which one of the following completesarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forward3.63 • Leaping the River II. A physics professor did daredevil stunts in his spare time. His last stunt was an attempt to jump across a river on a motorcycle (Fig. P3.63). The takeoff ramp was inclined at 53.0°, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. Ignore air resistance. (a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? (b) If his speed was only half the value found in part (a), where did he land? Figure P3.63 53.0° 100 m 40.0 m→ 15.0 marrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- You throw a small rock straight up from the edge of a highway bridge that crosses a river. The rock passes you on its way down, 5.00 s after it was thrown. What is the speed of the rock just before it reaches the water 25.0 m below the point where the rock left your hand? Ignore air resistance.arrow_forwardHelp me make a visualize experimental setup using a word document. For the theory below.arrow_forwardHow to solve this, given answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY