
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 14P
In Fig. 22-41, particle 1 of charge q1
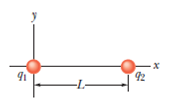
Figure 22-41 Problem 14.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Using the 95% Margin of Error (Confidence Level) values for the Experimental Acceleration due to Gravity determine the % error.= (abs value(A-E)/A)x Show calculations. MOE +- 1.84 m/s^2 --> interval 8.89,12.57 m/s^2
4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0?
A
30
PLEASE help with the experimental setup for this theory because i am so confused.
Chapter 22 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 22 - Figure 22-22 shows three arrangements of electric...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-23 shows two square arrays of charged...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-24, two particles of charge q are...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-25 shows four situations in which four...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-26 shows two charged particles fixed in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-27, two identical circular...Ch. 22 - The potential energies associated with four...Ch. 22 - a In Checkpoint 4, if the dipole rotates from...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-28 shows two disks and a flat ring, each...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-29, an electron e travels through a...
Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-30a, a circular plastic rod with...Ch. 22 - When three electric dipoles ire near each other,...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-32 shows three rods, each with the same...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-33 shows five protons that are launched...Ch. 22 - Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines both...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-34 the electric field lines on the left...Ch. 22 - SSM The nucleus of a plutonium-239 atom contains...Ch. 22 - Two charged particles are attached to an x axis:...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged particle produces an electric Held...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of a point charge that would...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-35, the four particles form...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-36, the four particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-37 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-38a shows two charged particles fixed...Ch. 22 - SSM Two charged particles are fixed to x axis:...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-39 shows an uneven arrangement of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-40 shows a proton on the central...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-41, particle 1 of charge q1 = 5.00q and...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-42, the three particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-43 shows a plastic ring of radius R =...Ch. 22 - Two charged beads are on the plastic ring in Fig....Ch. 22 - The electric field of an electric dipole along the...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-45 shows an electric dipole. What are...Ch. 22 - Equations 22-8 and 22-9 are approximations of the...Ch. 22 - SSM Electric quadrupole. Figure 22-46 shows a...Ch. 22 - Density, density, density. a A charge 300e is...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-47 shows two parallel nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-49 shows three circular arcs centered on...Ch. 22 - GO ILW In Fig. 22-50, a thin glass rod forms a...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig, 22-51, two curved plastic rods, one of...Ch. 22 - Charge is uniformly distributed around a ring of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-52a shows a nonconducting rod with a...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-53 shows two concentric rings, of...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-54, a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-56, a semi-infinite nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A disk of radius 2.5 cm has a surface charge...Ch. 22 - SSM WWW At what distance along the central...Ch. 22 - A circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm...Ch. 22 - Suppose you design an apparatus in which a...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-58a shows a circular disk that is...Ch. 22 - In Millikans experiment, an oil drop of radius...Ch. 22 - GO An electron with a speed of 5.00 108 cm/s...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged cloud system produces an electric...Ch. 22 - Humid air breaks down its molecules become ionized...Ch. 22 - SSM An electron is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 22 - An alpha particle the nucleus of a helium atom has...Ch. 22 - ILW An electron on the axis of an electric dipole...Ch. 22 - An electron is accelerated eastward at 1.80 ...Ch. 22 - SSM Beams of high-speed protons can be produced in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-59, an electron e is to be released...Ch. 22 - A 10.0 g block with a charge of 8.00 10-5 C is...Ch. 22 - At some instant the velocity components of an...Ch. 22 - Assume that a honeybee is a sphere of diameter...Ch. 22 - An electron eaters a region of uniform electric...Ch. 22 - GO Two large parallel copper plates are 5.0 cm...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-61, an electron is shot at an...Ch. 22 - ILW A uniform electric field exists in a region...Ch. 22 - An electric dipole consists of charges 2e and -2e...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole consisting of charges of...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - How much work is required to turn an electric...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - Find an expression for the oscillation frequency...Ch. 22 - a What is the magnitude of an electrons...Ch. 22 - A spherical water drop 1.20 m in diameter is...Ch. 22 - Three particles, each with positive charge Q, form...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-64a, a particle of charge Q produces an...Ch. 22 - A proton and an electron form two comers of an...Ch. 22 - A charge uniform linear density = 9.0 nC/m lies on...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-65, eight particles form a square in...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each with a charge of magnitude 12...Ch. 22 - The following table gives the charge seen by...Ch. 22 - A charge of 20 nC is uniformly distributed along a...Ch. 22 - An electron is constrained to the central axis of...Ch. 22 - SSM The electric field in an xy plane produced by...Ch. 22 - a What total excess charge q must the disk in Fig....Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 1.00 C,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-67, an electric dipole swings from an...Ch. 22 - A particle of charge q1 is at the origin of an x...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each of positive charge q, are...Ch. 22 - A clock face has negative point charges q, 2q,...Ch. 22 - Calculate the electric dipole moment of an...Ch. 22 - An electric field E with an average magnitude of...Ch. 22 - A circular rod has a radius of curvature R = 9.00...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole with dipole moment p= 3.00 ...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-68, a uniform, upward electric field E...Ch. 22 - For the data of Problem 70, assume that the charge...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 2.00 pC,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-69, particle 1 of charge q1 = 1.00pC...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The accompanying chromosome diagram represents a eukaryotic chromosome prepared with Giemsa stain. Indicate the...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Calculate the lattice energy of CaCl2 using a Born-Haber cycle and data from Appendices F and L and Table 7.5. ...
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
What two body structures contain flexible elastic cartilage?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
You microscopically examine scrapings from a case of Acan-thamoeba keratitis. You expect to see a. nothing. b. ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part 2 - Geometry and Trigonometry 1. Line B touches the circle at a single point. Line A extends radially through the center of the circle. A B (a) Which line is tangential to the circumference of the circle? (b) What is the angle between lines A and B. 2. In the figure below what is the angle C? 30 45 3. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0? 30° 4. In the figure below what is the value of the angle 0? A 30°arrow_forwardDetails solution No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem correctly please.Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Will you please walk me through the calculations in more detail for solving this problem? I am a bit rusty on calculus and confused about the specific steps of the derivation: https://www.bartleby.com/solution-answer/chapter-3-problem-15e-modern-physics-2nd-edition/9780805303087/7cf8c31d-9476-46d5-a5a9-b897b16fe6fcarrow_forwardplease help with the abstract. Abstract - This document outlines the format of the lab report and describes the Excel assignment. The abstract should be a short paragraph that very briefly includes the experiment objective, method, result and conclusion. After skimming the abstract, the reader should be able to decide whether they want to keep reading your work. Both the format of the report and the error analysis are to be followed. Note that abstract is not just the introduction and conclusion combined, but rather the whole experiment in short including the results. I have attacted the theory.arrow_forwardUsing the Experimental Acceleration due to Gravity values from each data table, Data Tables 1, 2, and 3; determine the Standard Deviation, σ, mean, μ, variance, σ2 and the 95% Margin of Error (Confidence Level) Data: Ex. Acc. 1: 12.29 m/s^2. Ex. Acc. 2: 10.86 m/s^2, Ex. Acc. 3: 9.05 m/s^2arrow_forward
- In the Super Smash Bros. games the character Yoshi’s has a “ground pound” down special move where he launches himself downward to attack an enemy beneath him. A) If Yoshi flings himself downwards at 9.76 miles per hour to hit an enemy 10.5 m below him, how fast is Yoshi traveling when he hits the enemy? 1 mile = 1609 m B) How much time does it take Yoshi to hit the enemy beneath him?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSolve No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Can someone help me solve this thank you.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward1.62 On a training flight, a Figure P1.62 student pilot flies from Lincoln, Nebraska, to Clarinda, Iowa, next to St. Joseph, Missouri, and then to Manhattan, Kansas (Fig. P1.62). The directions are shown relative to north: 0° is north, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west. Use the method of components to find (a) the distance she has to fly from Manhattan to get back to Lincoln, and (b) the direction (relative to north) she must fly to get there. Illustrate your solutions with a vector diagram. IOWA 147 km Lincoln 85° Clarinda 106 km 167° St. Joseph NEBRASKA Manhattan 166 km 235° S KANSAS MISSOURIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY