
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 9Q
Figure 22-28 shows two disks and a flat ring, each with the same uniform charge Q. Rank the objects according to the magnitude of the electric field they create at points P (which are at the same vertical heights), greatest first.
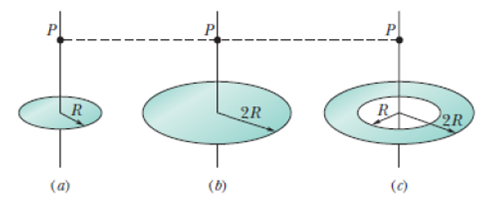
Figure 22-28 Question 9.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solution
how would i express force in vector form I keep getting a single number
please help me solve this questions. show all calculations and a good graph too :)
Chapter 22 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 22 - Figure 22-22 shows three arrangements of electric...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-23 shows two square arrays of charged...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-24, two particles of charge q are...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-25 shows four situations in which four...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-26 shows two charged particles fixed in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-27, two identical circular...Ch. 22 - The potential energies associated with four...Ch. 22 - a In Checkpoint 4, if the dipole rotates from...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-28 shows two disks and a flat ring, each...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-29, an electron e travels through a...
Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-30a, a circular plastic rod with...Ch. 22 - When three electric dipoles ire near each other,...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-32 shows three rods, each with the same...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-33 shows five protons that are launched...Ch. 22 - Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines both...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-34 the electric field lines on the left...Ch. 22 - SSM The nucleus of a plutonium-239 atom contains...Ch. 22 - Two charged particles are attached to an x axis:...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged particle produces an electric Held...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of a point charge that would...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-35, the four particles form...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-36, the four particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-37 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-38a shows two charged particles fixed...Ch. 22 - SSM Two charged particles are fixed to x axis:...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-39 shows an uneven arrangement of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-40 shows a proton on the central...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-41, particle 1 of charge q1 = 5.00q and...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-42, the three particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-43 shows a plastic ring of radius R =...Ch. 22 - Two charged beads are on the plastic ring in Fig....Ch. 22 - The electric field of an electric dipole along the...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-45 shows an electric dipole. What are...Ch. 22 - Equations 22-8 and 22-9 are approximations of the...Ch. 22 - SSM Electric quadrupole. Figure 22-46 shows a...Ch. 22 - Density, density, density. a A charge 300e is...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-47 shows two parallel nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-49 shows three circular arcs centered on...Ch. 22 - GO ILW In Fig. 22-50, a thin glass rod forms a...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig, 22-51, two curved plastic rods, one of...Ch. 22 - Charge is uniformly distributed around a ring of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-52a shows a nonconducting rod with a...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-53 shows two concentric rings, of...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-54, a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-56, a semi-infinite nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A disk of radius 2.5 cm has a surface charge...Ch. 22 - SSM WWW At what distance along the central...Ch. 22 - A circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm...Ch. 22 - Suppose you design an apparatus in which a...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-58a shows a circular disk that is...Ch. 22 - In Millikans experiment, an oil drop of radius...Ch. 22 - GO An electron with a speed of 5.00 108 cm/s...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged cloud system produces an electric...Ch. 22 - Humid air breaks down its molecules become ionized...Ch. 22 - SSM An electron is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 22 - An alpha particle the nucleus of a helium atom has...Ch. 22 - ILW An electron on the axis of an electric dipole...Ch. 22 - An electron is accelerated eastward at 1.80 ...Ch. 22 - SSM Beams of high-speed protons can be produced in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-59, an electron e is to be released...Ch. 22 - A 10.0 g block with a charge of 8.00 10-5 C is...Ch. 22 - At some instant the velocity components of an...Ch. 22 - Assume that a honeybee is a sphere of diameter...Ch. 22 - An electron eaters a region of uniform electric...Ch. 22 - GO Two large parallel copper plates are 5.0 cm...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-61, an electron is shot at an...Ch. 22 - ILW A uniform electric field exists in a region...Ch. 22 - An electric dipole consists of charges 2e and -2e...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole consisting of charges of...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - How much work is required to turn an electric...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - Find an expression for the oscillation frequency...Ch. 22 - a What is the magnitude of an electrons...Ch. 22 - A spherical water drop 1.20 m in diameter is...Ch. 22 - Three particles, each with positive charge Q, form...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-64a, a particle of charge Q produces an...Ch. 22 - A proton and an electron form two comers of an...Ch. 22 - A charge uniform linear density = 9.0 nC/m lies on...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-65, eight particles form a square in...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each with a charge of magnitude 12...Ch. 22 - The following table gives the charge seen by...Ch. 22 - A charge of 20 nC is uniformly distributed along a...Ch. 22 - An electron is constrained to the central axis of...Ch. 22 - SSM The electric field in an xy plane produced by...Ch. 22 - a What total excess charge q must the disk in Fig....Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 1.00 C,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-67, an electric dipole swings from an...Ch. 22 - A particle of charge q1 is at the origin of an x...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each of positive charge q, are...Ch. 22 - A clock face has negative point charges q, 2q,...Ch. 22 - Calculate the electric dipole moment of an...Ch. 22 - An electric field E with an average magnitude of...Ch. 22 - A circular rod has a radius of curvature R = 9.00...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole with dipole moment p= 3.00 ...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-68, a uniform, upward electric field E...Ch. 22 - For the data of Problem 70, assume that the charge...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 2.00 pC,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-69, particle 1 of charge q1 = 1.00pC...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
5. When the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, this patt...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Tycho Brahes contributions to astronom...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
What is the difference between transcription and translation?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
23. Gibbons, small Asian apes, move by brachiation, swinging below a handhold to move forward to the next handh...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Write an equation that uses the products of photosynthesis as reactants and the reactants of photosynthesis as ...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
17. How does the presence of a nonvolatile solute affect the boiling point and melting point of a solution rel...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forwardAn ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forward
- The outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forwardThe heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forward
- L₁ D₁ L₂ D2 Aluminum has a resistivity of p = 2.65 × 10 8 2. m. An aluminum wire is L = 2.00 m long and has a circular cross section that is not constant. The diameter of the wire is D₁ = 0.17 mm for a length of L₁ = 0.500 m and a diameter of D2 = 0.24 mm for the rest of the length. a) What is the resistance of this wire? R = Hint A potential difference of AV = 1.40 V is applied across the wire. b) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thin part of the wire? Hint J1 = c) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thick part of the wire? J₂ = d) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thin part of the wire? E1 = Hint e) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thick part of the wire? E2 =arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardA cheetah spots a gazelle in the distance and begins to sprint from rest, accelerating uniformly at a rate of 8.00 m/s^2 for 5 seconds. After 5 seconds, the cheetah sees that the gazelle has escaped to safety, so it begins to decelerate uniformly at 6.00 m/s^2 until it comes to a stop.arrow_forward
- A projectile is fired with an initial speed of 40.2 m/s at an angle of 35.0 degree above the horizontal on a long flat firing range. Determine. please help and show work for them so i can understand.arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forwardJ K L The graph in the figure shows the position of an object as a function of time. The letters H-L represent particular moments of time. At which moments shown (H, I, etc.) is the speed of the object the greatest? + Position H I K Timearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY