
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 12P
GO Figure 22-39 shows an uneven arrangement of electrons (e) and protons (p) on a circular arc of radius r = 2.00 cm. with angles θ1 = 30.0°, θ2 = 50.0°, θ3 = 30.0°, and θ4 = 20.0°. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the net electric field produced at the center of the arc?
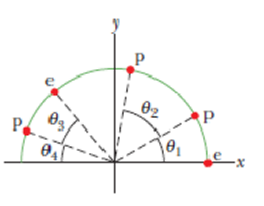
Figure 22-39 Problem 12.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 22 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 22 - Figure 22-22 shows three arrangements of electric...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-23 shows two square arrays of charged...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-24, two particles of charge q are...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-25 shows four situations in which four...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-26 shows two charged particles fixed in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-27, two identical circular...Ch. 22 - The potential energies associated with four...Ch. 22 - a In Checkpoint 4, if the dipole rotates from...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-28 shows two disks and a flat ring, each...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-29, an electron e travels through a...
Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-30a, a circular plastic rod with...Ch. 22 - When three electric dipoles ire near each other,...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-32 shows three rods, each with the same...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-33 shows five protons that are launched...Ch. 22 - Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines both...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-34 the electric field lines on the left...Ch. 22 - SSM The nucleus of a plutonium-239 atom contains...Ch. 22 - Two charged particles are attached to an x axis:...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged particle produces an electric Held...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of a point charge that would...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-35, the four particles form...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-36, the four particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-37 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-38a shows two charged particles fixed...Ch. 22 - SSM Two charged particles are fixed to x axis:...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-39 shows an uneven arrangement of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-40 shows a proton on the central...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-41, particle 1 of charge q1 = 5.00q and...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-42, the three particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-43 shows a plastic ring of radius R =...Ch. 22 - Two charged beads are on the plastic ring in Fig....Ch. 22 - The electric field of an electric dipole along the...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-45 shows an electric dipole. What are...Ch. 22 - Equations 22-8 and 22-9 are approximations of the...Ch. 22 - SSM Electric quadrupole. Figure 22-46 shows a...Ch. 22 - Density, density, density. a A charge 300e is...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-47 shows two parallel nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-49 shows three circular arcs centered on...Ch. 22 - GO ILW In Fig. 22-50, a thin glass rod forms a...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig, 22-51, two curved plastic rods, one of...Ch. 22 - Charge is uniformly distributed around a ring of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-52a shows a nonconducting rod with a...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-53 shows two concentric rings, of...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-54, a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-56, a semi-infinite nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A disk of radius 2.5 cm has a surface charge...Ch. 22 - SSM WWW At what distance along the central...Ch. 22 - A circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm...Ch. 22 - Suppose you design an apparatus in which a...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-58a shows a circular disk that is...Ch. 22 - In Millikans experiment, an oil drop of radius...Ch. 22 - GO An electron with a speed of 5.00 108 cm/s...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged cloud system produces an electric...Ch. 22 - Humid air breaks down its molecules become ionized...Ch. 22 - SSM An electron is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 22 - An alpha particle the nucleus of a helium atom has...Ch. 22 - ILW An electron on the axis of an electric dipole...Ch. 22 - An electron is accelerated eastward at 1.80 ...Ch. 22 - SSM Beams of high-speed protons can be produced in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-59, an electron e is to be released...Ch. 22 - A 10.0 g block with a charge of 8.00 10-5 C is...Ch. 22 - At some instant the velocity components of an...Ch. 22 - Assume that a honeybee is a sphere of diameter...Ch. 22 - An electron eaters a region of uniform electric...Ch. 22 - GO Two large parallel copper plates are 5.0 cm...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-61, an electron is shot at an...Ch. 22 - ILW A uniform electric field exists in a region...Ch. 22 - An electric dipole consists of charges 2e and -2e...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole consisting of charges of...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - How much work is required to turn an electric...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - Find an expression for the oscillation frequency...Ch. 22 - a What is the magnitude of an electrons...Ch. 22 - A spherical water drop 1.20 m in diameter is...Ch. 22 - Three particles, each with positive charge Q, form...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-64a, a particle of charge Q produces an...Ch. 22 - A proton and an electron form two comers of an...Ch. 22 - A charge uniform linear density = 9.0 nC/m lies on...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-65, eight particles form a square in...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each with a charge of magnitude 12...Ch. 22 - The following table gives the charge seen by...Ch. 22 - A charge of 20 nC is uniformly distributed along a...Ch. 22 - An electron is constrained to the central axis of...Ch. 22 - SSM The electric field in an xy plane produced by...Ch. 22 - a What total excess charge q must the disk in Fig....Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 1.00 C,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-67, an electric dipole swings from an...Ch. 22 - A particle of charge q1 is at the origin of an x...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each of positive charge q, are...Ch. 22 - A clock face has negative point charges q, 2q,...Ch. 22 - Calculate the electric dipole moment of an...Ch. 22 - An electric field E with an average magnitude of...Ch. 22 - A circular rod has a radius of curvature R = 9.00...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole with dipole moment p= 3.00 ...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-68, a uniform, upward electric field E...Ch. 22 - For the data of Problem 70, assume that the charge...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 2.00 pC,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-69, particle 1 of charge q1 = 1.00pC...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In mice, black coat color is dominant to white coat color. In the pedigree shown here, mice with a black coat a...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
1. The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is
A. (a) organ, organ system, cellular, che...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy & Physiology) Standalone Book
13.44 When furan and maleimide undergo a Diels–Alder reaction at 25°C, the major product is the endo adduct G. ...
Organic Chemistry
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Which type of cartilage is most plentiful in the adult body?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Fill in the blanks: a. The wrist is also known as the _________ region. b. The arm is also known as the _______...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY