
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781118230725
Author: David Halliday, Robert Resnick, Jearl Walker
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 22, Problem 19P
Figure 22-45 shows an electric dipole. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the dipole’s electric field at point P, located at distance r ≫ d?
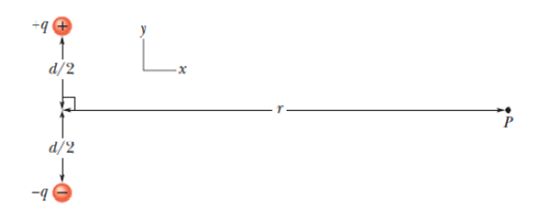
Figure 22-45 Problem 19.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The law of reflection applies to
Question 14Select one:
a.
specular reflection
b.
irregular reflection
c.
All of these
d.
diffuse reflection
According to your book "normal" human body temperature is considered to be ________?
Select one:
a. none of these
b.
98.6°C
c.
37°C
d.
100°C
Problem Seven. A football
receiver
running
straight
downfield at 5.60 m/s is 11.5 m
in front of the quarterback when
a pass is thrown downfield at an
angle of 35.0° above the
horizon.
8.) If the receiver never changes speed and the ball is caught at the same height from which it was
thrown, find the distance between the quarterback and the receiver when the catch is made.
(A) 21.3
(B) 17.8
(C) 18.8
(D) 19.9
(E) 67.5
Chapter 22 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Ch. 22 - Figure 22-22 shows three arrangements of electric...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-23 shows two square arrays of charged...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-24, two particles of charge q are...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-25 shows four situations in which four...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-26 shows two charged particles fixed in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-27, two identical circular...Ch. 22 - The potential energies associated with four...Ch. 22 - a In Checkpoint 4, if the dipole rotates from...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-28 shows two disks and a flat ring, each...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-29, an electron e travels through a...
Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-30a, a circular plastic rod with...Ch. 22 - When three electric dipoles ire near each other,...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-32 shows three rods, each with the same...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-33 shows five protons that are launched...Ch. 22 - Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines both...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-34 the electric field lines on the left...Ch. 22 - SSM The nucleus of a plutonium-239 atom contains...Ch. 22 - Two charged particles are attached to an x axis:...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged particle produces an electric Held...Ch. 22 - What is the magnitude of a point charge that would...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-35, the four particles form...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-36, the four particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-37 shows two charged particles on an...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-38a shows two charged particles fixed...Ch. 22 - SSM Two charged particles are fixed to x axis:...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-39 shows an uneven arrangement of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-40 shows a proton on the central...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-41, particle 1 of charge q1 = 5.00q and...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-42, the three particles are fixed in...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-43 shows a plastic ring of radius R =...Ch. 22 - Two charged beads are on the plastic ring in Fig....Ch. 22 - The electric field of an electric dipole along the...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-45 shows an electric dipole. What are...Ch. 22 - Equations 22-8 and 22-9 are approximations of the...Ch. 22 - SSM Electric quadrupole. Figure 22-46 shows a...Ch. 22 - Density, density, density. a A charge 300e is...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-47 shows two parallel nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-49 shows three circular arcs centered on...Ch. 22 - GO ILW In Fig. 22-50, a thin glass rod forms a...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig, 22-51, two curved plastic rods, one of...Ch. 22 - Charge is uniformly distributed around a ring of...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-52a shows a nonconducting rod with a...Ch. 22 - GO Figure 22-53 shows two concentric rings, of...Ch. 22 - SSM ILW WWW In Fig. 22-54, a nonconducting rod of...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-56, a semi-infinite nonconducting...Ch. 22 - A disk of radius 2.5 cm has a surface charge...Ch. 22 - SSM WWW At what distance along the central...Ch. 22 - A circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm...Ch. 22 - Suppose you design an apparatus in which a...Ch. 22 - Figure 22-58a shows a circular disk that is...Ch. 22 - In Millikans experiment, an oil drop of radius...Ch. 22 - GO An electron with a speed of 5.00 108 cm/s...Ch. 22 - SSM A charged cloud system produces an electric...Ch. 22 - Humid air breaks down its molecules become ionized...Ch. 22 - SSM An electron is released from rest in a uniform...Ch. 22 - An alpha particle the nucleus of a helium atom has...Ch. 22 - ILW An electron on the axis of an electric dipole...Ch. 22 - An electron is accelerated eastward at 1.80 ...Ch. 22 - SSM Beams of high-speed protons can be produced in...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-59, an electron e is to be released...Ch. 22 - A 10.0 g block with a charge of 8.00 10-5 C is...Ch. 22 - At some instant the velocity components of an...Ch. 22 - Assume that a honeybee is a sphere of diameter...Ch. 22 - An electron eaters a region of uniform electric...Ch. 22 - GO Two large parallel copper plates are 5.0 cm...Ch. 22 - GO In Fig. 22-61, an electron is shot at an...Ch. 22 - ILW A uniform electric field exists in a region...Ch. 22 - An electric dipole consists of charges 2e and -2e...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole consisting of charges of...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - How much work is required to turn an electric...Ch. 22 - A certain electric dipole is placed in a uniform...Ch. 22 - Find an expression for the oscillation frequency...Ch. 22 - a What is the magnitude of an electrons...Ch. 22 - A spherical water drop 1.20 m in diameter is...Ch. 22 - Three particles, each with positive charge Q, form...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-64a, a particle of charge Q produces an...Ch. 22 - A proton and an electron form two comers of an...Ch. 22 - A charge uniform linear density = 9.0 nC/m lies on...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-65, eight particles form a square in...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each with a charge of magnitude 12...Ch. 22 - The following table gives the charge seen by...Ch. 22 - A charge of 20 nC is uniformly distributed along a...Ch. 22 - An electron is constrained to the central axis of...Ch. 22 - SSM The electric field in an xy plane produced by...Ch. 22 - a What total excess charge q must the disk in Fig....Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 1.00 C,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-67, an electric dipole swings from an...Ch. 22 - A particle of charge q1 is at the origin of an x...Ch. 22 - Two particles, each of positive charge q, are...Ch. 22 - A clock face has negative point charges q, 2q,...Ch. 22 - Calculate the electric dipole moment of an...Ch. 22 - An electric field E with an average magnitude of...Ch. 22 - A circular rod has a radius of curvature R = 9.00...Ch. 22 - SSM An electric dipole with dipole moment p= 3.00 ...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-68, a uniform, upward electric field E...Ch. 22 - For the data of Problem 70, assume that the charge...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-66, particle 1 of charge 2.00 pC,...Ch. 22 - In Fig. 22-69, particle 1 of charge q1 = 1.00pC...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Chlorine has two isotopes, 35Cl and 37Cl; 75.77% of chlorine is 35Cl, and 24.23% is 37Cl. The atomic mass of 35...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
What are four functions of connective tissue?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
WHAT IF? A chicken has 78 chromosomes in its somatic cells. How many chromosomes did the chicken inherit from ...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
12.1 Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
a. CH3-CH2-OH
b.
c.
d.
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
A 500 g cart is released from rest 1.00 m from the bottom of a frictionless, 30.0° ramp. The cart rolls down th...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When two bar magnets are near each other, the north pole of one of the magnets experiences what type of force from the other magnet? 1. both an attractive force and a repulsive force 2. a Coulomb force 3. only an attractive force 4. only a repulsive forcearrow_forwardWhat can be said about the electric force between two charged particles? It varies as 1/r. It depends only on the magnitudes of the charges. It is much, much greater than the attractive gravitational force. It is repulsive for unlike charges.arrow_forwardA piece of copper originally 305mm long is pulled in tension with a stress of 276MPa. If the deformation is elastic, what will be the resultant elongation. E for copper is 110Gpaarrow_forward
- Please solve and answer the problem correctly please. Be sure to give explanations on each step and write neatly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardIn the figures, the masses are hung from an elevator ceiling. Assume the velocity of the elevator is constant. Find the tensions in the ropes (in N) for each case. Note that 0₁ = 35.0°, 0₂ = 55.0°, 03 = 60.0°, m₁ = 3.00 kg, and m2 = 7.00 kg. (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values-including answers submitted in WebAssign-in your calculations.) (a) Τι WY NY MY T3 e₁ T₁ = N = N = N (b) 18 Τι = Τι T3 = || || || = T T Ts m₂ N N N 02 T₂ T3 m₁arrow_forwardYou are working with a movie director and investigating a scene with a cowboy sliding off a tree limb and falling onto the saddle of a moving horse. The distance of the fall is several meters, and the calculation shows a high probability of injury to the cowboy from the stunt. Let's look at a simpler situation. Suppose the director asks you to have the cowboy step off a platform 2.55 m off the ground and land on his feet on the ground. The cowboy keeps his legs straight as he falls, but then bends at the knees as soon as he touches the ground. This allows the center of mass of his body to move through a distance of 0.660 m before his body comes to rest. (Center of mass will be formally defined in Linear Momentum and Collisions.) You assume this motion to be under constant acceleration of the center of mass of his body. To assess the degree of danger to the cowboy in this stunt, you wish to calculate the average force upward on his body from the ground, as a multiple of the cowboy's…arrow_forward
- A box of mass m = 2.00 kg is released from rest at the top of an inclined plane as seen in the figure. The box starts out at height h =0.200 m above the top of the table, the table height is H = 2.00 m, and 0 = 41.0°. H m (a) What is the acceleration (in m/s²) of the box while it slides down the incline? m/s² (b) What is the speed (in m/s) of the box when it leaves the incline? m/s (c) At what horizontal distance (in m) from the end of the table will the box hit the ground? m (d) How long (in s) from when the box is released does it hit the ground? S (e) Does the box's mass affect any of your above answers? Yes Noarrow_forward(a) A sphere made of rubber has a density of 0.940 g/cm³ and a radius of 7.00 cm. It falls through air of density 1.20 kg/m³ and has a drag coefficient of 0.500. What is its terminal speed (in m/s)? m/s (b) From what height (in m) would the sphere have to be dropped to reach this speed if it fell without air resistance? marrow_forwardThe systems shown below are in equilibrium. If the spring scales are calibrated in newtons, what do they read? Ignore the masses of the pulleys and strings and assume the pulleys and the incline are frictionless. (Let m = 2.19 kg and € = 29.0°.) scale in (a) N N scale in (b) scale in (c) N scale in (d) N a C m m m m m b d m Ꮎarrow_forward
- An elevator car has two equal masses attached to the ceiling as shown. (Assume m = 3.10 kg.) m m T₁ T2 (a) The elevator ascends with an acceleration of magnitude 2.00 m/s². What are the tensions in the two strings? (Enter your answers in N.) = N T₁ Τι = N (b) The maximum tension the strings can withstand is 78.8 N. What is the maximum acceleration of the elevator so that a string does not break? (Enter the magnitude in m/s².) m/s²arrow_forward(a) At what speed (in m/s) will a proton move in a circular path of the same radius as an electron that travels at 7.85 x 100 m/s perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic field at an altitude where the field strength is 1.20 x 10-5 T? 4.27e3 m/s (b) What would the radius (in m) of the path be if the proton had the same speed as the electron? 7.85e6 x m (c) What would the radius (in m) be if the proton had the same kinetic energy as the electron? 195.38 x m (d) What would the radius (in m) be if the proton had the same momentum as the electron? 3.7205 marrow_forward! Required information The block shown is made of a magnesium alloy, for which E = 45 GPa and v = 0.35. Know that σx = -185 MPa. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 25 mm B D 40 mm 100 mm Determine the magnitude of Oy for which the change in the height of the block will be zero. The magnitude of Oy is MPa.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Electric Fields: Crash Course Physics #26; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdulzEfQXDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY