
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 21.SE, Problem 39MP
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
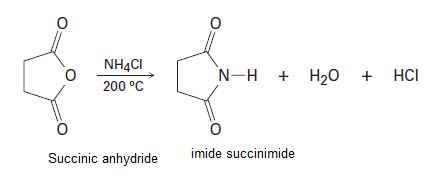
Succinic anhydride yields the cyclic imide succinimide when heated with ammonium chloride at 200°C. Propose a mechanism for this reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Indicate which of the following mechanisms is in operation: SN1, SN2, E1, or E2.
(c)
(4pts)
Mechanism:
heat
(E1)
CH3OH
+
1.5pts each
_E1 _ (1pt)
Br
CH3OH
(d)
(4pts)
Mechanism:
SN1
(1pt)
(e)
(3pts)
1111 I
H
10
Ill!!
H
LDA
THF (solvent)
Mechanism: E2
(1pt)
NC
(f)
Bri!!!!!
CH3
NaCN
(3pts)
acetone
Mechanism: SN2
(1pt)
(SN1)
-OCH3
OCH3
1.5pts each
2pts for either product
1pt if incorrect
stereochemistry
H
Br
(g)
“,、
(3pts)
H
CH3OH
+21
Mechanism:
SN2
(1pt)
H
CH3
2pts
1pt if incorrect
stereochemistry
H
2pts
1pt if incorrect
stereochemistry
A mixture of butyl acrylate and 4'-chloropropiophenone has been taken for proton NMR analysis. Based on this proton NMR, determine the relative percentage of each compound in the mixture
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 21.1 - Give IUPAC names for the following substances:Ch. 21.1 - Draw structures corresponding to the following...Ch. 21.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 21.2 - Rank the compounds in each of the following sets...Ch. 21.2 - Predict the products of the following nucleophilic...Ch. 21.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 21.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 21.3 - If the following molecule is treated with acid...Ch. 21.4 - How might you prepare the following esters using a...Ch. 21.4 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 21.4 - Prob. 11PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 12PCh. 21.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 21.5 - Prob. 14PCh. 21.5 - What product would you expect from reaction of one...Ch. 21.6 - Prob. 16PCh. 21.6 - Prob. 17PCh. 21.6 - Show the products you would obtain by reduction of...Ch. 21.6 - What ester and what Grignard reagent might you...Ch. 21.7 - Prob. 20PCh. 21.7 - How would you use the reaction of an amide with...Ch. 21.8 - Write the mechanism of the reaction shown in...Ch. 21.9 - Prob. 23PCh. 21.9 - Prob. 24PCh. 21.10 - Prob. 25PCh. 21.10 - Prob. 26PCh. 21.SE - Name the following compounds:Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 28VCCh. 21.SE - Prob. 29VCCh. 21.SE - Prob. 30VCCh. 21.SE - Predict the product(s) and provide the mechanism...Ch. 21.SE - Predict the product(s) and provide the mechanism...Ch. 21.SE - Predict the product(s) and provide the mechanism...Ch. 21.SE - Predict the product(s) and provide the complete...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 35MPCh. 21.SE - When 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) is added in...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 37MPCh. 21.SE - Prob. 38MPCh. 21.SE - Prob. 39MPCh. 21.SE - The hydrolysis of a biological thioester to the...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 41MPCh. 21.SE - Prob. 42MPCh. 21.SE - Prob. 43MPCh. 21.SE - In the iodoform reaction, a triiodomethyl ketone...Ch. 21.SE - Give IUPAC names for the following compounds:Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 46APCh. 21.SE - Draw and name compounds that meet the following...Ch. 21.SE - Predict the product, if any, of reaction between...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 49APCh. 21.SE - Prob. 50APCh. 21.SE - What product would you expect to obtain from...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 52APCh. 21.SE - Prob. 53APCh. 21.SE - The following reactivity order has been found for...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 55APCh. 21.SE - Outline methods for the preparation of...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 57APCh. 21.SE - When ethyl benzoate is heated in methanol...Ch. 21.SE - tert-Butoxycarbonyl azide, a reagent used in...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 60APCh. 21.SE - Prob. 61APCh. 21.SE - What is the structure of the polymer produced by...Ch. 21.SE - Polyimides with the structure shown are used as...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 64APCh. 21.SE - Propose a structure for a compound, C4H7ClO2, that...Ch. 21.SE - Assign structures to compounds with the following...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 67APCh. 21.SE - When a carboxylic acid is dissolved in...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 69APCh. 21.SE - Prob. 70APCh. 21.SE - Prob. 71APCh. 21.SE - Phenyl 4-aminosalicylate is a drug used in the...Ch. 21.SE - N,N-Diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) is the active...Ch. 21.SE - Tranexamic acid, a drug useful against blood...Ch. 21.SE - One frequently used method for preparing methyl...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 76APCh. 21.SE - Assign structures to compounds with the following...Ch. 21.SE - Propose structures for compounds with the...Ch. 21.SE - Propose a structure for the compound with the...Ch. 21.SE - Draw the structure of the compound that produced...Ch. 21.SE - Prob. 81APCh. 21.SE - Epoxy adhesives are prepared in two steps. SN2...
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Q5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts) R OCH 3 CI H S 2pts for each R/S HO R H !!! I OH CI HN CI R Harrow_forwardCalculate the proton and carbon chemical shifts for this structurearrow_forwardA. B. b. Now consider the two bicyclic molecules A. and B. Note that A. is a dianion and B. is a neutral molecule. One of these molecules is a highly reactive compound first characterized in frozen noble gas matrices, that self-reacts rapidly at temperatures above liquid nitrogen temperature. The other compound was isolated at room temperature in the early 1960s, and is a stable ligand used in organometallic chemistry. Which molecule is the more stable molecule, and why?arrow_forward
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
