
Concept explainers
a) p-Bromo phenyl acetamide.
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula from the given name. We retrace steps as in the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
To derive the structure corresponding to the given IUPAC name, we need to take recourse to the IUPAC system, but somewhat retracing the steps. Thus:
1) The given name p-Bromo phenyl acetamide than the suffix –amide.
At the very outset, Thus, the compound is invariably an amide.
2) The general formula for an amide is
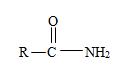
3) Identify now the alkyl group R attached to the carbonyl carbon. This, for the given name p-Bromo phenyl aceta is
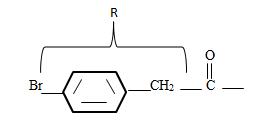
The phenyl ring with a Bromine for at the pare position curt the intervening –CH2. That is 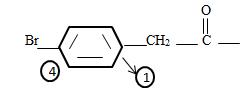
4) Recall the parent acetic acid is a 2-carbon acid system
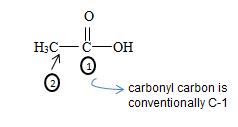
It the given compound the phenyl ring is at C2 ie
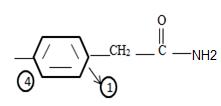
It is a substituted acetic acid. Hence the aceta naming
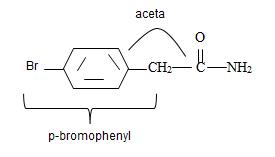
Combining these aspects, it follows that the parent 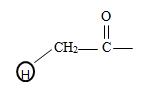 by
by
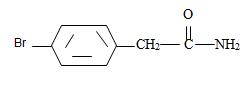
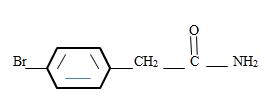
Thus the structure of the given compound where name is p-bromo phenyl acetamide is
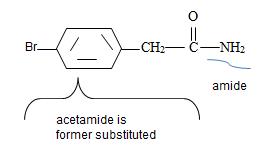
Is further substituted
Thus the structure corresponding to the given name p-bromo phenyl acetamide is
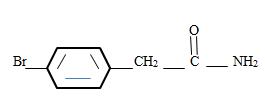
b) m-Benzoylbenzamide
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula from the given name. We retrace steps as in the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
The structure corresponding to the given name can be obtained by taking recourse to the IUPAC system, in a reverse way: Thus
1) First, the name ends with –amide as suffix. Thus, the compound is an amide and its general formula may be written
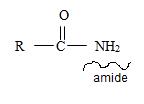
2) Now, identify the R ie alkyl group attached to the carbonyl carbon.
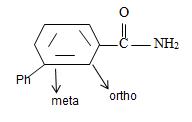
[Also, it must be noted that the amide is not substituted at nitrogen as the name has no N-alkyl prefix] the R is m-benzoyl benzoyl implying 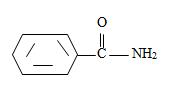 for Benzamide with a further benzoyl, at the meta carbon, C-3 of the phenyl ring.
for Benzamide with a further benzoyl, at the meta carbon, C-3 of the phenyl ring.
Thus,
or
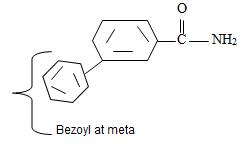
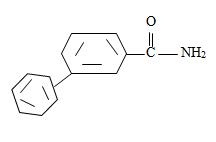
Thus the structure of the compounds as
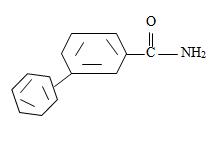
Thus the compound with the given IUPAC name m-benzoyl benzamide has the structure
c) 2,2-Dimethyl hexanamide
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula from the given name. We retrace steps as in the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
The structure corresponding to the given IUPAC mane 2,2-Dimethylhexanamide can be obtained by retracing the steps of the IUPAC system. Thus,
a) First, observe that the given, IUPAC name has the suffix–amide.
Thus the compound is an amide.
b) The name has no alkyl substituent at the nitrogen of the amino –NH2 group. So the compound should have a structure consistent with the general formula
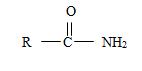
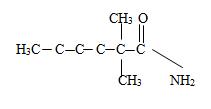
c) Now to identify the R-alkyl portion, we see it is 2,2-Dimethyl hexane chain, ie
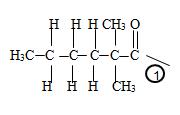
By convention, the carbonyl carbon is C-1, C-2 has 2 methyl groups. Thus the parent (longest) hydrocarbon chain –R is 2,2-dimethylhexane.
Thus the structure should be
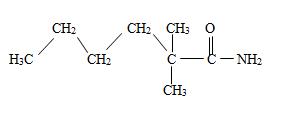
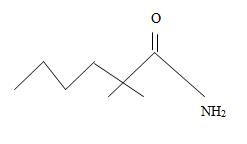
Thus the structure corresponding to the compound whose IUPAC name is 2,2-dimethyl hexanamide is
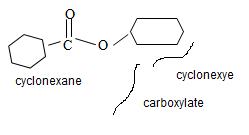
d) Cyclohexyl cyclohexane carboxylate
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula from the given name. We retrace steps as in the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound with the given IUPAC name
Cyclohexyl cyclohexane carboxylate can be obtained by retracing the rules of the IUPAC system: Thus.
1) First the, given name has its suffix: carboxylate
Thus it is an ester of a carboxylic acid.
2) Second, recall that the alkyl R1 of the ester oxygen comes first in the IUPAC name. In the given name this R1 is cyclohexyl. Thus the OR1 of the ester (general)
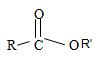
Is cyclohexyl structure is
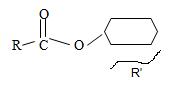
3) For the R (alkyl) component attached to the carbonyl carbon, it is given as cyclohexane. This implies the structure
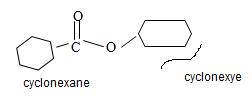
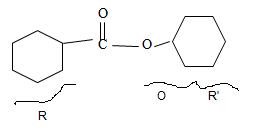
By convention, the cyclohexane carboxylic acid ester is named by replacing the carboxylic acid ending by carboxylate. Assembling all these rules, the structure of the compound corresponding to the name cyclohexyl cyclohexane carboxylate is
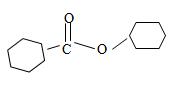
Thus the structure of the compound that best fits the given IUPAC name is
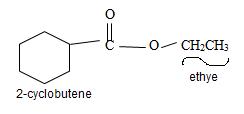
e) Ethyl-2-cyclobutene carboxylate
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula from the given name. We retrace steps as in the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is Ethyl 2-cyclobutene carboxyl may be obtained by retracing the rules of the IUPAC system. Thus,
1) First, we see that the suffix of the name is carboxylate.
Thus the compound is an ester.
2) Second, the general formula of the ester may be written
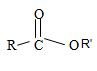
3) Third, by convention, the ester alkyl function R1 comes as prefix in the IUPAC name for the given compound it is ethyl –CH2CH3. Thus, the compound could be
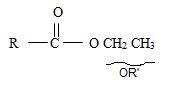
4) Next we identify that the alkyl component R of the carbonyl carbon from the name is 2-cyclobutene ie
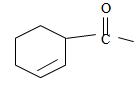
With the double bond at C-2; since C-1 of the cyclobutene ring must by convention carry the carboxylic carbon of the acyl group
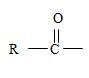
Finally the ester ending is carboxylate which agrees with the facts-is the compound is an ester of a cyclohexyl carboxylic acid
Thus the compound is an ester.
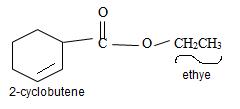
Thus the structure of the compound where IUPAC name is ethyl 2-cyclobutene carboxylate is
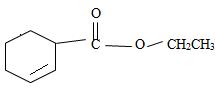
f) Succinic anhydride
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula from the given name. We retrace steps as in the IUPAC system.
Answer to Problem 46AP
Explanation of Solution
The structured formula of the compound corresponding to the given name succinic an hydride is obtained by retracing the rules of the IUPAC system. Thus,
1) First, the given name has its suffix anhydride. The compound is thus, an anhydride of a carboxylic acid.
2) The general formula for an acid anhydride of a mono carboxylic acid as
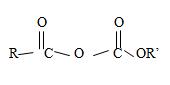
Where R and R1 are the two alkyl groups may be similar R=R in which care it is a synmetical an hydride, or R≠R1, for an unsynmetical an hydride. It is now needed to identify R and R1.
Now for this, we introspect the prefix of the name is succinic this implies the parent acid is a dicarboxylic acid is succinic acid. Its formula is
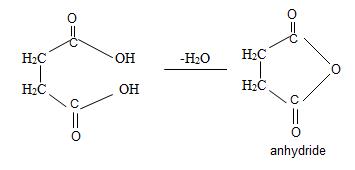
Since by reaction and convention, acid an hydride form by lon of a water molecule, thus,
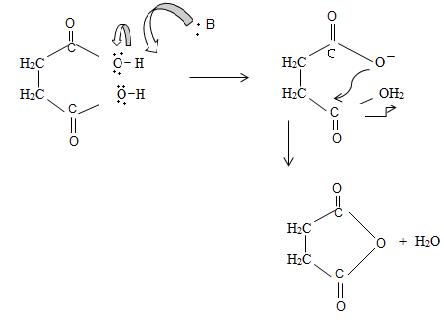
Thus consistent with the above facts the structural formula for succinic an hydride is
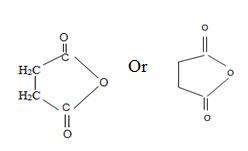
Thus the structural formula for succinic anhydride is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Where are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?arrow_forwardA mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forward
- A mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? Farrow_forwardcan someone give the curly arrow mechanism for this reaction written with every intermediate and all the side products pleasearrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole




