
Concept explainers
A
Interpretation:
The straight line structure of glucose needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
A monosaccharide is a simple carbohydrate consisting of only one sugar unit in their structures. Simple monosaccharides are pentose and hexoses sugar. Glucose and galactose both the monosaccharides represent hexoses sugar structure with six carbons.
A
Answer to Problem 30A
The straight line structure of glucose is given as −
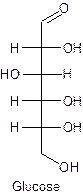
Explanation of Solution
Glucose is the example of a monosaccharide containing the
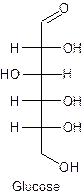
B
Interpretation:
The straight line structure of ribose needs to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
A monosaccharide is a simple carbohydrate consisting of only one sugar unit in their structures. Simple monosaccharides are pentose and hexoses sugar. Ribose and ribulose are pentose sugar-containing five-carbon.
B
Answer to Problem 30A
The straight line structure of ribose is given as −
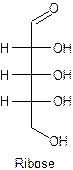
Explanation of Solution
Ribose is the example of a monosaccharide with five-carbon, and ribose contains the aldehyde as a functional group at the first carbon. Three hydroxyl groups are present at the right-hand side, and one is attached to the fifth carbon.
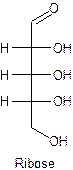
C
Interpretation:
The straight line structure of ribulose.
Concept Introduction:
A monosaccharide is a simple carbohydrate consisting of only one sugar unit in their structures. Simple monosaccharides are pentose and hexoses sugar. Ribose and ribulose are pentose sugar-containing five-carbon.
C
Answer to Problem 30A
The straight line structure of ribulose is given as −
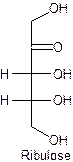
Explanation of Solution
Ribulose is the example of monosaccharide with five-carbon, ribose containing the
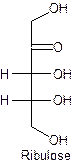
D
Interpretation:
The straight line structure of galactose.
Concept Introduction:
A monosaccharide is a simple carbohydrate consisting of only one sugar unit in their structures. Simple monosaccharides are pentose and hexoses sugar. Glucose and galactose both the monosaccharides represent hexoses sugar structure with six carbons.
D
Answer to Problem 30A
The straight line structure of galactose is given as −
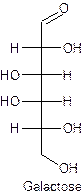
Explanation of Solution
Galactose is the example of a monosaccharide containing the aldehyde as a functional group at the first carbon. There are two hydroxyl groups present on the left-hand side at third and fourth carbon and the rest of the two hydroxyl groups are present on the right-hand side.
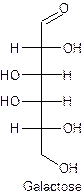
Chapter 21 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





