
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The secondary structure of proteins needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Protein − proteins are composed of the different types of amino acids and they are bonded together with the help of the peptide bonds.
There are four general classes are known for the proteins. The arrangements of the amino acid define the structure of the proteins.
Answer to Problem 11A
The complex structure of the proteins is known as a secondary structure. The amino acid interacts with each other by the formation of a peptide bond.
Explanation of Solution
The common secondary structure of proteins is consists of the beta-pleated sheet. In this structure, two different amino acid chains interact with the other one. The linkage is a polypeptide. The chains of the amino acid are bound by hydrogen bonds. The two types of beta-pleated sheets are parallel with other beta-pleated sheets and opposite with the beta-pleated sheets and form a complex secondary structure of proteins.
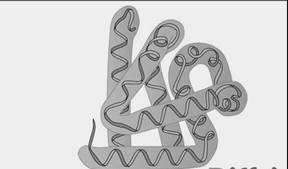
Secondary structure of protein
The coiled helical and pleated structure is representing the secondary structure of proteins. This structure is made up of two antiparallel strands. The secondary structure of proteins is composed of hydrogen bonds formed between atoms of the polypeptide backbone.
Chapter 21 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
- If I have 30% H2O2, indicate how to prepare a 6% H2O2 solution.arrow_forward7) 8) FCI II -C-C-C=C-C || Br Br || -C=C-Br -CEC-C-C- 10) 11) F Br i OH مله 12) Br i 13) 14) 15) CH3CHFCHFC=CH C(OH)Br2CHF(CH2)4CH2CH3 CH3(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)2CH3arrow_forwardName 1) 3-fluoro, 1-butene 2) 2-heptene 2,3-difluoro- 1-pentene 4) 6-iodo,4-methyl- 2-decyne 5) 4,4-dibromo- 1,2-butandiol Complete structural formula F -C=C-C-C- Line formula Condensed structural formula N F CH2=CHCHFCH3arrow_forward
- 1. Part 1: Naming Organic Compounds он H₁C-C-CH3 CH3 Br CI CI 2. Br-CH-CH-CH₂ H₂C-CH-C= -CH-CH2-CH3 3. HC-CH-CH-C-OH 5. H₂C-CH-CH₂-OH 7. OH 4. CH CH₂-CH₂ 6. сно CH-CH-CH-CH₂-CH₂ H₁₂C-CH-CH-CH-CH₁₂-CH₁₂ 8. OHarrow_forward11 Organic Chemistry Organic Nomenclature Practice Name/Functional Group n-butane Formula Structural Formula (1) C4tt10 H3C C- (2) CH3CH2CH2 CH 3 H₂ -CH3 Н2 name & functional group (1) and (2) OH H₁₂C Н2 name only (1) and (2) name only (1) and (2) H₁C - = - CH₂ Н2 HC=C-C CH3arrow_forwardUnder aqueous basic conditions, nitriles will react to form a neutral organic intermediate 1 that has an N atom in it first, and then they will continue to react to form the final product 2: NC H₂O он- H₂O 1 2 OH Draw the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2 in the box below. You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- Assign these COSY Spectrumarrow_forwardAssign these C-NMR and H-NMR Spectrumarrow_forwardPredict the product of this organic reaction: IZ + HO i P+H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of P. If there is no reasonable possibility for P, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No Answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ :arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: 0 O ----- A + KOH ? CH3-CH2-C-O-CH2-C-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. (If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching.) If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. X ⑤ èarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O CH3 + H2O + HCI A A? CH3-CH2-C-N-CH3 Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. No Reaction Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? R+ HO-C-CH2-CH3 0= CH3 CH3 —CH, C−NH—CH CH3 + H₂O Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume no products other than those shown above are formed. No Answer Click anywhere to draw the first atom of your structure. €arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





