
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given monosaccharide, all the chirality centers should be labeled. The monosaccharide should be classified as D or L. The enantiomers should be drawn.
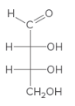
Concept Introduction:
Chirality center is an atom which has four different groups attached to it.
The D and L sugars are classified based on the position of OH group on the chirality center which is farthest from the carbonyl group. If the OH group is on the right side, it is a D sugar. If the OH group is on left side it is a L sugar.
An enantiomer is one of the two stereoisomers which are the mirror image of each other and these enantiomers are non-superimposable.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given monosaccharide, all the chirality centers should be labeled. The monosaccharide should be classified as D or L. The enantiomers should be drawn.
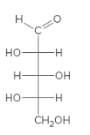
Concept Introduction:
Chirality center is an atom which has four different groups attached to it.
The D and L sugars are classified based on the position of OH group on the chirality center which is farthest from the carbonyl group. If the OH group is on the right side, it is a D sugar. If the OH group is on left side it is a L sugar.
An enantiomer is one of the two stereoisomers which are the mirror image of each other and these enantiomers are non-superimposable.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given monosaccharide, all the chirality centers should be labeled. The monosaccharide should be classified as D or L. The enantiomers should be drawn.
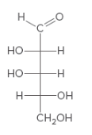
Concept Introduction:
Chirality center is an atom which has four different groups attached to it.
The D and L sugars are classified based on the position of OH group on the chirality center which is farthest from the carbonyl group. If the OH group is on the right side, it is a D sugar. If the OH group is on left side it is a L sugar.
An enantiomer is one of the two stereoisomers which are the mirror image of each other and these enantiomers are non-superimposable.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 20 Solutions
GENERAL,ORGANIC, & BIOLOGICAL CHEM-ACCES
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





