
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321948908
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 20, Problem 5P
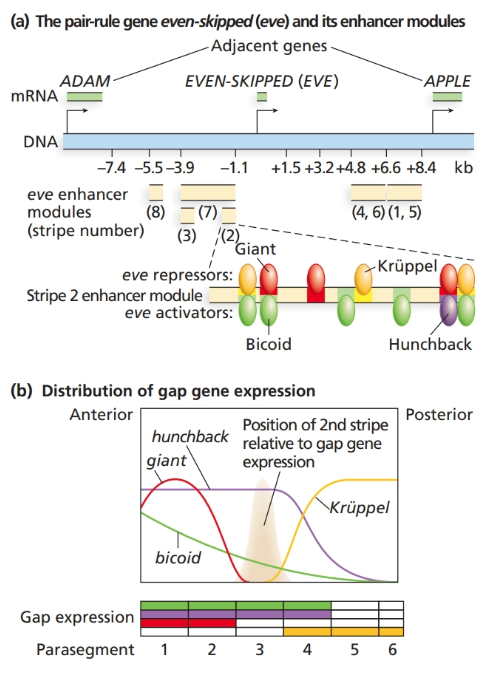
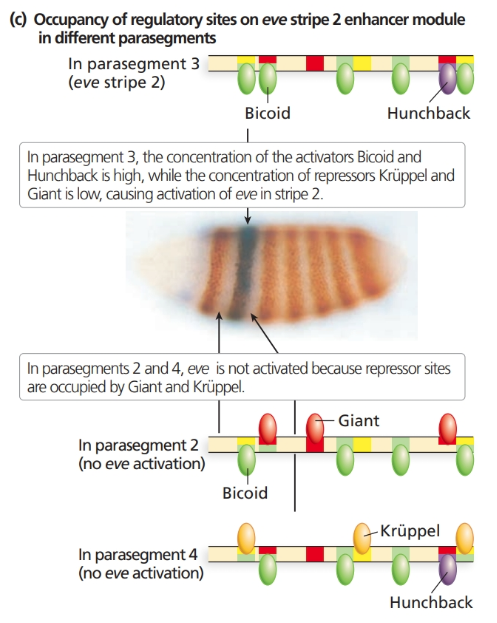
Consider the even
a. How are the sharp boundaries of expression of eve stripe
b. Consider the binding sites for gap proteins and Bicoid in the stripe
c. Explain what you expect to see happen to even-skipped stripe
Figure 18.9
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
MyoD is a transcriptional activator that turns on theexpression of several muscle-specific genes in humancells. The Id gene product inhibits MyoD action.a. One possibility is that the Id protein directly represses the expression of these muscle-specificgenes. Explain how Id would function if it were arepressor.b. Another possibility is that Id inhibits musclespecific gene transcription indirectly, by preventingMyoD function. Explain how Id could function asan indirect repressor.c. Suppose you know the amino acid sequence ofthe Id protein. How might this information supportthe hypothesis in part (a) or in part (b)?
Describe the common signal transduction event that is perturbed by cancer-promoting mutations in the genes encoding RAS and NF-1. Why are mutations in RAS more commonly found in cancers than mutations in NF-1?
In Figure 6-19,a. what do the square/triangular pegs and holesrepresent?b. is the suppressor mutation alone wild type inphenotype?
Chapter 20 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (2nd Edition)
Ch. 20 - 18.1 Explain why many developmental genes encode...Ch. 20 - Bird beaks develop from an embryonic group of...Ch. 20 - 18.3 How is positional information provided along...Ch. 20 - Early development in Drosophila is atypical in...Ch. 20 - 18.5 Consider the evenskipped regulatory sequences...Ch. 20 - What is the difference between a parasegment and...Ch. 20 - Why do loss-of-function mutations in Hox genes...Ch. 20 - 18.8 Compare and contrast the specification of...Ch. 20 - Prob. 9PCh. 20 - Ablation of the anchor cell in wild type C....
Ch. 20 - 18.11 In gain-of-function and. elegans mutants,...Ch. 20 - Prob. 12PCh. 20 - Prob. 13PCh. 20 - 18.14 Given that maternal Bicoid activates the...Ch. 20 - What phenotypes do you expect in flies homozygous...Ch. 20 - The pair rule gene fushitarazu is expressed in...Ch. 20 - 18.17 In contrast to Drosophila, some insects...Ch. 20 - Prob. 18PCh. 20 - 18.19 You are traveling in the Netherlands and...Ch. 20 - 19.20 A powerful approach to identifying genes of...Ch. 20 - Prob. 21PCh. 20 - The Hoxd 913 genes are thought to specify digit...Ch. 20 - Three-spined stickleback fish live in lakes formed...Ch. 20 - In C. elegans there are two sexes: hermaphrodite...Ch. 20 - The flowering jungle plant Lacandoniaschismatica,...Ch. 20 - 18.24 Homeotic genes are thought to regulate each...Ch. 20 - Prob. 27PCh. 20 - Basidiomycota is a monophyletic group of fungi...Ch. 20 - In Drosophila, recessive mutations in the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Understanding why these receptors are present when they are not supposed to be is important in finding new treatments for Cushing's syndrome. When the sequences for the promoters for the receptor genes were analyzed there was no common sequences found. This led to the theory that the loss of methylation of cytosine in the promoters of these genes was leading to their inappropriate expression. How could the loss of cytosine methylation lead to overexpression of the receptor genes? O a. Increased histone acetyltransferase activity O b. Decreased histone deacetylase activity Oc Decreased histone acetyltransferase activity O d. Increased histone deacetylase activityarrow_forwardPlease Explainarrow_forwardPlease answer A mutation within an enhancer sequence regulating the expression of the ABC1 gene was discovered. Specifically, the mutation was associated with decreased expression of ABC1 in skeletal muscle. In a heterozygous individual carrying a mutant enhancer and a wild type enhancer, which allele(s) would be affected by the mutant enhancer and why?arrow_forward
- Describe the various post-translational modifications of HIF- 1alpha and how it affects the regulation of HIF-1al pha signaling. How might HIF- alpha alter the tumor microenvironment to promote tumor growth? Propose a strategy to prevent HIF-alpha signaling in the TME. What do you think would happen in a transgenic mouse with a total knockout of HIF-alpha?arrow_forwardA. Based on this data, draw a conclusion about the promoter elements that Caudal specifically upregulates. B. Dr. Juven-Gershon also tested Caudal activation of core promoter sequences from twoother genes. Similar to the first experiment, one was DPE-dependent (from the E74Bgene), and the other was TATA-dependent (from the Adh gene). However, these two corepromoters lacked the BREU motif. The results from these additional core promoters areshown below. Based on these results and those shown above, propose a hypothesis thatexplains the differences in Caudal-mediated upregulation among all the different corepromoters Dr. Juven-Gershon tested. C. To test your hypothesis from Question 3B, you plan perform the same method of genereporter assays that Dr. Juven-Gershon has done. However, you will need to do somemutations to alter the core promoters. Make diagrams or clearly describe all the variouscore promoters mutants you wish to test. These include your controls, as well as any…arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions based on the information given below: Act>CD2>Gal4 is a Flip-out construct that will express CD2 under the control of the ubiquitous Actin promoter in the absence of FLP. Expression of FLP will cause excision of the CD2 cassette so that GAL4 will be expressed instead. Suppose you identified a new gene X and generated UAS-X flies. In an experiment to examine the possible functions of X in eye development, you used flies with the following genotype: HsFLP; Act>CD2>Gal4, UAS-GFP / +; UAS-X /+ After a brief heat shock to induce FLP expression, you went on to examine eye discs for cells that express gene X. How can you identify cells that have the expression of gene X? (1 point) I would identify cells that have the expression of gene X through an Epistatic screen in the following image, you stained eye disc with antibodies against atonal (shown in Red), Elav (shown in blue), and GFP (shown in green). The yellow arrows point to the…arrow_forward
- Aurora AAurora A is a protein that acts as a kinase (transfers phosphates to molecules). Many types of cancer cells, including breast cancer cells, have higher than normal levels of this protein.Expressions of Aurora A genes in normal breast tissues (n = 10), normal tissues adjacent to tumors (n = 12) and breast tumors (n = 14).Scientists studying the production of Aurora A protein in normal frog cells observed that the amount of this protein in the cells changed throughout the cell cycle.Scientists tested chemicals that block Aurora 2 to see if they could be used as anti-cancer drugs. They found that some of the candidate drugs did slow the growth of cancer cells in cell culture in the lab. But when they tested these drugs in cancer patients to see if the drugs could slow the growth of solid tumors, they found that the benefit to patients was small when compared to the development of severe side effects such as anemia (low red blood cell count) and leukopenia (low white blood cell…arrow_forwardA second hit might occur through epigenetic modification. There is a CpG island in the RB1 promoter. What epigenetic modification is associated with CpG islands? What does this type of modification usually do to gene expression? How could this CpG island/this epigenetic modification be related toRB1 expression and retinoblastoma?arrow_forwardProlactin is a protein hormone that, among other things, enables mammals to produced milk. Prolactin is secreted from cells in the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, ovulation, and nursing. a. Prolactin is encoded by the PRL A segment of the PRL gene and its regulatory regions are shown below. The +1 site (*) and part of the promoter (#) of PRL are indicated. What is the PRL mRNA transcribed from the PRL gene? 5'-AAGCCGACCGGATATACGACGCCATGAACATGACAGGATCGCCATGG-3' 3'-TTCGGCTGGCCTATATGCTGCGGTACTTGTACTGTCCTAGCGGTACC-5' #### * b. What is the 5'-UTR of PRL? c. Using the mRNA you transcribed in part a, what are the first 8 amino acids of prolactin that are translated? cis face trans face MTOC Rough ER Golgi complex Cell membrane c. In what organelle is prolactin glycosylated? What motor protein would be used to transport prolactin from the rough ER to this organelle? d. Where does exocytosis occur? What motor protein would be used to transport prolactin from the site of its…arrow_forward
- Using baker's yeast it is possible to generate point mutations that destroy the kinase activity of CDK9/P-TEFB protein kinase. When genome-wide ChIP studies using anti-phosphorylated CTD antibodies and RNA-seq analysis of the mRNA purified from these cells were performed it was found that RNA Polymerase II was present in the 5' region of the coding regions of most protein coding genes, but mRNA levels were reduced for all genes tested. The cells that had this mutation were very sick and the mutation caused many of the cells to die. The abundance of mature mRNAs was lower than in non-mutant cells, and often lower than the levels of their corresponding pre-mRNA. Some of the mature mRNAs had short poly A tails and some were detected with none at all. Based on this information: Provide one reason why this mutation in CDK9 affects the levels of mature mRNAs?arrow_forwardUsing baker's yeast it is possible to generate point mutations that destroy the kinase activity of CDK9/P-TEFB protein kinase. When genome-wide ChIP studies using anti-phosphorylated CTD antibodies and RNA-seq analysis of the mRNA purified from these cells were performed it was found that RNA Polymerase II was present in the 5' region of the coding regions of most protein coding genes, but mRNA levels were reduced for all genes tested. The cells that had this mutation were very sick and the mutation caused many of the cells to die. The abundance of mature mRNAs was lower than in non-mutant cells, and often lower than the levels of their corresponding pre-mRNA. Some of the mature mRNAs had short poly A tails and some were detected with none at all. Based on this information: Why are the poly A tails affected in this mutant?arrow_forwardYou have been analyzing wing development mutants in Drosophila and have collected the genetic/Western data below. Your epistasis analysis (not shown), suggested your current model that DW-2 is upstream of WL-1. What is a plausible mechanism for how DW-2 regulates WL-1? mutant name wingless-1 doublewing-2 Prated with Ants-Wingless MW standards || | | mutanttype ODW-2 inhibits transcription of WL-1 O DW-2 polyubiquitinates WL-1 null null phenotype Model Ac O DW-2 phosphorylates WL-1 and prevents it from entering the nucleus O DW-2 cleaves WL-1 proteolytically Wings Mode of regulation DW-2 Wings Wingsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education
Embryology | Fertilization, Cleavage, Blastulation; Author: Ninja Nerd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8-KF0rnhKTU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY