
Pipe 2 has been inserted snugly into Pipe I. but the holes Tor a connecting pin do not line up; there is a gap s. The user decides to apply either force P:lo Pipe I or force P-, to Pipe 2, whichever is smaller. Determine the following using the numerical properties in the box.
(a) If only P{is applied, find Pt{tips} required to close gap s; if a pin is then inserted and Ptremoved, what are reaction forces RAand RBfor this load case?
(b) If only P2is applied, find P2{kips) required to close gap a; if a pin is inserted and P2removed, what are reaction forces R^ and RBfor this load case?
(c) What is the maximum shear stress in the pipes, for the loads in parts (a) and (b)?
(d) If a temperature increase IT is to be applied to the entire structure to close gaps{instead of applying forces Ptand P2), find the AT required to close the gap. If a pin is inserted after the gaphas closed, what are reaction forces .''.', and RBfor this case? (e) Finally, if the structure (with pin inserted) then cools to the original ambient temperature, what are reaction forces Rtand P 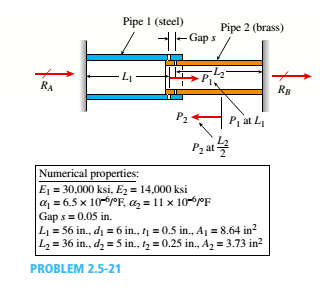
(a)
The reactions at A and B.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The reaction at A is =
The reaction at B is =
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for elongation in pipe 1.
Here, length of pipe 1 is
Write the expression for elongation at point B.
Here, elongation at point B is
Write the expression for net elongation at B.
Here, elongation at point 1 is
Substitute
Write the reaction at point A.
Here, reaction at A is
Calculation:
Substitute
The force required to close the gap is
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
(b)
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for force applied at pipe 2.
Here, force applied at pipe 2 is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
(b)
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 and pipe 2.
.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is
The maximum shear stress in pipe 2 is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for maximum shear stress in pipe 1.
Here, maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is
Write the expression for maximum shear stress in pipe.
Here, maximum shear stress in pipe 2 is
Calculation:
Substitute
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is =
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum shear stress in pipe 1 is =
The maximum shear stress in pipe 2 is =
(d)
The rise in temperature required to close the gap.
The reactions.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The rise in temperature required to close the gap is
The reactions are
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Write the expression for temperature raise.
Here, raise in temperature is
Calculation:
Substitute
Since the temperature remains constant, so the reactions are zero.
Conclusion:
The temperature raise required to close the gap is
The reactions are
(e)
The reaction at A.
The reaction at B.
Answer to Problem 2.5.21P
The reaction at A is
The reaction at B is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The gap between the pipes is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The reaction at A is =
The reaction at B is =
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- The members of a truss are connected to the gusset plate as shown in (Figure 1). The forces are concurrent at point O. Take = 90° and T₁ = 7.5 kN. Part A Determine the magnitude of F for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. F= 7.03 Submit ? kN Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 21 attempts remaining ▾ Part B Determine the magnitude of T2 for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure T₂ = 7.03 C T2 |? KN Submit Previous Answers Request Answer × Incorrect; Try Again; 23 attempts remaining Provide Feedbackarrow_forwardConsider the following acid-base reaction: Fe3+(aq) +3H2O -Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3H* ← A. Using thermodynamics, calculate the equilibrium constant K at 25°C (The AG° of formation of Fe(OH)3(s) is -699 kJ/mol). B. Using the value of K you calculated in part a, if a solution contains 10-4 M Fe3+ and has a pH of 7.5, will Fe(OH)3(s) precipitate? Show all calculations necessary to justify your answer. Note that the reaction as written is for precipitation, not dissolution like Ksp-arrow_forwardA vertical force of F = 3.4 kN is applied to the hook at A as shown in. Set d = 1 m. Part A 3 m 3m 0.75 m 1.5 m. Determine the tension in cable AB for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB= Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the tension in cable AC for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAC = Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in cable AD for equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward
- Consider the heat engine operating at steady state between the two thermal reservoirs shown at the right while producing a net power output of 700 kW. If 1000 kW of heat (Q̇H) is transferred to the heat engine from a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TH = 900 K, and heat is rejected to a thermal reservoir at a temperature of TL = 300 K, is this heat engine possible? Can you answer this question for me and show all of the workarrow_forward1.12 A disk of constant radius r is attached to a telescoping rod that is extending at a constant rate as shown in Fig. P1.12. Both the disk and the rod are rotating at a constant rate. Find the inertial velocity and acceleration of point P at the rim of the disk. ท2 L 0 SS P α e 0 O' êL Fig. P1.12 Rotating disk attached to telescoping rod. 60 LLarrow_forwardTwo different options A and B with brake pads for disc brakes are connected to the rope drum. The diameter of the rope drum is 150 mm. What distance must the pads B be at from the center of rotation to cover the same distance as A?A B- Width 50 mm - Width 60 mm- Evidence center 120mm - Construction power 900 N from rotation center.- Maintains a weight of 200 kgwhen the installation force is 1.4kN (μ is missing from the data)M=μF(Ry-Ri)Right answer R=187 mmarrow_forward
- Assume the xy plane is level ground, and that the vertical pole shown in the diagram lies along the z-axis with its base at the origin. If the pole is 5 m tall, and a rope is used to pull on the top of the pole with a force of 400 N as shown, determine the magnitudes of the parallel and perpendicular components of the force vector with respect to the axis of the post i.e. with respect to the z-axis.arrow_forward4-1 Q4: Q5: (20 Marks) Find √48 using False Position Method with three iterations. Hint: the root lies between 3 and 4. (20 Marks)arrow_forwardDetermine the angle between vectors FA and FB that is less than 180 degrees. FA is the vector drawn from the origin to point A (-4, 4, 2) while FB is the vector drawn from the origin to point B (3, 1, -3).arrow_forward
- Find the resultant force vector from adding F1, F2 and F3, where … F1 = {-8i+10j-32k} N F2 is 40 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α, β, and γ, of 45, 120 and 60 degrees, respectively and F3 is 22 N in magnitude with transverse and azimuth angles of 65 and 40 degrees, respectively Express your final answer as a Cartesian vector as well as a magnitude with angles.arrow_forwardA 2-kW resistance heater wire with thermal conductivity of k=20 W/mK, a diameter of D=4mm, and a length of L=0.9m is used to boil water. If the outer surface temp of the resistance wire is Ts=110 degrees C, determine the temp at the center of the wire.arrow_forwardA flat-plate solar collector is used to heat water by having water flow through tubes attached at the back of the thin solar absorber plate. The absorber plate has emmisssivity and an absorptivity of 0.9. The top surface where x=0 temp of the absorber is T0=35 degrees C, and solar radiation is incident on the basorber at 500 W/m^2 with a surrounding temp of 0 degrees C. The convection heat transfer coefficient at the absorber surface is 5 W/m^2 K, while the ambient temp is 25 degrees C. Show that the variation of the temp in the basorber plate can be expressed as T(x)=-(q0/k)x+T0, and determine net heat flux, q, absorbed by solar collector.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
