
Concept explainers
The plane truss in the figure is assembled From steel C 10 X 20 shapes (see Table 3(a) in Appendix F). Assume that L = 10 ft and b = 0 71 L.
(a) If load variable P = 49 kips, what is the maximum shear stress Tmaxin each truss member?
(b) What is the maximum permissible value of load variable P if the allowable normal stress is 14 ksi and the allowable shear stress is 7.5 ksi?
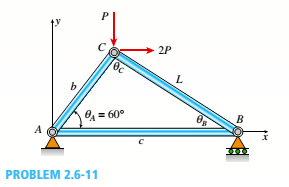
(a)
The maximum shear stress in the member AC.
The maximum shear stress in the member AB.
The maximum shear stress in the member BC.
Answer to Problem 2.6.11P
The maximum shear stress in the member AC is =
The maximum shear stress in the member AB is =
The maximum shear stress in the member BC is =
Explanation of Solution
The following figure shows the forces on the truss:
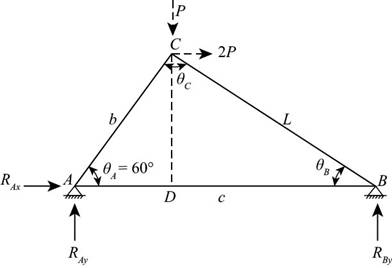
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the length
Write the expression for the length CD.
Here, the length of
Write the expression for the length AD.
Write the expression for the angle
Here, the length of the member CB is
Write the expression for the length DB.
Write the expression for the length AB.
Write the expression for the moment at point A.
Here, the variable load is
Write the equilibrium equation for the horizontal forces.
Write the equilibrium equation for the vertical forces.
Write the expression for the forces at joint A.
Write the expression for the horizontal forces at joint A.
Write the expression for the horizontal forces at joint B.
Write the expression for the maximum shear stress in the member AC.
Write the expression for the maximum shear stress in the member AB.
Write the expression for the maximum shear stress in the member BC.
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Refer to table F-3 (a), “Properties of channel sections” to obtain the area of cross-section of
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The maximum shear stress in the member AC is =
The maximum shear stress in the member AB is =
The maximum shear stress in the member BC is =
(b)
The maximum permissible load.
Answer to Problem 2.6.11P
The maximum permissible load is =
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the maximum permissible load on member
Here, permissible normal stress is
Write the expression for the maximum permissible load on member
Here, permissible normal stress is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
The lowest value of the maximum permissible load is =
Conclusion:
The maximum permissible load is =
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- A plastic bar of rectangular cross section (ft = 1.5 in. and h = 3 in.) fits snugly between rigid supporls at room temperature (68oF) but with no initial stress (see Figure). When the temperature of the bar is raised to 160oF, the compressive stress on an inclined plane pq at mid-span becomes 1700 psi. (a) What is the shear stress on plane pq? (Assume a = 60 × 10-6/*t and E = 450 × 103psi.) (b) Draw a stress element oriented to plane pq and show the stresses acting on all laces of this element. (c) If the allowable normal stress is 3400 psi and the allowable shear stress is 1650 psi. what is the maximum load P (in the positive x direction), which can be added at the quarter point (in addition to thermal effects given) without exceeding allowable stress values in the bar?arrow_forwardA stepped bar ACB with circular cross sections is held between rigid supports and loaded by an axial force P at midlength (see figure). The diameters for the two parts of the bar are d1= 20 ram and d2= 25 mm, and the material is elastoplastic with yield stress s = 250 MPs. Determine the plastic load Pp.arrow_forwardAround brass bar of a diameter d1= 20mm has upset ends each with a diameter d2= 26 mm (see figure). The lengths of the segments of the bar are L1= 0.3 m and L2= 0.1 m. Quarter-circular fillets are used at the shoulders of the bar, and the modulus of elasticity of the brass is E = 100 GPa. If the bar lengthens by 0.12 mm under a tensile load P, what is the maximum stress ??maxin the bar?arrow_forward
- Truss members supporting a roof are connected to a 26-mm-thick gusset plate by a 22-mm diameter pin, as shown in the figure and photo. The two end plates on the truss members are each 14 mm thick. (a) If the load P = 80 kN, what is the largest bearing stress acting on the pin? (b) If the ultimate shear stress for the pin is 190 MPa, what force Pult is required to cause the pin to fail in shear? Disregard friction between the plates.arrow_forwardSolve the preceding problem using the following data: beam cross section is 100 x 150 mm, length is 3 m, and point load is P = 5 kN at mid-span, Point C is located 25 mm below the top of the beam and 0.5 m to the right of support A.arrow_forwardA steel riser pipe hangs from a drill rig located offshore in deep water (see figure). (a) What is the greatest length (meters) it can have without breaking if the pipe is suspended in the air and the ultimate strength (or breaking strength) is 550 MPa? (b) If the same riser pipe hangs from a drill rig at sea, what is the greatest length? (Obtain the weight densities of steel and sea water from Table M, Appendix I. Neglect the effect of buoyant foam casings on the pipe.)arrow_forward
- An aluminum bar has length L = 6 ft and diameter d = 1.375 in. The stress-strain curse for the aluminum is shown in Fig. 1.34. The initial straight, line part of the curve has a slope (modulus of elasticity) of 10.6 × 106 psi. The bar is loaded by tensile forces P = 44.6 k and then unloaded. (a) That is the permanent set of the bar? (b) If the bar is reloaded. what is the proportional limit? hint: Use the concepts illustrated in Figs. l.39b and 1.40.arrow_forwardContinuous cable A DB runs over a small friction less pulley al D to support beam OABC, which is part of an entrance canopy for a building (see figure}. The canopy segment has a weight W = 1700 lb that acts as a concentrated load in the middle of segment AB. (a) What is the maximum permissible value of load P at C if the allowable force in the cable is 4200 lb? (b) If P = 2300 lb, what is the required diameter of pins A, B, and D? Assume that the pins are in double shear and the allowable shear stress in the pins is 10 ksi.arrow_forwardA large precast concrete panel for a warehouse is raised using two sets of cables at two lift lines, as shown in the figure part a. Cable 1 has a length L1 = 22 Ft, cable 2 has a length L2= 10 ft, and the distance along the panel between lift points Band D is d = 14 ft (see figure part b). The total weight of the panel is W = 85 kips. Assuming the cable lift Forces F at each lift line are about equal, use the simplified model of one half of the panel in figure part b to perform your analysis for the lift position shown. Find the required cross-sectional area AC of the cable if its breaking stress is 91 ksi and a factor of safety of 4 with respect to failure is desired.arrow_forward
- A plane truss is subjected to loads 2P and P at joints B and C, respectively, as shown in the figure part a. The truss bars are made of two L 102 X 76 X 6.4 steel angles (see Table F-5(b): cross-sectional area or the two angles, A = 2180 mm2, and figure part b) having an ultimate stress in tension equal to 390 MPa. The angles are connected to a 12-mm-thick gusset plate at C(figure part c) with 16-mm diameter rivets; assume each rivet transfers an equal share of the member force to the gusset plate. The ultimate stresses in shear and bearing for the rivet steel are 190 MPa and 550 MPa, respectively. Determine the allowable load Pallowif a safety factor of 2.5 is desired with respect to the ultimate load that can be carried. Consider tension in the bars, shear in the rivets, bearing between the rivets and gusset plate. Disregard friction between the plates the bars, and also bearing between the rivets and the and the weight of the truss itself.arrow_forwardA cantilever beam(Z, = 6 ft) with a rectangular cross section (/> = 3.5 in., h = 12 in.) supports an upward load P = 35 kips at its free end. (a) Find the state of stress ((7T, o^., and r in ksi) on a plane-stress element at L/2 that is i/ = 8 in. up from the bottom of the beam. Find the principal normal stresses and maximum shear stress. Show these stresses on sketches of properly oriented elements. (b) Repeat part (a) if an axial compressive centroidal load N = 40 kips is added at Barrow_forwardA steel post (E=30×106) having thickness t = 1/8 in. and height L = 72 in. support a stop sign (see figure), where s = 12.5 in. The height of the post L is measured from the base to the centroid of the sign. The stop sign is subjected to wind pressure p = 20 lb/ft2 normal to its surface. Assume that the post is fixed at its base. What is the resultant load on the sign? (Sec Appendix E, Case 25, for properties of an octagon, n =8.) What is the maximum bending stress in the post? Repeat part (b) if the circular cut-outs arc eliminated over the height of the post.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
