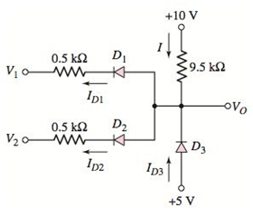
Problem 2.1EP: Repeat Example 2.1 if the input voltage is s(t)=12sint(V) , VB=4.5V , and R=250 . (Ans.... Problem 2.2EP: Consider the bridge circuit shown in Figure 2.6(a) with an input voltage S=VMsint . Assume a diode... Problem 2.3EP: Assume the input signal to a rectifier circuit has a peak value of VM=12V and is at a frequency of... Problem 2.4EP: The input voltage to the halfwave rectifier in Figure 2.8(a) is S=75sin[2(60)t]V . Assume a diode... Problem 2.1TYU: Consider the circuit in Figure 2.4. The input voltage is s(t)=15sint(V) and the diode cutin voltage... Problem 2.2TYU: The circuit in Figure 2.5(a) is used to rectify a sinusoidal input signal with a peak voltage of 120... Problem 2.3TYU: The secondary transformer voltage of the rectifier circuit shown in Figure 2.6(a) is... Problem 2.4TYU: Determine the fraction (percent) of the cycle that each diode is conducting in (a) Exercise EX2.4,... Problem 2.5EP: The Zener diode regulator circuit shown in Figure 2.16 has an input volt age that varies between 10... Problem 2.6EP: Repeat Example 2.6 for rz=4 . Assume all other parameters are the same as listed in the example.... Problem 2.5TYU: Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.19. Let VPS=12V , VZO=6.2V , and rz=3 . The power rating of... Problem 2.6TYU: Suppose the currentlimiting resistor in Example 2.5 is replaced by one whose value is Ri=20 .... Problem 2.7TYU: Suppose the power supply voltage in the circuit shown in Figure 2.17 drops to VPS=10V . Let Ri=15.3... Problem 2.7EP: Design a parallelbased clipper that will yield the voltage transfer function shown in Figure 2.24.... Problem 2.8EP: Sketch the steadystate output voltage for the input signal given for the circuit shown in Figure... Problem 2.8TYU: Consider the circuit in Figure 2.23(a). Let R1=5k , R2=2k , V1=1V , and V2=3V . Let V=0.7V for each... Problem 2.9TYU: Determine the steadystate output voltage O for the circuit in Figure 2.31(a), if the input is as... Problem 2.10TYU: Design a parallelbased clipper circuit that will yield the voltage transfer characteristics shown in... Problem 2.9EP: Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.38, in which the diode cutin voltages are V=0.6V . Plot O... Problem 2.10EP: Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.39. The cutin voltage of each diode is V=0.7V . (a) Let I=5V... Problem 2.11EP: Repeat Example 2.11 for the case when R1=8k , R2=4k , and R3=2k . (Ans. VB=0.7V , ID3=2.15mA , ID2=0... Problem 2.11TYU: The cutin voltage of each diode in the circuit shown in Figure 2.43 is V=0.7V . Determine... Problem 2.12TYU Problem 2.13TYU: Consider the OR logic circuit shown in Figure 2.41. Assume a diode cut in voltage of V=0.6V . (a)... Problem 2.14TYU: Consider the AND logic circuit shown in Figure 2.42. Assume a diode cutin voltage of V=0.6V . (a)... Problem 2.12EP: (a) Photons with an energy of hv=2eV are incident on the photodiode shown in Figure 244. The... Problem 2.13EP: Determine the value of resistance R required to limit the current in the circuit shown in Figure... Problem 1RQ: What characteristic of a diode is used in the design of diode signal processing circuits? Problem 2RQ Problem 3RQ: Describe a simple fullwave diode rectifier circuit and sketch the output voltage versus time. Problem 4RQ Problem 5RQ Problem 6RQ: Describe a simple Zener diode voltage reference circuit. Problem 7RQ: What effect does the Zener diode resistance have on the voltage reference circuit operation? Define... Problem 8RQ: What are the general characteristics of diode clipper circuits? Problem 9RQ: Describe a simple diode clipper circuit that limits the negative portion of a sinusoidal input... Problem 10RQ Problem 11RQ: What one circuit element, besides a diode, is present in all diode clamper circuits? Problem 12RQ Problem 13RQ: Describe a diode OR logic circuit. Compare a logic 1 value at the output compared to a logic 1 value... Problem 14RQ: Describe a diode AND logic circuit. Compare a logic 0 value at the output compared to a logic 0... Problem 15RQ: Describe a simple circuit that can be used to turn an LED on or off with a high or low input... Problem 2.1P: Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.1. Let R=1k , V=0.6V , and rf=20 . (a) Plot the voltage... Problem 2.2P: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.1, show that for I0 , the output voltage is approximately given... Problem 2.3P: A halfwave rectifier such as shown in Figure 2.2(a) has a 2k load. The input is a 120V(rms) , 60 Hz... Problem 2.4P: Consider the battery charging circuit shown in Figure 2.4(a). Assume that VB=9V , VS=15V , and... Problem 2.5P: Figure P2.5 shows a simple fullwave battery charging circuit. Assume VB=9V , V=0.7V , and... Problem 2.6P: The fullwave rectifier circuit shown in Figure 2.5(a) in the text is to deliver 0.2 A and 12 V (peak... Problem 2.7P: The input signal voltage to the fullwave rectifier circuit in Figure 2.6(a) in the text is... Problem 2.8P: The output resistance of the fullwave rectifier in Figure 2.6(a) in the text is R=150 . A filter... Problem 2.9P: Repeat Problem 2.8 for the halfwave rectifier in Figure 2.2(a). Problem 2.10P: Consider the halfwave rectifier circuit shown in Figure 2.8(a) in the text. Assume... Problem 2.11P: The parameters of the halfwave rectifier circuit in Figure 2.8(a) in the text are R=1k , C=350F ,... Problem 2.12P: The fullwave rectifier circuit shown in Figure P2.12 has an input signal whose frequency is 60 Hz.... Problem 2.13P: Consider the fullwave rectifier circuit in Figure 2.7 of the text. The output resistance is RL=125 ,... Problem 2.14P: The circuit in Figure P2.14 is a complementary output rectifier. If S=26sin[2(60)t]V , sketch the... Problem 2.15P Problem 2.16P: A fullwave rectifier is to be designed using the bridge circuit configuration. The peak output... Problem 2.17P Problem 2.18P: (a) Sketch o versus time for the circuit in Figure P2.18. The input is a sine wave given by... Problem 2.19P: Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.19. The Zener diode voltage is VZ=3.9V and the Zener diode... Problem 2.20P: Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure P2.20. Assume VZ=12V and rz=0 . (a) Calculate the... Problem 2.21P: Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure P2.21. Let V1=60V , Ri=150 , and VZO=15.4V . Assume... Problem 2.22P: In the voltage regulator circuit in Figure P2.21, VI=20V , VZ=10V , Ri=222 , and PZ(max)=400mW . (a)... Problem 2.23P: A Zener diode is connected in a voltage regulator circuit as shown in Figure P221. The Zener voltage... Problem 2.24P: Consider the Zener diode circuit in Figure 2.19 in the text. Assume parameter values of VZO=5.6V... Problem D2.25P: Design a voltage regulator circuit such as shown in Figure P2.21 so that VL=7.5V . The Zener diode... Problem 2.26P: The percent regulation of the Zener diode regulator shown in Figure 2.16 is 5 percent. The Zener... Problem 2.27P: A voltage regulator is to have a nominal output voltage of 10 V. The specified Zener diode has a... Problem 2.28P: Consider the circuit in Figure P2.28. Let V=0 . The secondary voltage is given by s=Vssint , where... Problem 2.29P: The secondary voltage in the circuit in Figure P228 is S=12sintV . The Zener diode has parameters... Problem 2.30P: The parameters in the circuit shown in Figure P2.30 are V=0.7V , VZ1=2.3V , and VZ2=5.6V . Plot O... Problem 2.31P: Consider the circuit in Figure P2.31. Let V=0 (a) Plot O versus I over the range 10I+10V . (b) Plot... Problem 2.32P Problem 2.33P: Each diode cutin voltage is 0.7 V for the circuits shown in Figure P2.33. (a) Plot O versus I over... Problem 2.34P: The diode in the circuit of Figure P2.34(a) has piecewise linear parameters V=0.7V and rf=10 . (a)... Problem 2.35P: Consider the circuits shown in Figure P2.35. Each diode cutin voltage is V=0.7V . (a) Plot O versus... Problem 2.36P: Plot O for each circuit in Figure P2.36 for the input shown. Assume (a) V=0 and (b) V=0.6V . Figure... Problem 2.37P: Consider the parallel clipper circuit in Figure 2.26 in the text. Assume VZ1=6V , VZ2=4V , and... Problem 2.38P: A car’s radio may be subjected to voltage spikes induced by coupling from the ignition system.... Problem 2.39P: Sketch the steadystate output voltage O versus time for each circuit in Figure P2.39 with the input... Problem D2.40P Problem D2.41P: Design a diode clamper to generate a steadystate output voltage O from the input voltage I in Figure... Problem 2.42P: For the circuit in Figure P2.39(b), let V=0 and I=10sint(V) . Plot O versus time over three cycles... Problem 2.43P: Repeat Problem 2.42 for the circuit in Figure P2.39(c) for (i) VB=5V and (ii) VB=5V . Problem 2.44P: The diodes in the circuit in Figure P2.44 have piecewise linear parameters of V=0.6V and rf=0 .... Problem 2.45P: In the circuit in Figure P2.45 the diodes have the same piecewise linear parameters as described in... Problem 2.46P: The diodes in the circuit in Figure P2.46 have the same piecewise linear parameters as described in... Problem 2.47P: Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.47. Assume each diode cutin voltage is V=0.6V . (a)... Problem 2.48P: The diode cutin voltage for each diode in the circuit shown in Figure P2.48 is 0.7V. Determine the... Problem 2.49P: Consider the circuit in Figure P2.49. Each diode cutin voltage is V=0.7V . (a) For R2=1.1k ,... Problem 2.51P: Assume V=0.7V for each diode in the circuit in Figure P251. Plot O versus I for 10I+10V . Figure... Problem 2.52P: The cutin voltage of each diode in the circuit shown in Figure P2.52 is V=0.7V . Determine... Problem 2.53P: Let V=0.7V for each diode in the circuit in Figure P253. (a) Find ID1 and VO for R1=5k and R2=10k .... Problem 2.54P: For the circuit shown in Figure P2.54, let V=0.7V for each diode. Calculate ID1 and VO for (a)... Problem 2.55P: Assume each diode cutin voltage is V=0.7V for the circuit in Figure P2.55. Determine ID1 and VO for... Problem 2.56P: If V=0.7V for the diode in the circuit in Figure P2.56 determine ID and VO . Figure P2.56 Problem 2.57P: Let V=0.7V for the diode in the circuit in Figure P2.57. Determine ID,VD,VA , and VB for (a)... Problem 2.59P: Each diode cutin voltage in the circuit in Figure P2.59 is 0.7 V. Determine ID1,ID2,ID3 , and O for... Problem 2.60P: Let V=0.7V for each diode in the circuit shown in Figure P2.60. Plot ID2 versus I over the range... Problem 2.61P: Consider the circuit in Figure P2.61. The output of a diode OR logic gate is connected to the input... Problem 2.62P: Consider the circuit in Figure P2.62. The output of a diode AND logic gate is connected to the input... Problem 2.63P Problem 2.64P: Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.64. The forwardbias cutin voltage of the diode is 1.5 V and... Problem 2.65P: The lightemitting diode in the circuit shown in Figure P2.64 has parameters V=0.7V and rf=0 . Light... Problem 2.66P: The parameters of D1 and D2 in the circuit shown in Figure P2.66 are V=1.7V and rf=20 . The current... Problem 2.67P: If the resistor in Example 2.12 is R=2 and the diode is to be reverse biased by at least 1 V,... Problem 2.68P: Consider the photodiode circuit shown in Figure 2.44. Assume the quantum efficiency is 1. A... Problem D2.73DP: Consider the fullwave bridge rectifier circuit. The input signal is 120V(rms) at 60 Hz. The load... Problem D2.74DP: Design a simple dc voltage source using a 120V(rms) , 60 Hz input signal to a nominal 10 V output... Problem D2.75DP: A clipper is to be designed such that O=2.5V for I2.5V and O=1.25V for I1.25V . Problem D2.76DP: Design a circuit to provide the voltage transfer characteristics shown in Figure P2.76. Use diodes... format_list_bulleted


 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,




