
The cut−in voltage of each diode in the circuit shown in Figure P2.52 is
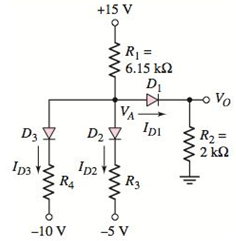
Figure P2.52
(a)
The values of
Answer to Problem 2.52P
The current flowing through diodes is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
The cut-in voltage for each diode is,
Assume all diodes are ON.
Draw the circuit diagram with node voltages and cut-in voltages.
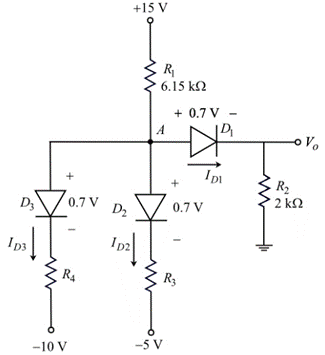
Apply Kirchhoff’s current law node A.
Substitute
Therefore, the voltage at node
Calculate the current flowing through diode,
Substitute
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Calculate the current flowing through diode,
Substitute
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Calculate the current flowing through diode,
Substitute
Therefore, the current flowing through diodes is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current flowing through diodes is
(b)
The values of
Answer to Problem 2.52P
The current flowing through diodes is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Assume diode
Draw the circuit diagram with node voltages and cut-in voltages.
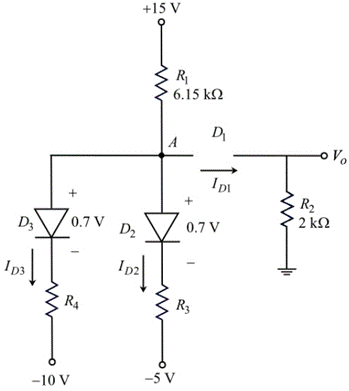
Apply Kirchhoff’s current law node A.
Substitute
Therefore, the voltage at node
The diode
That is,
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Calculate the current flowing through diode,
Substitute
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Calculate the current flowing through diode,
Substitute
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current flowing through diodes is
(c)
The values of
Answer to Problem 2.52P
The current flowing through diodes is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Calculation:
Assume diode
Draw the circuit diagram with node voltages and cut-in voltages.
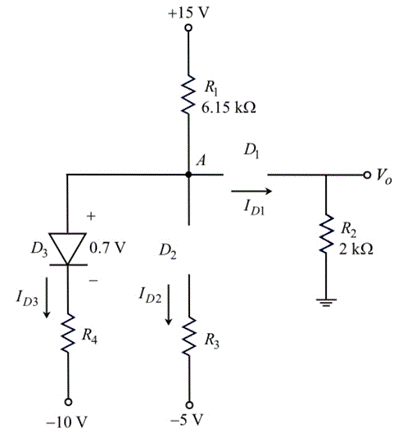
Apply Kirchhoff’s current law node A.
Substitute
Therefore, the voltage at node
The Diode
That is,
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
The current flowing through the diode,
That is,
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Calculate the current flowing through diode,
Substitute
Therefore, the current flowing through diode
Conclusion:
Therefore, the current flowing through diodes is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
MICROELECT. CIRCUIT ANALYSIS&DESIGN (LL)
- Determine the power radiated for the antenna has the following specifications (48 ohm radiation resistance, 2 ohm loss resistance and 50 ohms reactance) connected to generator with 12 V open circuit and internal impedance 50 ohm via à long transmission line with 100 ohm characteristic impedance.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardThe former expert solved the question, but I didn't understand how he simplified the fractions. A communication satellite is in stationary (synchronous) orbit about the carch (assume altitude of 22.300 statute miles). Its transmitter generates 8.0 W. Assume the transmit- ting antenna is isotropic. Its signal is received by the 210-ft diameter tracking parabo- loidal antenna on the earth at the NASA tracking station at Goldstone, California. Also assume no resistive loss in either antenna, perfect polarization match, and perfect impedance match at both antennas. At a frequency of 2 GHz, determine the: (a) power density (in watts/m²) incident on the receiving antenna. (b) power received by the ground-based antenna whose gain is 60 dB.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- A communication satellite is in stationary (synchronous) orbit about the earch (assume altitude of 22.300 statute miles). Its transmitter generates 8.0 W. Assume the transmit- ting antenna is isotropic. Its signal is received by the 210-ft diameter tracking parabo- loidal antenna on the earth at the NASA tracking station at Goldstone, California. Also assume no resistive loss in either antenna, perfect polarization match, and perfect impedance match at both antennas. At a frequency of 2 GHz. determine the: (a) power density (in watts/m²) incident on the receiving antenna. (b) power received by the ground-based antenna whose gain is 60 dB.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardA plane wave traveling in z-direction through a medium with &=8, μ-2 and has the electric and magnetic field intensity at z=0 shown in Fig. 6.1 and Fig. 6.2, respectively. Utilize the provided information to find the following: (a) w (b) The intrinsic impedance of the medium © B (d) a (e) The expression of the magnetic field intensity, H (f) The time-average power carried by the wave Magnetic Field Intensity (mA/m) Electric Field Intensity (V/m) 0.5 0.4- 0.3 0.2 ཧཱུྃ༔ཤྲུསྦྱ ཌུ ཋ ; སྟྲི " ° ཝཱ 0.1 -0.5 Ex -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 Fig 6.2 Hy 2.0 Time (ns)². -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0; 0.5 1.0 Time (ns) 2.0 0.083 ns or 0.0415 Tarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





