
MICROELECT. CIRCUIT ANALYSIS&DESIGN (LL)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781266368622
Author: NEAMEN
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.12P
The full−wave rectifier circuit shown in Figure P2.12 has an input signal whose frequency is 60 Hz. The rms value of
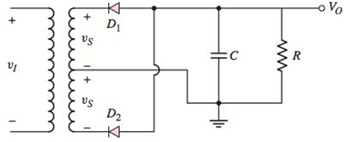
Figure P2.12
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
2 Find Inverse Fourier transform of
F(jw)
=
2w
-16+w2, and plot the f(t).
Need Handwritten Solution. Do not use chatgpt or AI
Solve by pen & paper without using chatgpt or AI
Mesh analysis
Chapter 2 Solutions
MICROELECT. CIRCUIT ANALYSIS&DESIGN (LL)
Ch. 2 - Repeat Example 2.1 if the input voltage is...Ch. 2 - Consider the bridge circuit shown in Figure 2.6(a)...Ch. 2 - Assume the input signal to a rectifier circuit has...Ch. 2 - The input voltage to the halfwave rectifier in...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure 2.4. The input...Ch. 2 - The circuit in Figure 2.5(a) is used to rectify a...Ch. 2 - The secondary transformer voltage of the rectifier...Ch. 2 - Determine the fraction (percent) of the cycle that...Ch. 2 - The Zener diode regulator circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Repeat Example 2.6 for rz=4 . Assume all other...
Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.19. Let...Ch. 2 - Suppose the currentlimiting resistor in Example...Ch. 2 - Suppose the power supply voltage in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Design a parallelbased clipper that will yield the...Ch. 2 - Sketch the steadystate output voltage for the...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure 2.23(a). Let R1=5k...Ch. 2 - Determine the steadystate output voltage O for the...Ch. 2 - Design a parallelbased clipper circuit that will...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.38, in...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure 2.39. The...Ch. 2 - Repeat Example 2.11 for the case when R1=8k ,...Ch. 2 - The cutin voltage of each diode in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.12TYUCh. 2 - Consider the OR logic circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the AND logic circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - (a) Photons with an energy of hv=2eV are incident...Ch. 2 - Determine the value of resistance R required to...Ch. 2 - What characteristic of a diode is used in the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2RQCh. 2 - Describe a simple fullwave diode rectifier circuit...Ch. 2 - Prob. 4RQCh. 2 - Prob. 5RQCh. 2 - Describe a simple Zener diode voltage reference...Ch. 2 - What effect does the Zener diode resistance have...Ch. 2 - What are the general characteristics of diode...Ch. 2 - Describe a simple diode clipper circuit that...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10RQCh. 2 - What one circuit element, besides a diode, is...Ch. 2 - Prob. 12RQCh. 2 - Describe a diode OR logic circuit. Compare a logic...Ch. 2 - Describe a diode AND logic circuit. Compare a...Ch. 2 - Describe a simple circuit that can be used to turn...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.1. Let...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.1, show that...Ch. 2 - A halfwave rectifier such as shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the battery charging circuit shown in...Ch. 2 - Figure P2.5 shows a simple fullwave battery...Ch. 2 - The fullwave rectifier circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - The input signal voltage to the fullwave rectifier...Ch. 2 - The output resistance of the fullwave rectifier in...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.8 for the halfwave rectifier in...Ch. 2 - Consider the halfwave rectifier circuit shown in...Ch. 2 - The parameters of the halfwave rectifier circuit...Ch. 2 - The fullwave rectifier circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the fullwave rectifier circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - The circuit in Figure P2.14 is a complementary...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.15PCh. 2 - A fullwave rectifier is to be designed using the...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.17PCh. 2 - (a) Sketch o versus time for the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.19. The...Ch. 2 - Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the Zener diode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - In the voltage regulator circuit in Figure P2.21,...Ch. 2 - A Zener diode is connected in a voltage regulator...Ch. 2 - Consider the Zener diode circuit in Figure 2.19 in...Ch. 2 - Design a voltage regulator circuit such as shown...Ch. 2 - The percent regulation of the Zener diode...Ch. 2 - A voltage regulator is to have a nominal output...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure P2.28. Let V=0 ....Ch. 2 - The secondary voltage in the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - The parameters in the circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure P2.31. Let V=0 (a)...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.32PCh. 2 - Each diode cutin voltage is 0.7 V for the circuits...Ch. 2 - The diode in the circuit of Figure P2.34(a) has...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuits shown in Figure P2.35. Each...Ch. 2 - Plot O for each circuit in Figure P2.36 for the...Ch. 2 - Consider the parallel clipper circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - A car’s radio may be subjected to voltage spikes...Ch. 2 - Sketch the steadystate output voltage O versus...Ch. 2 - Prob. D2.40PCh. 2 - Design a diode clamper to generate a steadystate...Ch. 2 - For the circuit in Figure P2.39(b), let V=0 and...Ch. 2 - Repeat Problem 2.42 for the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - The diodes in the circuit in Figure P2.44 have...Ch. 2 - In the circuit in Figure P2.45 the diodes have the...Ch. 2 - The diodes in the circuit in Figure P2.46 have the...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.47. Assume...Ch. 2 - The diode cutin voltage for each diode in the...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure P2.49. Each diode...Ch. 2 - Assume V=0.7V for each diode in the circuit in...Ch. 2 - The cutin voltage of each diode in the circuit...Ch. 2 - Let V=0.7V for each diode in the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - For the circuit shown in Figure P2.54, let V=0.7V...Ch. 2 - Assume each diode cutin voltage is V=0.7V for the...Ch. 2 - If V=0.7V for the diode in the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - Let V=0.7V for the diode in the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - Each diode cutin voltage in the circuit in Figure...Ch. 2 - Let V=0.7V for each diode in the circuit shown in...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure P2.61. The output...Ch. 2 - Consider the circuit in Figure P2.62. The output...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.63PCh. 2 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P2.64. The...Ch. 2 - The lightemitting diode in the circuit shown in...Ch. 2 - The parameters of D1 and D2 in the circuit shown...Ch. 2 - If the resistor in Example 2.12 is R=2 and the...Ch. 2 - Consider the photodiode circuit shown in Figure...Ch. 2 - Consider the fullwave bridge rectifier circuit....Ch. 2 - Design a simple dc voltage source using a...Ch. 2 - A clipper is to be designed such that O=2.5V for...Ch. 2 - Design a circuit to provide the voltage transfer...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 49. For the circuit below, what is the best connection of the capacitor to filte voltage? ბი DO A O BO wwwww wwwww M m H E LOADarrow_forward5.25. Determine the corner frequency resulting from Cin in Fig. 5.47(d). For simplicity, assume C₁ is a short circuit. TVDD C₁ M2 RF Vin H w - Vout Cin M₁arrow_forwardIn the below circuit, find out the value of equivalent Thevenin's voltage and Thevenin's resistance at the terminal. 2000 0.25 A 400 2 800 2 0.1 Aarrow_forward
- Q1: For the circuit shown in Figure-1, (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit, RAB at the terminals A and B. [10] (b) When 50V dc source is switched at terminals A-B, solve for the voltage V₁ at the location shown. [10] 50V www 12Ω 10Ω 5Ω www www A + B 200 Figure-1 www 10Ω ww 25Ω 100arrow_forwarda. Write a PLC ladder diagram that allows the teacher to teach AND, OR, and XOR logic gates through using three PLC's digital input points and only one digital output point.arrow_forwardrately by PRACTICE 4.2 For the circuit of Fig. 4.5, compute the voltage across each curren source. 202 ww 3A 30 ww 4Ω S 50 www Reference node FIGURE 4.5 Ans: V3A =5.235 V; 7A = 11.47 V. 7 Aarrow_forward
- Q2) a) design and show me your steps to convert the following signal from continuous form to digital form: s(t)=3sin(3πt) -1 373 Colesarrow_forwardA sequence is defined by the relationship r[n] = [h[m]h[n+m]=hn*h-n where h[n] is a minimum-phase sequence and r[n]= 4 4 (u[n]+ 12" [n-1] 3 (a) Find R(z) and sketch the pole-zero diagram. (b) Determine the minimum-phase sequence h[n] to within a scale factor of ±1. Also, determine the z-transform H(z) of h[n].arrow_forwardusıng j-k and D flipflop design a counter that counts 0,2,1 again as shown below ın the tablearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Three-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier Operation; Author: katkimshow;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uhbr6tbMB9A;License: Standard Youtube License