
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780134641621
Author: Dean R. Appling, Spencer J. Anthony-Cahill, Christopher K. Mathews
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 20P
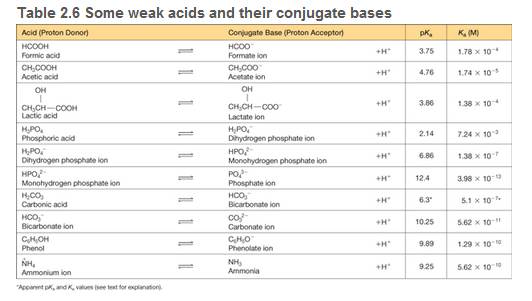
A biochemical reaction takes place in a 1.00 ml solution of 0.0250 M phosphate buffer initially at pH = 7.20 (see Table 2.6 for pkas of phosphate species).
a. Are the concentrations of any of the four possible phosphate species negligible? If so, identify them and explain your answer.
b. During the reaction, 3.80 µmol of HCI are produced. Calculate the final pH of the reaction solution. Assume that the HCI is completely neutralized by the buffer.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
What are some topics of interest that neurotoxicologists study? For example, toxin-induced seizures, brain death, and such along those lines?
Could you help me with the explanation of the answer to exercise 15, chapter 1 of Lehinger
Question
Nombramiento de estereoisómeros con dos carbonos quirales utilizando el sistema RS(R,R)El isómero del metilfenidato (Ritalin) se utiliza para tratar el trastorno por déficit de atención con hiperactividad (TDAH).(S,S)El isómero es un antidepresivo. Identifique los dos carbonos quirales en la siguiente estructura. ¿Es este el(R,R)o el(S,S)¿isómero? Dibuja el otro isómero.
Nombramiento de estereoisómeros con dos carbonos quirales utilizando el sistema RS(R,R)El isómero del metilfenidato (Ritalin) se utiliza para tratar el trastorno por déficit de atención con hiperactividad (TDAH).(S,S)El isómero es un antidepresivo.
The reaction A+B → C + D AG°' = -7.3 kcal/mol
can be coupled with which of the following unfavorable reactions to
drive it forward?
A. EFG+HAG° = 5.6 kcal/mol.
B. J+KZ+A AG° = 2.3 kcal/mol.
C. P+RY+DAG° = 8.2 kcal/mol.
D. C + T → V + W AG°' = -5.9 kcal/mol.
E. AN→ Q+KAG°' = 4.3 kcal/mol.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Ch. 2 - Suppose a chloride ion and a sodium ion are...Ch. 2 - Draw two different possible hydrogen-bonding...Ch. 2 - Prob. 3PCh. 2 - 4. What is the pH of each of the following...Ch. 2 - Prob. 5PCh. 2 - The weak acid HA is 2% ionized (dissociated) in a...Ch. 2 - 7. Calculate the pH values and draw the titration...Ch. 2 - What is the pH of the following buffer mixtures?...Ch. 2 - a. Suppose you wanted to make a buffer of exactly...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 2 - You need to make a buffer whose pH is 7.0, and you...Ch. 2 - Describe the preparation of 2.00 L of 100 glycine...Ch. 2 - Carbon dioxide is dissolved in blood (pH 7.4) to...Ch. 2 - What is the molecular basis for the observation...Ch. 2 - The anno acid arginine ionizes according to the...Ch. 2 - It is possible to make a buffer that functions...Ch. 2 - A student is carrying out a biological preparation...Ch. 2 - Histidine is an amino acid with three titratable...Ch. 2 - Prob. 19PCh. 2 - A biochemical reaction takes place in a 1.00 ml...Ch. 2 - Is RNA-binding enzyme RNase A more likely to have...Ch. 2 - Consider a protein in which a negatively charged...Ch. 2 - Prob. 23PCh. 2 - Prob. 24P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What would be the toxicological endpoints for neurotoxicity?arrow_forwardWhat are "endpoints" in toxicology exactly? Please give an intuitive easy explanationarrow_forwardFura-2 Fluorescence (Arbitrary Unit) 4500 4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 [Ca2+]=2970nM, 25°C [Ca2+] 2970nM, 4°C [Ca2+]=0.9nM, 25°C [Ca2+] = 0.9nM, 4°C 0 260 280 300 340 360 380 400 420 440 Wavelength (nm) ← < The figure on the LHS shows the excitation spectra of Fura-2 (Em = 510 nm) in 2 solutions with two different Ca2+ ion concentration as indicated. Except for temperature, the setting for excitation & signal acquisition was identical.< ப a) The unit in Y-axis is arbitrary (unspecified). Why? < < b) Compare & contrast the excitation wavelength of the Isosbestic Point of Fura-2 at 25 °C & 4 °C. Give a possible reason for the discrepancy. < c) The fluorescence intensity at 25 °C & 4 °C are different. Explain why with the concept of electronic configuration. <arrow_forward
- draw in the structure of each amino acid (as L-amino acids) using the Fischer projection style. an example has been included. Draw the structure for glycine, alanine, valine, isoleucine, methionine, proline, phenylalanine, tryptophan, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, lysine, arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, histidine, tyrosine, cysteinearrow_forwarddraw in the structure of each amino acid (as L-amino acids) using the Fischer projection style. an example has been includedarrow_forwarddraw in the structure of each amino acid (as L-amino acids) using the Fischer projection style. an example has been includedarrow_forward
- Draw out the following peptide H-R-K-E-D at physiological pH (~7.4). Make sure toreference table 3.1 for pKa values.arrow_forwardThe table provides the standard reduction potential, E', for relevant half-cell reactions. Half-reaction E'° (V) Oxaloacetate² + 2H+ + 2e malate²- -0.166 Pyruvate + 2H+ + 2e → lactate -0.185 Acetaldehyde + 2H+ + 2e¯ →→→ ethanol -0.197 NAD+ + H+ + 2e--> NADH -0.320 NADP+ + H+ + 2e →→ NADPH Acetoacetate + 2H+ + 2e¯ - -0.324 B-hydroxybutyrate -0.346 Which of the reactions listed would proceed in the direction shown, under standard conditions, in the presence of the appropriate enzymes? Malate + NAD+ oxaloacetate + NADH + H+ Malate + pyruvate oxaloacetate + lactate Pyruvate + NADH + H+ lactate + NAD+ Pyruvate + p-hydroxybutyrate lactate + acetoacetate Acetaldehyde + succinate ethanol + fumerate Acetoacetate + NADH + H+ → B-hydroxybutyrate + NAD+arrow_forwardArrange the four structures in order from most reduced to most oxidized. Most reduced R-CH2-CH3 R-CH2-CH₂-OH R-CH,-CHO R-CH₂-COO Most oxidizedarrow_forward
- for each pair of biomolecules, identify the type of reaction (oxidation-reduction, hydrolysis, isomerization, group transfer, or nternal rearrangement) required to convert the first molecule to the second. In each case, indicate the general type of enzyme and cofactor(s) c reactants required, and any other products that would result. R-CH-CH-CH-C-S-COA A(n) A(n) A(n) A(n) Palmitoyl-CoA R-CH-CH=CH-C-S-CoA ° trans-A-Enoyl-CoA reaction converts palmitoyl-CoA to trans-A2-enoyl-CoA. This reaction requires and also produces Coo HN-C-H CH₂ CH₂ CH CH CH, CH, L-Leucine CH, CH, D-Leucine 8/6881 COO HÌNH: reaction converts L-leucine to D-leucine. This reaction is catalyzed by a(n) H-C-OH H-C-OH C=0 HO-C-H HO-C-H H-C-OH H-C-OH H-C-OH CH,OH Glucose H-C-OH CH,OH Fructose OH OH OH CH-C-CH₂ reaction converts glucose to fructose. This reaction is catalyzed by a(n) OH OH OPO I CH-C-CH H Glycerol Glycerol 3-phosphate H reaction converts glycerol to glycerol 3-phosphate. This reaction requires H,N- H,N H…arrow_forwardAfter adding a small amount of ATP labeled with radioactive phosphorus in the terminal position, [7-32P]ATP, to a yeast extract, a researcher finds about half of the 32P activity in P; within a few minutes, but the concentration of ATP remains unchanged. She then carries out the same experiment using ATP labeled with 32P in the central position, [ẞ-³2P]ATP, but the 32P does not appear in P; within such a short time. Which statements explain these results? Yeast cells reincorporate P; released from [ß-³2P]ATP into ATP more quickly than P¡ released from [y-³2P]ATP. Only the terminal (y) phosphorous atom acts as an electrophilic target for nucleophilic attack. The terminal (y) phosphoryl group undergoes a more rapid turnover than the central (B) phosphate group. Yeast cells maintain ATP levels by regulating the synthesis and breakdown of ATP. Correct Answerarrow_forwardCompare the structure of the nucleoside triphosphate CTP with the structure of ATP. NH₂ 0- 0- 0- ·P—O—P—O—P—O—CH₂ H H H H OH OH Cytidine triphosphate (CTP) Consider the reaction: ATP + CDP ADP + CTP NH 0- 0- 0- ¯0— P—O— P—O—P-O-CH₂ H Η о H H OH OH Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) NH₂ Now predict the approximate K'eq for this reaction. Now predict the approximate AG for this reaction. Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Essentials of Pharmacology for Health Professions
Nursing
ISBN:9781305441620
Author:WOODROW
Publisher:Cengage
Enzyme Kinetics; Author: MIT OpenCourseWare;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FXWZr3mscUo;License: Standard Youtube License