
Concept explainers
Suppose a chloride ion and a sodium ion are separated by a center—center distance of 5 Å. Is
the interaction energy (the energy required to pull them infinitely far apart) predicted to be larger if the medium between them is water, or if it is n-pentane? (See Table 2.5)
If Ca2+, Na+ and F¯ each have ionic radii ~1.16. Which ionic bond is stronger: Ca-F or Na-F? If Ca2+ is often bound on the surface of a protein by
Table 2.5 Important properties of liquid water compared with those of n-pentane, a nonpolar,
Nonhydrogen-bonding liquida
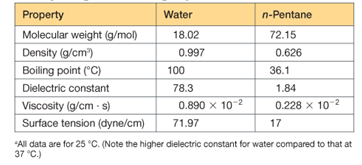
Interpretation:
Interaction energy will be more in which of the given ion pairs must be predicted. The stronger ionic bond must be predicted among the given ionic compounds. In which of the given pH the interaction between
Concept introduction:
Ionic interaction depends on Columbic interaction which depends on the charge of ions and distance by which those ions are separated. It aslo depends on the dielectric constant of the medium and the viscosity of the medium. The ionic bond is stronger when the size of the ions is small, charge in ions is high. Lattice energy depends on Columbic interaction. The bond between
Answer to Problem 1P
The interaction energy between sodium ion and chlorine ion will be larger in case of n-pentane.
Explanation of Solution
The interaction of ion pair will be more in case of n-pentane.
This is because the dielectric constant of n-pentane is
Now,
This is because of Columbic interaction
where
As calcium ion has the double charge of sodium ion so
The
This is because at pH greater than
So, the best pH is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy & Physiology) Standalone Book
- Assume that an enzyme-catalyzed reaction follows the scheme shown: E+S SES →E + P k₁ = 1 x 109/M-s k-1=2.5 x 10%/s k₂ = 3.4 x 107/s What is the dissociation constant for the enzyme-substrate, K,? What is the Michaelis constant, Km, for this enzyme? What is the turnover number, Keat, for this enzyme? What is the catalytic efficiency for the enzyme? If the initial Et concentration is 0.25mM, what is Vmax?arrow_forwardAn enzyme lowers the activation energy, (AG) of a reaction from 50.0 kcal/mol to 40.0 kcal/mol. Calulate the catalytic power at 310K. (R-1.987x10 kcal/mol)arrow_forwardDraw a typical axodendritic synapse, including a specific neurotransmitter of your choice, its associated postsynaptic receptors (indicating whether they are ionotropic or metabotropic), and any associated reuptake transporters or degradation enzymes. Please include a description of what specific steps would occur as an action potential reaches the axonal terminal.arrow_forward
- Give a full arrow pushing mechanism of the spontaneous redox reaction between NAD+/NADH and oxaloacetate/malate. Please include diagram drawing of the mechanism! (Thank You!)arrow_forward18. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following series of reactions? 1. BH3 2. H2O2, NaOH H₂CrO4 CH2N2 oro ororos A B C D Earrow_forward17. Which one of the compounds below is the major organic product obtained from the following series of reactions? CI benzyl alcohol OH PBr3 Mg 1. CO2 SOCl2 ? ether 2. H+, H₂O CI Cl HO OH CI Cl A B C D Earrow_forward
- 14. What is the IUPAC name of this compound? A) 6-hydroxy-4-oxohexanenitrile B) 5-cyano-3-oxo-1-pentanol C) 5-cyano-1-hydroxy-3-pentanone D) 1-cyano-5-hydroxy-3-pentanone E) 5-hydroxy-3-oxopentanenitrile HO. CNarrow_forward13. What is the IUPAC name of this compound? A) 5-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylpentanoic acid B) 3,3-dimethylpentanoic acid C) 3,3-dimethyl-1-oxo-1,5-pentanediol D) 1,5-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylpentanal E) 4-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylbutanoic acid HO OHarrow_forwardHelp me understand how carbon disulfide leads to toxicity in the brain, using terms like distal axonopathy, neurofilaments, covalent cross-linking, adducts, etc.,...please intuitively explain what is happening and where and the effects of it. For example, I know that CS2 reacts with amide and sulfhydryl groups on proteins, but what proteins exactly and where are they located?arrow_forward
- What is the standard free energy change (in kJ/mole) of the spontaneous reaction between Oxygen and NADH to form H2O2 and NAD+?arrow_forwardRedox Chemistry: Give standard free energy changes expected for the following reactions:-Succinate -> fumarate (using FAD/FADH2)-Oxaloacetate -> Malate (using NAD/NADH)-NADH --> NAD+ (using FMN/FMNH2)-CoQ --> CoQH2 (using Cytochrome C)arrow_forwardGive examples of balanced redox reactions that match the following:-Catabolic-Anabolic-Oxidative-Reductivearrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





