
(a)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is chiral is to be stated. If aspartame is chiral, then the possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
A compound that contains a chiral carbon is known as chiral compound. Carbon atom that contains all the four different atoms or group of atoms attached to it is referred as the chiral atom. This carbon is also known as stereocenter.
The possible number of stereoisomers is calculated by the expression
Answer to Problem 19.13P
Aspartame is a chiral compound. The possible number of stereoisomers for aspartame is
Explanation of Solution
The aspartame is a chiral compound. The structure of aspartame which contains chiral carbon atoms is shown as,
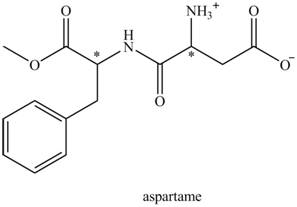
There are two chiral carbon atoms present in aspartame which are marked with asterisk sign. In the structure of aspartame, one carbon atom is directly bonded to
Thus, the possible number of stereoisomers in aspartame is,
Where,
- is the number of stereocenter.
Thus, the possible stereoisomers of aspartame is
(b)
Interpretation:
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The name of each functional group present in aspartame is ester group
Explanation of Solution
According to the structure of aspartame shown in Figure 1, there are four functional groups present in the structure of aspartame.
The name of all the functional group of aspartame is ester group
(c)
Interpretation:
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Concept Introduction:
The negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration of the solution is known as
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The net charge on aspartame molecule in an aqueous solution at
Explanation of Solution
In an aqueous solution of
Hence, there is no change of charge takes place in aspartame and it possesses zero net charge.
(d)
Interpretation:
The validation corresponding to the fact that aspartame is whether soluble in water or not is to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
According to the concept of solubility, it is mentioned that like dissolves like. Generally, polar compound can only be dissolved in polar solvents and non-polar or weakly polar compounds can only be dissolved in non-polar solvents or weakly polar solvents.
Answer to Problem 19.13P
Aspartame is soluble in water.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure of asparatame is present in zwitterion form which suggests that it is a polar molecule. According to the concept of like dissolves like, aspartame is soluble in water because water is also a polar molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
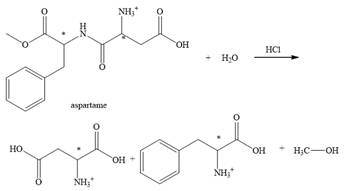
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
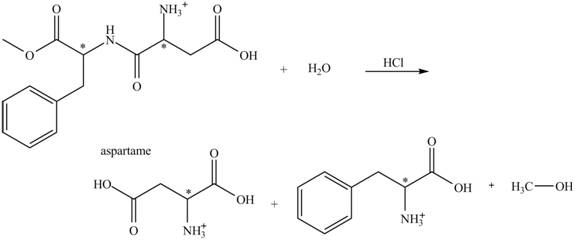
Figure 2.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
(f)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
Concept Introduction:
An atom or a group of atoms that shows characteristic physical and chemical properties are collectively known as functional groups. The functional group is the most reactive part present in the molecule. The main functional groups are
The addition of water molecule to the compound is known as hydrolysis that compound.
Answer to Problem 19.13P
The structural formulas for the products that are obtained by the complete hydrolysis of aspartame in aqueous
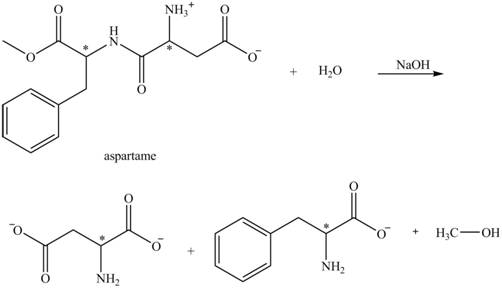
Explanation of Solution
The hydrolysis of aspartame in the presence of aqueous
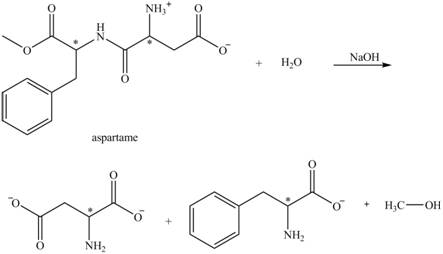
Figure 3.
The reaction of aspartame with aqueous
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Draw the complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of this alkene. esc 田 Explanation Check 1 888 Q A slock Add/Remove step Q F4 F5 F6 A བྲA F7 $ % 5 @ 4 2 3 & 6 87 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce W E R T Y U S D LL G H IK DD 요 F8 F9 F10 F1 * ( 8 9 0 O P J K L Z X C V B N M H He commandarrow_forwardExplanation Check F1 H₂O H₂ Pd 1) MCPBA 2) H3O+ 1) Hg(OAc)2, H₂O 2) NaBH4 OH CI OH OH OH hydration halohydrin formation addition halogenation hydrogenation inhalation hydrogenation hydration ☐ halohydrin formation addition halogenation formation chelation hydrogenation halohydrin formation substitution hydration halogenation addition Ohalohydrin formation subtraction halogenation addition hydrogenation hydration F2 80 F3 σ F4 F5 F6 1 ! 2 # 3 $ 4 % 05 Q W & Å © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. F7 F8 ( 6 7 8 9 LU E R T Y U A F9arrow_forwardShow the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forward
- Soap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the mechanism for this transformation: *see imagearrow_forwardAssign all the signals individually (please assign the red, green and blue)arrow_forwardThe two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


