
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134015187
Author: John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17.1, Problem 17.1P
Identify the following molecules as a
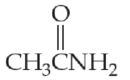
- (a) CH3OCH3
- (b) CH3COOH
- (c) CH3COOCH2CH3
- (d) CH3COCH3
- (e) CH3CH2CONHCH3
- (f) CH3CH2NH2
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Acetone, CH3–(C=0) –CH3, and urea, NH2–(C=0)–NH2, have similar chemical structures.
(a) Compare the possible intermolecular forces for acetone with those for urea.
(b) Compare the intermolecular forces between phycocyanin and acetone with those between phycocyanin and water. Briefly explain how acetone disrupts the folding in phycocyanin.
(c) Compare the intermolecular forces between phycocyanin and urea with those between phycocyanin and water. Briefly explain how urea disrupts the folding in phycocyanin.
(d) Compare your experimental observation on the disruption of phycocyanin folding in the presence of acetone with that in the presence of urea. Briefly explain whether your comparison is consistent with the properties of acetone and urea.
Name and draw the structures of the amino acids that fit the following descriptions:(a) Contains an isopropyl group(b) Contains a secondary alcohol group
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(8)
(9)
(10)
E
Which of the following residues would be most likely to make contact with the aqueous medium?
(A) Lysine
(B)
Glycine
(12)
The native state of a protein is the conformation that is the
(A)
(8)
The
(A)
(B)
(B)
When an atom or ion is reduced, its oxidation number
(A)
Decreases
(8)
Increases
Ribose is an example of a
(A)
Pentose
Hexose
(A)
(8)
Palmitate (16:0) is a/an
Saturated
Unsaturated
(7)
A certain unfavorable process has an associated standard free energy (AG) of 38 kJ/mol. To which reaction
could it be coupled to make it favorable?
ATP+H₂O → ADP + P
ATP + H₂O → AMP + PP,
Neither one
(A)
(B)
(C)
Least
Most
Lesser
Greater
(A)
(8)
(A)
the value of ko, the more efficient the enzyme will be.
(8)
Generally, if the concentration of ATP is low, then
Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis
(A)
(8)
sugar.
In the first step of the citric acid cycle,
Acetyl CoA
Pyruvate
fatty acid.
(AG"=-32 kl/mol)
(AG"=-45kl/mol)
Under conditions when glycogen synthesis is favored,…
Chapter 17 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 17.1 - Identify the following molecules as a carboxylic...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.2PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.3PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.4PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.5PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.6PCh. 17.1 - In the following pairs of compounds, which would...Ch. 17.1 - Write both condensed and line structures for (a)...Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.9PCh. 17.1 - Draw structures corresponding to these names: (a)...
Ch. 17.1 - Prob. 17.11PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.12PCh. 17.1 - Prob. 17.13KCPCh. 17.2 - Salsalate, which is an ester formed by the...Ch. 17.2 - Prob. 17.2CIAPCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.3CIAPCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.14PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.15PCh. 17.2 - Prob. 17.16PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.17PCh. 17.3 - Raspberry oil contains an ester that is made by...Ch. 17.3 - Prob. 17.19PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.20PCh. 17.3 - Prob. 17.21PCh. 17.4 - If a bottle of aspirin tablets has the aroma of...Ch. 17.4 - Prob. 17.23PCh. 17.4 - What carboxylic acids and amines result from...Ch. 17.5 - Prob. 17.25PCh. 17.5 - Prob. 17.26KCPCh. 17.6 - Prob. 17.27PCh. 17.6 - Prob. 17.28PCh. 17.6 - Prob. 17.4CIAPCh. 17.6 - Prob. 17.5CIAPCh. 17.6 - Prob. 17.29PCh. 17 - Prob. 17.30UKCCh. 17 - Prob. 17.31UKCCh. 17 - One phosphorylated form of glycerate is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.33UKCCh. 17 - Prob. 17.34UKCCh. 17 - Prob. 17.35UKCCh. 17 - Prob. 17.36UKCCh. 17 - For the following compounds, give the systematic...Ch. 17 - Write the equation for the ionization of hexanoic...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.39APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.40APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.41APCh. 17 - Give systematic names for the following carboxylic...Ch. 17 - Give systematic names for the following carboxylic...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.44APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.45APCh. 17 - Draw structures corresponding to the following...Ch. 17 - Draw structures corresponding to the following...Ch. 17 - Malic acid, a dicarboxylic acid found in apples,...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.49APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.50APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.51APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.52APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.53APCh. 17 - Give systematic names for the following structures...Ch. 17 - Give systematic names for the following structures...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.56APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.57APCh. 17 - Give systematic names for the following structures...Ch. 17 - Give systematic names for the following structures...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.60APCh. 17 - What compounds are produced from hydrolysis of...Ch. 17 - Procaine, a local anesthetic whose hydrochloride...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.63APCh. 17 - Lactones are cyclic esters in which the carboxylic...Ch. 17 - When both the carboxylic acid and the amine are in...Ch. 17 - LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), a semisynthetic...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.67APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.68APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.69APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.70APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.71APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.72APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.73APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.74APCh. 17 - Prob. 17.75APCh. 17 - Three amide isomers, N,N-dimethylformamide,...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.77CPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.78CPCh. 17 - Mention at least two simple chemical tests by...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.80CPCh. 17 - Name the following compounds.Ch. 17 - Each of the following materials has an ester that...Ch. 17 - Prob. 17.83GPCh. 17 - Prob. 17.84GP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. (a) Draw a three-dimensional line structure of (4S,5Z)-4-amino-5,6-difluorohept-5-enal. Place the aldehyde group on the right-hand side of your drawing. (b) Give the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority order of the four groups (-C3H3F2. -NH2, -H, -C3H50) at the C4 stereocentre (Highest 1> 2> 3>4 Lowest). 2. Study the curved arrows in the reactions below and provide structures of all the products that form for the given mechanistic step in the following reactions. (a) +0-H (b) H.arrow_forwardOne or more of the compounds shown below will satisfy each of the following statements. Not all compounds may be used; some may be used twice. Put the number(s) in the blank. (1) Found in chitin. (2) An L-saccharide. (3) The first residue attached to asparagine in N-linked glycans. (4) A uronic acid. (5) A ketose. CH,OH CoO COO OH H H H H ОН Н но OH OH H OH H HO OH H NHC- CH, Oso, OH (a) (b) (c) CH,OH CH,OH CH,OH C=0 CHOH C=0 H-C- OH CH,OH но -с-н ČH,OH CH,OH (d) (e)arrow_forwarddraw all the structures of the tribasic amino acid lysine involved in the equilibrium reactions that would take place during titration against NaOH, starting with the fully protonated form below (draw the R-group in full). H;N+- CH - COOH (CH2)4 NH3+arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements about aromatic amino acids is correct? (a) All are strongly hydrophilic. (b) Histidine's ring structure results in its being categorized as aromatic or basic, depending on pH. (c) On a molar basis, tryptophan absorbs more ultraviolet light than tyrosine. (d) The major contribution to the characteristic absorption of light at 280 nm by proteins is the phenylalanine R group. (e) The presence of a ring structure in its R group determines whether or not an amino acid is aromatic.arrow_forwardWrite chemical names for the following compounds: (a) Thymidine (b) Cytosine (c) Uracil (d) Xanthine (e) Guanine () 2,4-dioxy-6-carboxy pyrimidine (g) CAMP (h) dTTParrow_forwardFor the tripeptide: methionylisoleucylcysteine (i) draw the structure of each tripeptide (ii) label the amide bonds in your structures (iii) identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acidsarrow_forward
- DHA is a fatty acid derived from fish oil and an abundant fatty acid invertebrate brains. Hydrogenation of DHA forms docosanoic acid[CH3(CH2)20CO2H], and ozonolysis forms CH3CH2CHO, CH2(CHO)2 (fiveequivalents), and HCOCH2CH2CO2H. What is the structure of DHA if all double bonds have the Z configuration?arrow_forwardThe skeletal structures of the two amino acids, glycine and lysine, are given below along with the values of the relevant acid dissociation constants (pKa). NH,* PK, - 10.79 - HạN*CH2CO,¯ S pK¸=2.35 (CH2)4 - H3N*CHCO,- pK,=9,78 lysine (Lys) glycine (Gly) pK, = 9.18 pK, - 2.16 For an aqueous solution of glycine alone, calculate the value of pH at which the ratio of the concentration of neutral glycine zwitterions to the concentration of protonated cation is 102. On your under each of the following conditions. In the blank, provide the total charge of the dipeptide. (Example: If the charge is two plus write the answer simply as 2, if the charge is negative two write the answer as -2). draw the skeletal structure of the dipeptide, Lys-Gly, when it is solvated in an aque us solution i. pH= 1 ii. pH= 12arrow_forwardThe structure of the amino acid isoleucine is(a) How many chiral centers does it have?(b) How many optical isomers?(c) Draw perspective formulas for all the optical isomers of isoleucine.arrow_forward
- The amino acid arginine ionizes according to the following scheme: NH, NH2 NH2 H NH, C=N C=N C=N C=N-H pk = 2.17 -H pK. = 8.99 -H pK = 125 -H* H. NH NH NH NH H (CH,)a H (CH), +H* (CH)a (CH,)a H,N-C-coo- +H* +H* H-N*-C-COOH H-N-C-Co- H,N-C-co- H. нн H. H II II IV (a) Calculate the isoelectric point of arginine. You can neglect contributions from form I. Why? (b) Calculate the average charge on arginine when pH = 9.20. (Hìnt: Find the average charge for each ionizable group and sum these together.) (c) Is the value of average charge you calculated in part b reasonable, given the pl you calculated in part a? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardA) Describe the glycosidic bond (using standard convention) indicated by “Arrow a.” B) Draw the open chain Fischer projection formula of the monosaccharide labeled “B” C) Describe the glycosidic bond (as in question A) indicated by “Arrow b.”arrow_forwardThe structures of three amino acids are given as below. Glycine -H Cysteine - CH2 - SH Glutamate - CH2 CH2 (i) Describe the properties of each of these amino acids. (ii) Draw the tripeptide Glu-Cys-Gly.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON
Macromolecules | Classes and Functions; Author: 2 Minute Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5hhrDFo8Vk;License: Standard youtube license