
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 96P
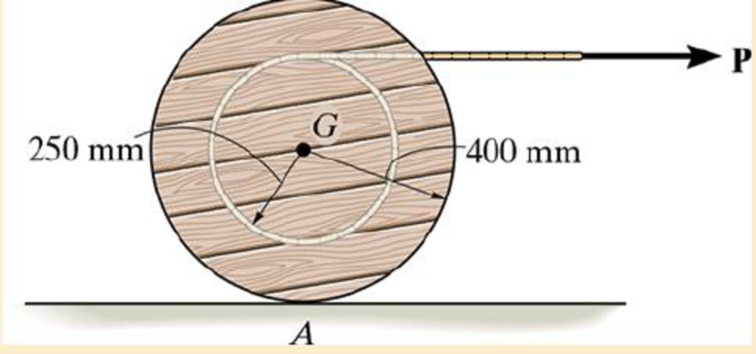
The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of gyration of kG = 0.3 m. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction at A are μs = 0.2 and μk = 0.15, respectively, determine the angular acceleration of the spool if P = 50 N.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Figure: 06_P041
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall
2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N
forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also
a pin at F.
400 mm
15°
20 mm
A
15°
15
D
B
30 mm² 80 mm
20 mm
400 mm
Figure: 06_P090
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall
15°
100 N
100 N
15°
A telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump.
The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant.
At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.
For Problems 18-22 (Table 7-27), design a V-belt drive.
Specify the belt size, the sheave sizes, the number of belts, the
actual output speed, and the center distance.
Chapter 17 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia Iy for the slender...Ch. 17 - The solid cylinder has an outer radius R1 height...Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the thin ring...Ch. 17 - Prob. 9PCh. 17 - The pendulum consists of a 4-kg circular plate and...Ch. 17 - Prob. 12PCh. 17 - The wheel consists of a thin ring having a mass of...Ch. 17 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia about an axis...Ch. 17 - Prob. 16P
Ch. 17 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17 - Prob. 18PCh. 17 - Prob. 19PCh. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel about...Ch. 17 - The pendulum consists of the 3-kg slender rod and...Ch. 17 - Prob. 22PCh. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the overhung...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1FPCh. 17 - Prob. 2FPCh. 17 - Prob. 3FPCh. 17 - Prob. 4FPCh. 17 - At the instant shown both rods of negligible mass...Ch. 17 - Prob. 6FPCh. 17 - The door has a weight of 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17 - The door has a weight or 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17 - The jet aircraft has a total mass of 22 Mg and a...Ch. 17 - The sports car has a weight of 4500 lb and center...Ch. 17 - The bar has a weight per length w and is supported...Ch. 17 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 44PCh. 17 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 50PCh. 17 - Prob. 53PCh. 17 - Prob. 54PCh. 17 - The 100-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17 - Prob. 8FPCh. 17 - Prob. 9FPCh. 17 - Prob. 10FPCh. 17 - Prob. 11FPCh. 17 - Prob. 12FPCh. 17 - The 10-kg wheel has a radius of gyration kA = 200...Ch. 17 - The uniform 24-kg plate is released from rest at...Ch. 17 - The uniform slender rod has a mass m. If it is...Ch. 17 - The tent rod has a mass of 2 kg/m. If it is...Ch. 17 - Disk A has a weight of 5 lb and disk B has a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 66PCh. 17 - The reel of cable has a mass of 400 kg and a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 72PCh. 17 - Cable is unwound from a spool supported on small...Ch. 17 - The 5-kg cylinder is initially at rest when it is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 76PCh. 17 - Disk D turns with a constant clockwise angular...Ch. 17 - Prob. 78PCh. 17 - Prob. 81PCh. 17 - Prob. 85PCh. 17 - The Catherine wheel is a firework that consists of...Ch. 17 - The uniform 60-kg slender bar is initially at rest...Ch. 17 - Prob. 14FPCh. 17 - Prob. 15FPCh. 17 - The 20- kg sphere rolls down the inclined plane...Ch. 17 - The 200-kg spool has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17 - The 12-kg slender rod is pinned to a small roller...Ch. 17 - If the disk in Fig. 17-19 rolls without slipping,...Ch. 17 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17 - A force of F= 10 N is applied to the 10-kg ring as...Ch. 17 - If the coefficient of static friction at C is s =...Ch. 17 - If P = 30 lb, determine the angular acceleration...Ch. 17 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 17 - The semicircular disk having a mass of 10 leg is...Ch. 17 - The circular concrete culvert rols with an angular...Ch. 17 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17 - The uniform beam has a weight W. If it is...Ch. 17 - The 500-lb beam is supported at A and B when it is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1RPCh. 17 - Prob. 2RPCh. 17 - Prob. 3RPCh. 17 - Prob. 4RPCh. 17 - Prob. 5RPCh. 17 - Prob. 6RPCh. 17 - Prob. 7RPCh. 17 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- only 21arrow_forwardonly 41arrow_forwardNormal and tangential components-relate to x-y coordinates A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I need help with finding the y component of the total acceleration. I had put -32 but its incorrect. but i keep getting figures around that numberarrow_forward
- The bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a control cable at B. Let F₁ = 275 N and F2 = 275 N. F1 B a=0.18 m C A 0.4 m -0.4 m- 0.24 m Determine the reaction at C. The reaction at C N Z F2 Darrow_forwardConsider the angle bar shown in the given figure A W 240 mm B 80 mm Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the reactions at A and B when a = 150 mm. This problem could also be approached as a 3-force body using method of Section 4.2B.arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forward
- For the stop bracket shown, locate the x coordinate of the center of gravity. Consider a = = 16.50 mm. 34 mm 62 mm 51 mm 10 mm 100 mm 88 mm 55 mm 45 mm The x coordinate of the center of gravity is mm.arrow_forwardIn the given figure, the bent rod ABEF is supported by bearings at C and D and by wire AH. The portion AB of the rod is 250 mm long, and the load W is 580 N. Assume that the bearing at D does not exert any axial thrust. H B A с 30° 250 mm D Z 50 mm 300 mm F 250 mm 50 mm W Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the tension in wire AH and the reactions at C and D.arrow_forwardA 10-ft boom is acted upon by the 810-lb force as shown in the figure. D 6 ft 6 ft E B 7 ft C 6 ft x 4 ft W Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the ball-and-socket joint at A.arrow_forward
- Locate the center of gravity of the sheet-metal form shown. Given: r = 26.40 mm . 50 mm 40 mm X 150 mm The center of gravity (✗) of the sheet-metal form is The center of gravity (Y) of the sheet-metal form is The center of gravity ( Z ) of the sheet-metal form is mm. mm. (Round the final answer to three decimal places.) mm.arrow_forwardDetermine the reactions at the beam supports for the given loading if W = 300 lb/ft . W 6 ft A 9 ft. 6 ft- The reaction at Bis lb. The reaction at A is lb. Barrow_forwardIn the given figure, the bent rod ABEF is supported by bearings at C and D and by wire AH. The portion AB of the rod is 250 mm long, and the load W is 580 N. Assume that the bearing at D does not exert any axial thrust. 30° 250 mm 300 mm 50 mm H B C D 50 mm W 250 mm Determine the reactions at C and D. (Include a minus sign if necessary.) The reaction at Cis N) j + N)k The reaction at Dis N) j + ( N)karrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY