
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 90P
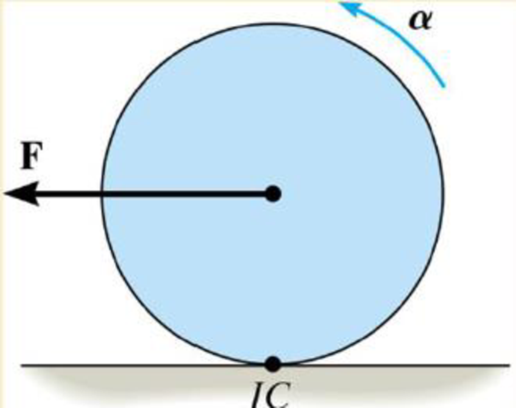
If the disk in Fig. 17-19 rolls without slipping, show that when moments are summed about the instantaneous center or zero velocity, IC, it is possible to use the moment equation ΣMrc = IIC, α, where IIC represent the moment of inertia of the disk calculated about the instantaneous axis of zero velocity.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
| Link BC has a mass mgc = 4 kg, with a moment of inertia about its mass center of:
laac = maclic
Link AB has a mass mAR = 2.4 kg, with a moment of inertia about point A of:
The wheel at point C is of negligible mass. At the moment pictured below, the velocity of point C is 1.5 m/s to
the right. Find the velocity of pin B after link AB has rotated through 90°.
B2
Calculate the center of mass acceleration of the cylinder rolling down the
inclined plane in the below figure for the case of no slipping. Choose an
axis that passes through the point of contact. Will need to determine the
moment of inertia of the cylinder about this point.
FP
FN
Chapter 17 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia Iy for the slender...Ch. 17 - The solid cylinder has an outer radius R1 height...Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the thin ring...Ch. 17 - Prob. 9PCh. 17 - The pendulum consists of a 4-kg circular plate and...Ch. 17 - Prob. 12PCh. 17 - The wheel consists of a thin ring having a mass of...Ch. 17 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia about an axis...Ch. 17 - Prob. 16P
Ch. 17 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17 - Prob. 18PCh. 17 - Prob. 19PCh. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel about...Ch. 17 - The pendulum consists of the 3-kg slender rod and...Ch. 17 - Prob. 22PCh. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the overhung...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1FPCh. 17 - Prob. 2FPCh. 17 - Prob. 3FPCh. 17 - Prob. 4FPCh. 17 - At the instant shown both rods of negligible mass...Ch. 17 - Prob. 6FPCh. 17 - The door has a weight of 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17 - The door has a weight or 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17 - The jet aircraft has a total mass of 22 Mg and a...Ch. 17 - The sports car has a weight of 4500 lb and center...Ch. 17 - The bar has a weight per length w and is supported...Ch. 17 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 44PCh. 17 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 50PCh. 17 - Prob. 53PCh. 17 - Prob. 54PCh. 17 - The 100-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17 - Prob. 8FPCh. 17 - Prob. 9FPCh. 17 - Prob. 10FPCh. 17 - Prob. 11FPCh. 17 - Prob. 12FPCh. 17 - The 10-kg wheel has a radius of gyration kA = 200...Ch. 17 - The uniform 24-kg plate is released from rest at...Ch. 17 - The uniform slender rod has a mass m. If it is...Ch. 17 - The tent rod has a mass of 2 kg/m. If it is...Ch. 17 - Disk A has a weight of 5 lb and disk B has a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 66PCh. 17 - The reel of cable has a mass of 400 kg and a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 72PCh. 17 - Cable is unwound from a spool supported on small...Ch. 17 - The 5-kg cylinder is initially at rest when it is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 76PCh. 17 - Disk D turns with a constant clockwise angular...Ch. 17 - Prob. 78PCh. 17 - Prob. 81PCh. 17 - Prob. 85PCh. 17 - The Catherine wheel is a firework that consists of...Ch. 17 - The uniform 60-kg slender bar is initially at rest...Ch. 17 - Prob. 14FPCh. 17 - Prob. 15FPCh. 17 - The 20- kg sphere rolls down the inclined plane...Ch. 17 - The 200-kg spool has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17 - The 12-kg slender rod is pinned to a small roller...Ch. 17 - If the disk in Fig. 17-19 rolls without slipping,...Ch. 17 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17 - A force of F= 10 N is applied to the 10-kg ring as...Ch. 17 - If the coefficient of static friction at C is s =...Ch. 17 - If P = 30 lb, determine the angular acceleration...Ch. 17 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 17 - The semicircular disk having a mass of 10 leg is...Ch. 17 - The circular concrete culvert rols with an angular...Ch. 17 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17 - The uniform beam has a weight W. If it is...Ch. 17 - The 500-lb beam is supported at A and B when it is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1RPCh. 17 - Prob. 2RPCh. 17 - Prob. 3RPCh. 17 - Prob. 4RPCh. 17 - Prob. 5RPCh. 17 - Prob. 6RPCh. 17 - Prob. 7RPCh. 17 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A dancer is spinning at 72 rpm about an axis through her center with her arms outstretched, as shown in (Figure 1). From biomedical measurements, the typical distribution of mass in a human body is as follows: Part A Head: 7.0% Arms: 13% (for both) Trunk and legs: 80.0% Calculate moment of inertia about the dancer's spin axis. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Suppose the mass of the dancer is 64.5 kg, the diameter of her head is 16 cm, the width of her body is 24 length of her arms is 60 cm. cm, and the HÀ ? I = Value Units Submit Request Answer Figure 1 of 1 > Part B Calculate dancer's rotational kinetic energy. Express your answer with the appropriate units. ? K = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardM M 1.5m m M m = 2kg. M = 3.5kg a) justify whether the moment of inertia about the vertical or horizontal axis have smaller value. Show your calculation. (b) Given angular velocity of 80 rev s¹ in 240 rev. Has a moment of inertia of 1.41x10-3 kg m2. Find: (i) angular acceleration. (ii) net constant torque must apply (c) A space station consists of a giant rotating hollow cylinder of mass 10 kg including people on the station and a radius of 100 m. Given initial angular velocity of 3.3rpm in order to generate artificial gravity. If 100. people, each with an average mass of 65 kg spacewalk to an awaiting spaceship. Find the new angular velocity (in rpm) once all the people are off the station. (d) Suppose a child walks from the outer edge of a rotating merry-go-round to the center. What happend to the angular velocity of the merry-go-round does it increase, decrease, or remain the same? By using the conservation of angular momentum, explain your answer qualitatively.. A large train has…arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- In the mechanism shown below, the wheel is pinned at the center. The radius from O to C is 0.2 m and link CB is 0.55 m long. CB makes an initial angle of 25° with the horizontal as shown. The hydraulic ram at B is moving left at 7 m/s. At the moment shown, what is the angular velocity of link BC and the wheel pivoted at 0? 0000 Ninbet tatis rad/sarrow_forwardThe crankshaft of a vertical sıngle-cylinder engine, stroke 250 mm, rotates at 300 r/min The reciprocating parts ( including part of the connecting rod) have a mass of 100kg The connecting rod has a mass of 120 kg, it is 450 mm long, the centre of mass is 300 mm from the gudgeon pin axıs and the radiųs of gyration about the same axıs is 363 mm When the crank is 30° from the t dc position and moving downwards, determine 31 the side thrust on the cylınder walls due to the inertia of the reciprocatıng parts, and 32 the crankshaft torque on the crankshaft due to inertiaarrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- 3 The object below can rotate in the plane of the page about a fixed axis at A. The object is symmetric about A in the vertical and horizontal directions. A time=0, the object is rotating counterclockwise at 5 rad/s. The material has a uniform area density of 120 kg/m². a. What is the mass moment of inertia of the object about Point A? b. The net moment applied about Point A is shown on the graph. What is the angular velocity, w₁5, of the object at t-15 seconds? MA [Nm] 16 0.15 m 120 kg/m² 0.3 m H wo = 5 rad/s A 0.8 m 0.3 m 0.6 m 0 -8 0.15 m 10 15 time [s]arrow_forwardA wheel is attached by a cable to a block The wheel has a radius of 2ft and weighs 300lbs, the block weights 20lbs. If the radius of gyration about the point of rotation of the disk is 1.5ft, how many revolutions will it take for the wheel to come to a stop assuming it was moving at 10 rad/s CW. Assume the block is on the left side of the wheel and thus causes a CCW moment.arrow_forwardCan I please get a step by step explanation for this question. Thank youarrow_forward
- calculate w4 the angular velocity of the mechanismarrow_forwardit is partially correct A = -.4329 is wrong can you checkarrow_forwardThe mass of flywheel of an engine is 8 tonnes and the radius of gyration is 1.8 metres. It is found from the turning moment diagram that the fluctuation of energy is 100 kN-m. If the mean speed of the engine is 150 r.p.m., find the maximum and minimum speeds.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Thermal Radiation; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FDmYCI_xYlA;License: Standard youtube license