
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137514724
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 17, Problem 92P
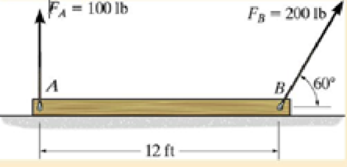
The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when the forces are applied to the cables Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of the mass center and the angular acceleration of the beam at this instant.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(read image)
Qu. 13 What are the indices for the Direction 2 indicated by vector in the following sketch?
Qu. 14 Determine the indices for the direction A and B shown in the following cubic unit cell.
please show all work step by step from material engineering
The thin-walled open cross section shown is transmitting torque 7. The angle of twist ₁ per unit length of each leg can be
determined separately using the equation
01
=
3Ti
GLIC
3
where G is the shear modulus, ₁ is the angle of twist per unit length, T is torque, and L is the length of the median line.
In this case, i = 1, 2, 3, and T; represents the torque in leg i. Assuming that the angle of twist per unit length for each
leg is the same, show that
T= Lic³ and Tmaz = G01 Cmax
Consider a steel section with Tallow = 12.40 kpsi.
C1
2 mm
L1
20 mm
C2
3 mm
L2
30 mm
C3
2 mm
L3
25 mm
Determine the torque transmitted by each leg and the torque transmitted by the entire section.
The torque transmitted by the first leg is |
N-m.
The torque transmitted by the second leg is
N-m.
The torque transmitted by the third leg is
N-m.
The torque transmitted by the entire section is
N-m.
Chapter 17 Solutions
PEARSON ETEXT ENGINEERING MECH & STATS
Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia Iy for the slender...Ch. 17 - The solid cylinder has an outer radius R1 height...Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the thin ring...Ch. 17 - Prob. 9PCh. 17 - The pendulum consists of a 4-kg circular plate and...Ch. 17 - Prob. 12PCh. 17 - The wheel consists of a thin ring having a mass of...Ch. 17 - If the large ring, small ring and each of the...Ch. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia about an axis...Ch. 17 - Prob. 16P
Ch. 17 - Determine the location y of the center of mass G...Ch. 17 - Prob. 18PCh. 17 - Prob. 19PCh. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the wheel about...Ch. 17 - The pendulum consists of the 3-kg slender rod and...Ch. 17 - Prob. 22PCh. 17 - Determine the moment of inertia of the overhung...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1FPCh. 17 - Prob. 2FPCh. 17 - Prob. 3FPCh. 17 - Prob. 4FPCh. 17 - At the instant shown both rods of negligible mass...Ch. 17 - Prob. 6FPCh. 17 - The door has a weight of 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17 - The door has a weight or 200 lb and a center of...Ch. 17 - The jet aircraft has a total mass of 22 Mg and a...Ch. 17 - The sports car has a weight of 4500 lb and center...Ch. 17 - The bar has a weight per length w and is supported...Ch. 17 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17 - The smooth 180-lb pipe has a length of 20 ft and a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 44PCh. 17 - If the carts mass is 30 kg and it is subjected to...Ch. 17 - Prob. 50PCh. 17 - Prob. 53PCh. 17 - Prob. 54PCh. 17 - The 100-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17 - Prob. 8FPCh. 17 - Prob. 9FPCh. 17 - Prob. 10FPCh. 17 - Prob. 11FPCh. 17 - Prob. 12FPCh. 17 - The 10-kg wheel has a radius of gyration kA = 200...Ch. 17 - The uniform 24-kg plate is released from rest at...Ch. 17 - The uniform slender rod has a mass m. If it is...Ch. 17 - The tent rod has a mass of 2 kg/m. If it is...Ch. 17 - Disk A has a weight of 5 lb and disk B has a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 66PCh. 17 - The reel of cable has a mass of 400 kg and a...Ch. 17 - Prob. 72PCh. 17 - Cable is unwound from a spool supported on small...Ch. 17 - The 5-kg cylinder is initially at rest when it is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 76PCh. 17 - Disk D turns with a constant clockwise angular...Ch. 17 - Prob. 78PCh. 17 - Prob. 81PCh. 17 - Prob. 85PCh. 17 - The Catherine wheel is a firework that consists of...Ch. 17 - The uniform 60-kg slender bar is initially at rest...Ch. 17 - Prob. 14FPCh. 17 - Prob. 15FPCh. 17 - The 20- kg sphere rolls down the inclined plane...Ch. 17 - The 200-kg spool has a radius of gyration about...Ch. 17 - The 12-kg slender rod is pinned to a small roller...Ch. 17 - If the disk in Fig. 17-19 rolls without slipping,...Ch. 17 - The uniform 150-lb beam is initially at rest when...Ch. 17 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17 - Solve Prob.17-96 if the cord and force P = 50 N...Ch. 17 - The spool has a mass of 100 kg and a radius of...Ch. 17 - A force of F= 10 N is applied to the 10-kg ring as...Ch. 17 - If the coefficient of static friction at C is s =...Ch. 17 - If P = 30 lb, determine the angular acceleration...Ch. 17 - If the coefficient of static friction between the...Ch. 17 - The semicircular disk having a mass of 10 leg is...Ch. 17 - The circular concrete culvert rols with an angular...Ch. 17 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17 - The uniform disk of mass m is rotating with an...Ch. 17 - The uniform beam has a weight W. If it is...Ch. 17 - The 500-lb beam is supported at A and B when it is...Ch. 17 - Prob. 1RPCh. 17 - Prob. 2RPCh. 17 - Prob. 3RPCh. 17 - Prob. 4RPCh. 17 - Prob. 5RPCh. 17 - Prob. 6RPCh. 17 - Prob. 7RPCh. 17 - Prob. 8RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help, make sure it's to box out and make it clear what answers go where...arrow_forwardThe cylinder floats in the water and oil to the level shown. Determine the weight of the cylinder. (rho)o=910 kg/m^3arrow_forwardPlease help, make sure it's to box out and make it clear what answers go where..arrow_forward
- Please help, make sure it's to box out and make it clear what answers go where...arrow_forwardPlease help, make sure it's to box out and make it clear what answers go where...arrow_forwardA triangular distributed load of max intensity w acts on beam AB. The beam is supported by a pin at A and member CD, which is connected by pins at C and D respectively. Determine the largest load intensity, Wmax, that can be applied if the pin at D can support a maximum force of 18000 N. Also determine the reactions at A and C and express each answer in Cartesian components. Assume the masses of both beam and member ✓ are negligible. Dwas шал = A BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl C D -a- Ур -b- X B W Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 6.6 m b 11.88 m C 4.29 m The maximum load intensity is = wmax N/m. The reaction at A is A = The reaction at C is = i+ Ĵ N. ĴN. 12 i+arrow_forward
- The beam is supported by a pin at B and a roller at C and is subjected to the loading shown with w =110 lb/ft, and F 205 lb. a.) If M = 2,590 ft-lb, determine the support reactions at B and C. Report your answers in both Cartesian components. b.) Determine the largest magnitude of the applied couple M for which the beam is still properly supported in equilibrium with the pin and roller as shown. 2013 Michael Swanbom CC BY NC SA M ру W B⚫ C F ka b Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 3.2 ft b 6.4 ft C 3 ft a.) The reaction at B is B = The reaction at C is C = ĵ lb. i+ Ĵ lb. b.) The largest couple that can be applied is M ft-lb. == i+arrow_forwardThe beam ABC has a mass of 79.0 kg and is supported by the rope BDC that runs through the frictionless pulley at D . The winch at C has a mass of 36.5 kg. The tension in the rope acts on the beam at points B and C and counteracts the moments due to the beam's weight (acting vertically at the midpoint of its length) and the weight of the winch (acting vertically at point C) such that the resultant moment about point A is equal to zero. Assume that rope segment CD is vertical and note that rope segment BD is NOT necessarily perpendicular to the beam. a.) Compute the tension in the rope. b.) Model the two forces the rope exerts on the beam as a single equivalent force and couple moment acting at point B. Enter your answer in Cartesian components. c.) Model the two forces the rope exerts on the beam as a single equivalent force (no couple) and determine the distance from A to the point along the beam where the equivalent force acts (measured parallel to the beam from A ). Enter your answer…arrow_forwardw1 Three distributed loads act on a beam as shown. The load between A and B increases linearly from 0 to a maximum intensity of w₁ = 12.8 lb/ft at point B. The load then varies linearly with a different slope to an intensity of w₂ = 17.1 lb/ft at C. The load intensity in section CD of the beam is constant at w3 10.2 lb/ft. For each load region, determine the resultant force and the location of its line of action (distance to the right of A for all cases). cc 10 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl = WI W2 W3 -b- C Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 4.50 ft b 5.85 ft с 4.28 ft The resultant load in region AB is FR₁ = lb and acts ft to the right of A. The resultant load in region BC is FR2 lb and acts = ft to the right of A. The resultant load in region CD is FR3 = lb and acts ft to the right of A.arrow_forward
- The T-shaped structure is embedded in a concrete wall at A and subjected to the force F₁ and the force-couple system F2 1650 N and M = 1,800 N-m at the locations shown. Neglect the weight of the structure in your calculations for this problem. = a.) Compute the allowable range of magnitudes for F₁ in the direction shown if the connection at A will fail when subjected to a resultant moment with a magnitude of 920 N- m or higher. b.) Focusing on the forces and igonoring given M for now. Using the value for F1, min that you calculated in (a), replace the two forces F₁ and F2 with a single force that has equivalent effect on the structure. Specify the equivalent →> force Feq in Cartesian components and indicate the horizontal distance from point A to its line of action (note this line of action may not intersect the structure). c.) Now, model the entire force system (F1,min, F2, and M) as a single force and couple acting at the junction of the horizontal and vertical sections of the…arrow_forwardThe heated rod from Problem 3 is subject to a volumetric heating h(x) = h0 x L in units of [Wm−3], as shown in the figure below. Under the heat supply the temperature of the rod changes along x with the temperature function T (x). The temperature T (x) is governed by the d following equations: − dx (q(x)) + h(x) = 0 PDE q(x) =−k dT dx Fourier’s law of heat conduction (4) where q(x) is the heat flux through the rod and k is the (constant) thermal conductivity. Both ends of the bar are in contact with a heat reservoir at zero temperature. Determine: 1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem. 2. The temperature function T (x). 3. The heat flux function q(x). Side Note: Please see that both ends of bar are in contact with a heat reservoir at zero temperature so the boundary condition at the right cannot be du/dx=0 because its not thermally insulated. Thank youarrow_forwardThe elastic bar from Problem 1 spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω2x. Under this radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement d u(x) is governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (2) where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ is the mass density, and E is the (constant) Young’s modulus. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0 and it is also pinned at x = L. Determine: 1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem. 2. The displacement function u(x). 3. The stress function σ(x). SIDE QUESTION: I saw a tutor solve it before but I didn't understand why the tutor did not divide E under the second term (c1x) before finding u(x). The tutor only divided E under first term. please explain and thank youarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY