
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134042282
Author: Paula Yurkanis Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 57P
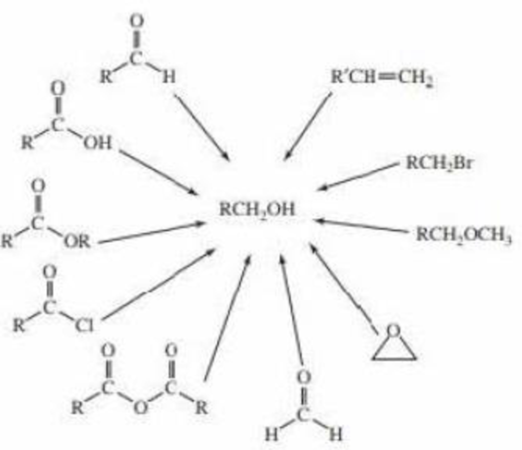
a. Show the reagents required to form the primary alcohol in each of the following reactions.
b. Which of the reactions cannot be used for the synthesis of isobutyl alcohol?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
12.
CH3
OH
OH
H&C
CH3
H₂C
N
OH H₂C
CH3
H&C
CH3 H₂C'
CH3
H.C
CH3OH
H.C
CH2CH3OH
CH3CEN
Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR
spectrum?
IR Spectrum
3000
4000
3000
NMR Spectrum
2000
£500
RAVENUMBER
2000
1500
9
8
6
5
10
HP-00-290
ppm
m
1000
500
1000
4
°
Draw the structure of (E,6R) 6-methoxy-4-hepten-2-one.
Give the IUPAC name of this compound,
including stereochemistry.
Draw the most stable chair conformation of
(cis) 1,3-isobutylcyclohexane.
H
HC=CCH₂
CH2CH3
EN(CH3)2
-CN(CH3)2
10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate
stereochemistry in product.
H3C
CH₂OH
CH3
SN1
H
Chapter 16 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 16.1 - Give two names for each of the following:Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 16.1 - Name the following:Ch. 16.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 16.4 - What products are formed when the following...Ch. 16.4 - We saw on the previous page that...Ch. 16.4 - a. How many stereoisomers are obtained from the...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 16.4 - Write the mechanism for the reaction of acetyl...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 11P
Ch. 16.4 - Show how the following compounds can be...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 16.4 - Prob. 14PCh. 16.4 - In the mechanism for cyanohydrin formation, why is...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 16PCh. 16.4 - Prob. 17PCh. 16.4 - Show two ways to convert an alkyl halide into a...Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 20PCh. 16.5 - Prob. 21PCh. 16.5 - Prob. 22PCh. 16.5 - Prob. 23PCh. 16.6 - Prob. 24PCh. 16.7 - What reducing agents should be used to obtain the...Ch. 16.7 - Prob. 26PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 27PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 28PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 29PCh. 16.8 - The pKa of protonated acetone is about 7.5. and...Ch. 16.8 - Prob. 31PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 32PCh. 16.8 - Prob. 33PCh. 16.8 - Excess ammonia must be used when a primary amine...Ch. 16.8 - The compounds commonly known as amino acids are...Ch. 16.9 - Hydration of an aldehyde is also catalyzed by...Ch. 16.9 - Which ketone forms the most hydrate in an aqueous...Ch. 16.9 - When trichloroacetaldehyde is dissolved in water,...Ch. 16.9 - Which of the following are a. hermiacetals? b....Ch. 16.9 - Prob. 40PCh. 16.9 - Explain why an acetal can be isolated but most...Ch. 16.10 - Prob. 42PCh. 16.10 - Prob. 43PCh. 16.10 - What products would be formed from the proceedings...Ch. 16.10 - a. In a six-step synthesis, what is the yield of...Ch. 16.10 - Show how each of the following compounds could be...Ch. 16.12 - Prob. 47PCh. 16.13 - Prob. 49PCh. 16.14 - Prob. 50PCh. 16.15 - Prob. 51PCh. 16.16 - Prob. 52PCh. 16 - Draw the structure for each of the following: a....Ch. 16 - Prob. 54PCh. 16 - Prob. 55PCh. 16 - Prob. 56PCh. 16 - a. Show the reagents required to form the primary...Ch. 16 - Prob. 58PCh. 16 - Prob. 59PCh. 16 - Using cyclohexanone as the starting material,...Ch. 16 - Propose a mechanism for each of the following...Ch. 16 - Show how each of the following compounds can be...Ch. 16 - Fill in the boxes:Ch. 16 - Prob. 64PCh. 16 - Identify A through O:Ch. 16 - Prob. 66PCh. 16 - Prob. 67PCh. 16 - Prob. 68PCh. 16 - How many signals would the product of the...Ch. 16 - Prob. 70PCh. 16 - Prob. 71PCh. 16 - Prob. 72PCh. 16 - Prob. 73PCh. 16 - Prob. 74PCh. 16 - Prob. 75PCh. 16 - Prob. 76PCh. 16 - Prob. 77PCh. 16 - Prob. 78PCh. 16 - Draw structure for A-D for each of the following:Ch. 16 - Prob. 80PCh. 16 - a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 16 - Prob. 82PCh. 16 - A compound gives the following IR spectrum. Upon...Ch. 16 - How can be following compounds be prepared from...Ch. 16 - Prob. 85PCh. 16 - Prob. 86PCh. 16 - Prob. 87PCh. 16 - In the presence of an acid catalyst, acetaldehyde...Ch. 16 - Prob. 89PCh. 16 - Prob. 90PCh. 16 - Prob. 91PCh. 16 - A compound reacts with methylmagnesium bromide...Ch. 16 - Show how each of the following compounds can be...Ch. 16 - Prob. 94PCh. 16 - The pKa values of the carboxylic acid groups of...Ch. 16 - The Baylis-Hillman reaction is a DABCO...Ch. 16 - Prob. 97PCh. 16 - Prob. 98P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Write "most" under the member of each trio which is most stable. Write "least under the member of each trio which is least stable. b) Draw a Fischer projection of a pair of enantiomers with three chiral carbons. Which of these two would you expect to be more soluble in water? Why? 1-butanol 1-heptanol Which of these two would you expect to have the higher boiling point? Why? hexyl methyl ether 1-heptanolarrow_forwardWrite "most" under the most acidic compound. Write "least" under the least acidic compound. OH NO₂ OCH3 Br 9. Compound X, C50H84F2, reacts with excess H2/Pd to give a C50H88F2 compound. How many rings are in X? How many double bonds are in X? Show your work.arrow_forward4. State whether these two are: a) the same molecule b) c) d) different compounds that are not isomers constitutional isomers diastereomers e) enantiomers CH3 CH₁₂ H OH HO H H OH HO H CH, CH₂ 5. a) How many stereocenters does this compound have? b) How many stereoisomers are possible for this compound? CH₂ OH CHCHarrow_forward
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.1003 M hydrobromic acid (HBr) solution with 0.7550M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ☑ o0o 18 Ararrow_forwardDo you do chemistry assignmentsarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A This reaction is always spontaneous, but proceeds slower at temperatures above 120. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except above 117. °C. AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is (pick one) This reaction is slower below 20. °C than C above. AS is |(pick one) ? 18 Ar 1arrow_forward
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration Try Again Your answer is incorrect. 0/5 a A chemist titrates 70.0 mL of a 0.7089 M hydrocyanic acid (HCN) solution with 0.4574M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK of hydrocyanic acid is 9.21. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = 11.43] G 00. 18 Ar B•arrow_forwardBiological Macromolecules Naming and drawing the products of aldose oxidation and reduction aw a Fischer projection of the molecule that would produce L-ribonic acid if it were subjected to mildly oxidizing reaction conditions. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X AP ‡ 1/5 Naor Explanation Check McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibilarrow_forward● Biological Macromolecules Identifying the parts of a disaccharide Take a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH O H H H OH OH OH H H CH2OH H O OH H OH H H H H OH Is this a reducing sugar? Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. Explanation Check O yes X O no ○ yes O no Uarrow_forward
- The aim of the lab is to measure the sodium content from tomato sauce using the Mohr titration method. There are two groups being: Regular Tomato sauce & Salt Reduced tomato sauce QUESTION: State how you would prepare both Regular & Salt reduced tomato sauce samples for chemical analysis using the Mohr titration methodarrow_forwardUsing the conditions of spontaneity to deduce the signs of AH and AS Use the observations about each chemical reaction in the table below to decide the sign (positive or negative) of the reaction enthalpy AH and reaction entropy AS. Note: if you have not been given enough information to decide a sign, select the "unknown" option. reaction observations conclusions A The reverse of this reaction is always spontaneous but proceeds faster at temperatures above -48. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) ✓ AS is (pick one) B This reaction is spontaneous except below 114. °C but proceeds at a slower rate below 135. °C. ΔΗ is (pick one) AS is (pick one) ΔΗ is C This reaction is exothermic and proceeds faster at temperatures above -43. °C. (pick one) AS is (pick one) v Х 5 ? 18 Ararrow_forwardion. A student proposes the following Lewis structure for the perchlorate (CIO) io : :0: : Cl : - - : :0: ك Assign a formal charge to each atom in the student's Lewis structure. atom central O formal charge ☐ top O ☐ right O ☐ bottom O ☐ Cl ☐arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Characteristic Reactions of Benzene and Phenols; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tjEqEjDd87E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
An Overview of Aldehydes and Ketones: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #27; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-fBPX-4kFlw;License: Standard Youtube License