
Concept explainers
17-9 Answer true or false.
(a) The one aldehyde and the one ketone with a molecular formula of C3H6O are constitutional isomers.
(b)
(c) The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of 1200 about the carbonyl carbon of aldehydes and ketones.
(d) The carbonyl carbon of a ketone is a stereocenter.
(a)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The one aldehyde and one ketone with a molecular formula of
Concept Introduction:
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas or connectivity with atoms is different. In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom and ketones carbonyl group is bonded to two carbon atoms.
Answer to Problem 1P
The one aldehyde and one ketone with a molecular formula of
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula:
For this molecular formula we can draw both aldehyde and ketone. They are as follows.
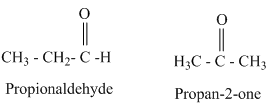
From the above structures aldehydes and ketones having same molecular formula are constitutional isomers.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
Aldehydes and ketones both contain a carbonyl group.
Concept Introduction:
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom and ketones carbonyl group is bonded to two carbon atoms.
Answer to Problem 1P
Aldehydes and ketones both contain a carbonyl group is true statement.
Explanation of Solution
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom and in ketone carbonyl group is bonded to two carbon atoms. Hence, both an aldehyde and a ketone have a carbonyl group.

Where, R is an alkyl group.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of 1200 about the carbonyl carbon of aldehydes and ketones.
Concept Introduction:
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom and ketones carbonyl group is bonded to two carbon atoms. VSEPR model predicts the geometry of the molecule with the help of number of pair of electrons present around the central atoms and bond angle of the molecule.
Answer to Problem 1P
The VSEPR model predicts bond angles of 1200 about the carbonyl carbon if aldehydes and ketones is the true statement.
Explanation of Solution
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom and ketones carbonyl group is bonded to two carbon atoms. The carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketone are represented are as follows.
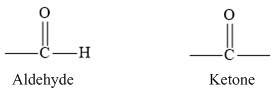
According to VSEPR theory, three pair of electron groups forms a Trigonal planar geometry with bond angle of 1200.
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(d)
Interpretation:
Answer true or false for the following statement.
The carbonyl carbon of ketone is a stereocentre.
Concept Introduction:
A stereocentre is a tetrahedral carbon atom in which four different groups are attached to it. When an atom generally carbon is linked with four different groups, then that centre is known as chiral centre.
Answer to Problem 1P
The carbonyl carbon of ketone is a stereocenter is the false statement.
Explanation of Solution
In aldehydes, the carbonyl group is bonded to a hydrogen atom and in ketone carbonyl group is bonded to two carbon atoms. The carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketone are represented are as follows.

In ketones, the carbonyl carbon is boded to carbonyl oxygen by a double bond group and bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Therefore, the given statement is false.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- For each of the following, indicate whether the arrow pushes are valid. Do we break any rules via the arrows? If not, indicate what is incorrect. Hint: Draw the product of the arrow and see if you still have a valid structure. a. b. N OH C. H N + H d. e. f. مه N COHarrow_forwardDecide which is the most acidic proton (H) in the following compounds. Which one can be removed most easily? a) Ha Нь b) Ha Нь c) CI CI Cl Ha Ньarrow_forwardProvide all of the possible resonanse structures for the following compounds. Indicate which is the major contributor when applicable. Show your arrow pushing. a) H+ O: b) c) : N :O : : 0 d) e) Оarrow_forward
- Draw e arrows between the following resonance structures: a) b) : 0: :0: c) :0: N t : 0: بار Narrow_forwardDraw the major substitution products you would expect for the reaction shown below. If substitution would not occur at a significant rate under these conditions, check the box underneath the drawing area instead. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products. Note for advanced students: you can assume that the reaction mixture is heated mildly, somewhat above room temperature, but strong heat or reflux is not used. Cl Substitution will not occur at a significant rate. Explanation Check :☐ O-CH + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw the major substitution products you would expect for the reaction shown below. If substitution would not occur at a significant rate under these conditions, check the box underneath the drawing area instead. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products. Note for advanced students: you can assume that the reaction mixture is heated mildly, somewhat above room temperature, but strong heat or reflux is not used. Cl C O Substitution will not occur at a significant rate. Explanation Check + O-CH3 Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- ✓ aw the major substitution products you would expect for the reaction shown below. If substitution would not occur at a significant rate under these conditions, check the box underneath the drawing area instead. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products. Note for advanced students: you can assume that the reaction mixture is heated mildly, somewhat above room temperature, but strong heat or reflux is not used. C Cl HO–CH O Substitution will not occur at a significant rate. Explanation Check -3 ☐ : + D Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Determine whether the following reaction is an example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction: Br OH HO 2 -- Molecule A Molecule B + Br 义 ollo 18 Is this a nucleophilic substitution reaction? If this is a nucleophilic substitution reaction, answer the remaining questions in this table. Which of the reactants is referred to as the nucleophile in this reaction? Which of the reactants is referred to as the organic substrate in this reaction? Use a ŏ + symbol to label the electrophilic carbon that is attacked during the substitution. Highlight the leaving group on the appropriate reactant. ◇ Yes O No O Molecule A Molecule B Molecule A Molecule B टेarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




