
Concept explainers
17-73 Alcohols can be prepared by the acid-catalyzed hydration of
(a) Ethanol
(b) Cyclohexanol
(c) 2-Propanol
(d) 1-Phenylethanol
(a)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of ethanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
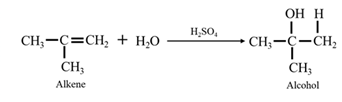
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
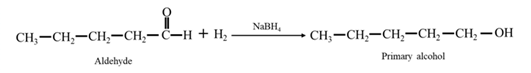
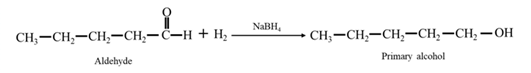
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
Answer to Problem 67P
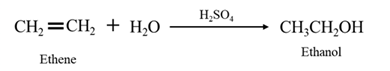
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
By Reduction of ethanal:
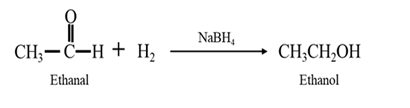
Explanation of Solution
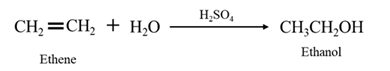
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
When ethene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives ethanol.
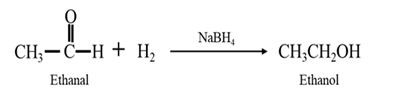
By Reduction of ethanal: When ethanal is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives ethanol.
(b)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of cyclohexanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
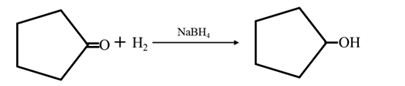
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
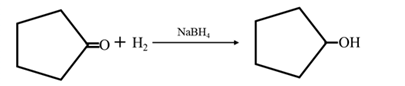
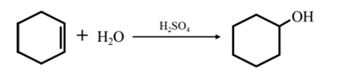
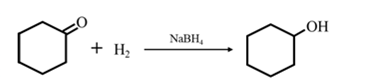
Answer to Problem 67P
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
By Reduction of ethanal:
Explanation of Solution
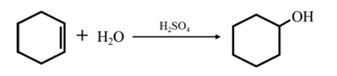
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane: When cyclohexene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives cyclohexanol.
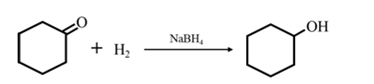
By Reduction of ethanal: When cyclohexanone is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives cyclohexanol.
(c)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of 2-propanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
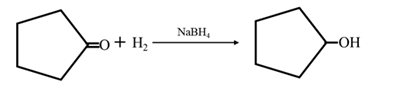
Answer to Problem 67P
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
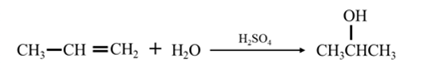
By Reduction of ethanal:
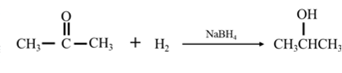
Explanation of Solution
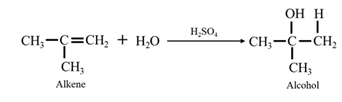
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane: When propene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives 2-propanol.
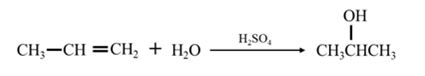
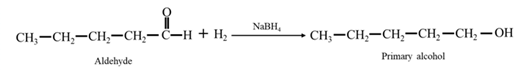
By Reduction of ethanal: When acetone is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives 2-propanol.
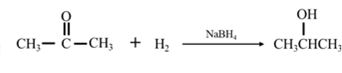
(d)
Interpretation:
Show the preparation of 1-phenylethanol by acid-catalyzed hydration of an alkene and by reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone.
Concept Introduction:
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: In the presence of an acid catalyst
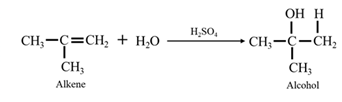
Reduction of an aldehyde or a ketone: The C=C double bond of an alkene is reduced by hydrogen in the presence of a transition metal catalyst to a C−C single bond. The same is true for the C=O double bond of an aldehyde or a ketone. Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohol.
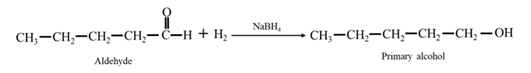
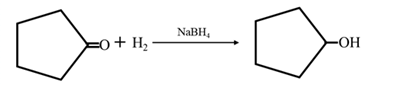
Answer to Problem 67P
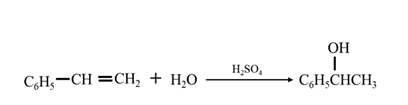
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane:
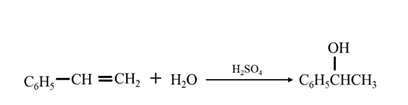
By Reduction of ethanal:
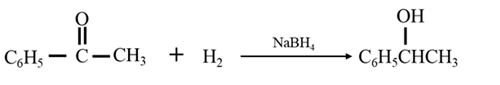
Explanation of Solution
By acid-catalyzed hydration of ethane: When 1-phenylethene is allowed to react with water in presence of an acid catalyst it gives 1-phenylethanol.
By Reduction of ethanal: When acetophenone is reduced in the presence of sodium borohydride it gives 1-phenylethanol.
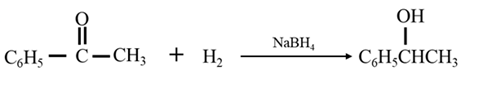
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- A composite material reinforced with aligned fibers, consisting of 20% by volume of silicon carbide (SiC) fibers and 80% by volume of polycarbonate (PC) matrix. The mechanical characteristics of the 2 materials are in the table. The stress of the matrix when the fiber breaks is 45 MPa. Calculate the longitudinal strength? SiC PC Elastic modulus (GPa) Tensile strength (GPa) 400 2,4 3,9 0,065arrow_forwardQuestion 2 What starting materials or reagents are best used to carry out the following reaction? 2Fe, 3Br2 ○ FeCl3 2Fe, 4Br2 O Heat and Br2 Heat and HBr Brarrow_forwardWhat is/are the major product(s) of the following reaction? O AICI -Chts +arrow_forward
- Shown below is the major resonance structure for a molecule. Draw the second best resonance structure of the molecule. Include all non-zero formal charges. H. C H H C H :Ö: Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardShown below is the major resonance structure for a molecule. Draw the second best resonance structure of the molecule. Include all non-zero formal charges. H. C H H C. H H H H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardA new brand of lotion is causing skin rush unlike the old brand of the same lotion. With the aid of well labelled diagram describe an experiment that could be done to isolate the pigment that cause the skin rusharrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forwardRelative Intensity Part VI. consider the multi-step reaction below for compounds A, B, and C. These compounds were subjected to mass spectrometric analysis and the following spectra for A, B, and C was obtained. Draw the structure of B and C and match all three compounds to the correct spectra. Relative Intensity Relative Intensity 100 HS-NJ-0547 80 60 31 20 S1 84 M+ absent 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100- MS2016-05353CM 80- 60 40 20 135 137 S2 164 166 0-m 25 50 75 100 125 150 m/z 60 100 MS-NJ-09-43 40 20 20 80 45 S3 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 m/zarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


