
Concept explainers
A hydrogen atom in the organic base pyridine, C5H5N, can be substituted by various atoms or groups to give XC5H4N, where X is an atom such as Cl or a group such as CH3. The following table gives Ka values for the conjugate acids of a variety of substituted pyridines.
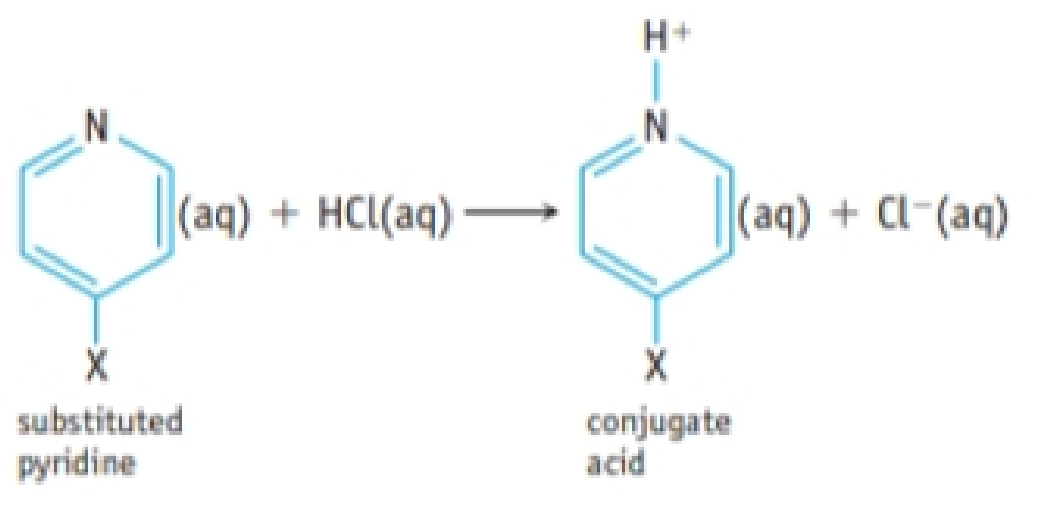
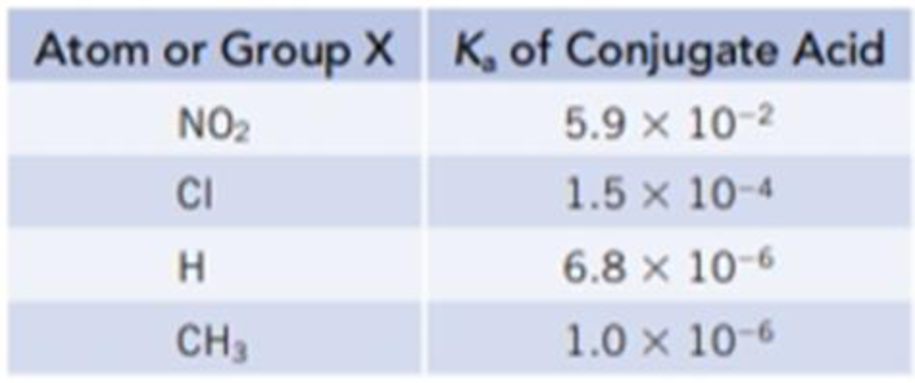
- (a) Suppose each conjugate acid is dissolved in sufficient water to give a 0.050 M solution. Which solution would have the highest pH? The lowest pH?
- (b) Which of the substituted pyridines is the strongest Brønsted base? Which is the weakest Brønsted base?
(a)
Interpretation:
The conjugate acid which have the highest
Concept Introduction:
The
Higher the value of
Answer to Problem 112IL
The solution containing
Explanation of Solution
An equilibrium constant
For Any acid HA,
The relative strength of an acid and base in water can be also expressed quantitatively with an equilibrium constant as follows:
An equilibrium constant
Given:
The
Initial Concentration of each solution is
Set up an ICE table for the reaction of
Substitute the values in equation (2) to calculate
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the value of hydronium ion concentration in equation (1) to calculate the value of
Therefore, the value of
Similarly, Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the concentration of hydronium ion in equation (1) to calculate the value of
Therefore, the value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the concentration of hydronium ion in equation (1) to calculate the value of
Therefore, the value of
Substitute the value of
The value of
Substitute the concentration of hydronium ion in equation (1) to calculate the value of
Therefore, the value of
The solution containing
(b)
Interpretation:
Strongest
Concept Introduction:
A conjugate acid-base pair contains two compounds that differ only by a hydrogen ion and a charge of
The stronger the acid, the weaker its conjugate base and vice-verca. That is, the larger the values of
Answer to Problem 112IL
The strongest bronsted base is
Explanation of Solution
The dissociation of
A small value of
The dissociation of
A large value of
The strongest bronsted base is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- (Please be sure that 7 carbons are available in the structure )Based on the 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT 135 NMR and DEPT 90 NMR, provide a reasoning step and arrive at the final structure of an unknown organic compound containing 7 carbons. Dept 135 shows peak to be positive at 128.62 and 13.63 Dept 135 shows peak to be negative at 130.28, 64.32, 30.62 and 19.10.arrow_forward-lease help me answer the questions in the photo.arrow_forwardDefine electronegativity.arrow_forward
- Why do only the immediately adjacent H's show up in the number of peaks? Are there normally peaks for the H's that are 2-3 carbons away?arrow_forwardPlease help me understand this question. Thank you. Organic Chem 1arrow_forwardFor the reaction below, the concentrations at equilibrium are [SO₂] = 0.50 M, [0] = 0.45 M, and [SO3] = 1.7 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) Report your answer using two significant figures. Provide your answer below:arrow_forward
- scratch paper, and the integrated rate table provided in class. our scratch work for this test. Content attribution 3/40 FEEDBACK QUESTION 3 - 4 POINTS Complete the equation that relates the rate of consumption of H+ and the rate of formation of Br2 for the given reaction. 5Br (aq) + BrO3 (aq) + 6H (aq) →3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Your answers should be whole numbers or fractions without any decimal places. Provide your answer below: Search 尚 5 fn 40 * 00 99+ 2 9 144 a [arrow_forward(a) Write down the structure of EDTA molecule and show the complex structure with Pb2+ . (b) When do you need to perform back titration? (c) Ni2+ can be analyzed by a back titration using standard Zn2+ at pH 5.5 with xylenol orange indicator. A solution containing 25.00 mL of Ni2+ in dilute HCl is treated with 25.00 mL of 0.05283 M Na2EDTA. The solution is neutralized with NaOH, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with acetate buffer. The solution turns yellow when a few drops of indicator are added. Titration with 0.02299 M Zn2+ requires 17.61 mL to reach the red end point. What is the molarity of Ni2+ in the unknown?arrow_forwardA compound has the molecular formula CH40, and shows a strong IR absorption at 2850-3150 cm. The following signals appear in the 'H NMR spectrum: 1.4 ppm (triplet, 6H), 4.0 ppm (quartet, 4H), 6.8 ppm (broad singlet, 4H). Which of the following structures is consistent with these data? Select the single best answer. OCH CH₂ x OCH2CH3 CH₂OCH3 OH CH₂OCH OH CH, OCH₁ CH₂OCH, CH₂OCH HO OH ° CH₂OCH3arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





