
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 16, Problem 119SCQ
The halogens form three stable, weak acids, HOX.
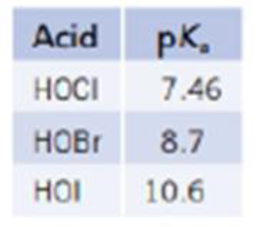
- (a) Which is the strongest of these acids?
- (b) Explain why the acid strength changes as the halogen atom is changed.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
help me solve this HW
Molecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)
Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Ch. 16.1 - 1. H3PO4 phosphoric acid, can donate two protons...Ch. 16.1 - 2. The cyanide ion, CN−, accepts a proton from...Ch. 16.1 - 3. In the following reaction, identify the acid on...Ch. 16.1 - Prob. 4RCCh. 16.2 - What are the hydronium ion and hydroxide ion...Ch. 16.2 - What is the pH of a 0.0012 M NaOH solution at 25C?...Ch. 16.2 - The pH of a diet soda is 432 at 25C. What is the...Ch. 16.2 - If the pH of a solution containing the strong base...Ch. 16.3 - Prob. 1RCCh. 16.3 - Which acid has the strongest conjugate base? (a)...
Ch. 16.3 - Prob. 3RCCh. 16.3 - Prob. 4RCCh. 16.3 - Prob. 5RCCh. 16.4 - For each of the following salts in water, predict...Ch. 16.4 - Prob. 1RCCh. 16.4 - Prob. 2RCCh. 16.5 - (a) Which is the stronger Bronsted acid, HCO3 or...Ch. 16.5 - Prob. 1RCCh. 16.5 - 2. In the following reaction, does the equilibrium...Ch. 16.6 - Equal amounts (moles) of HCl(aq) and NaCN(aq) are...Ch. 16.6 - 2. Equal amounts (moles) of acetic acid(aq) and...Ch. 16.6 - Prob. 3RCCh. 16.7 - A solution prepared from 0.055 mol of butanoic...Ch. 16.7 - What are the equilibrium concentrations of acetic...Ch. 16.7 - What are the equilibrium concentrations of HF, F...Ch. 16.7 - The weak base, CIO (hypochlorite ion), is used in...Ch. 16.7 - Calculate the pH after mixing 15 mL of 0.12 M...Ch. 16.7 - 1. What is [H3O+] in a 0.10 M solution of HCN at...Ch. 16.7 - 2. A 0.040 M solution of an acid, HA, has a pH of...Ch. 16.7 - What are the pH and ion concentrations in a...Ch. 16.7 - Prob. 4RCCh. 16.7 - Prob. 1QCh. 16.7 - Prob. 2QCh. 16.7 - The pKa, of the conjugate acid of atropine is...Ch. 16.8 - What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of oxalic...Ch. 16.8 - Hydrazine (N2H4) is like CO32 in that it is a...Ch. 16.9 - Which of the following is the stronger acid? (a)...Ch. 16.9 - Prob. 2RCCh. 16.9 - Prob. 3RCCh. 16.10 - 1. Which of the following can act as a Lewis acid?...Ch. 16.10 - 2. The molecule whose structure is illustrated...Ch. 16.10 - Convert the pK values to K values for the...Ch. 16.10 - Other solvents also undergo autoionization. (a)...Ch. 16.10 - Prob. 3QCh. 16.10 - Prob. 4QCh. 16.10 - To measure the relative strengths of bases...Ch. 16 - Write the formula and the give the name of the...Ch. 16 - Write the formula and give the name of the...Ch. 16 - What are the products of each of the following...Ch. 16 - What are the products of each of the following...Ch. 16 - Write balanced equations showing how the hydrogen...Ch. 16 - Write a balanced equation showing how the HPO42...Ch. 16 - In each of the following acid-base reactions,...Ch. 16 - In each of the following acid-base reactions,...Ch. 16 - An aqueous solution has a pH of 3.75. What is the...Ch. 16 - A saturated solution of milk of magnesia. Mg(OH)2,...Ch. 16 - What is the pH of a 0.0075 M solution of HCl? What...Ch. 16 - What is the pH of a 1.2 104 M solution of KOH?...Ch. 16 - What is the pH of a 0.0015 M solution of Ba(OH)2?Ch. 16 - The pH of a solution of Ba(OH)2 is 10.66 at 25 ....Ch. 16 - Several acids are listed here with their...Ch. 16 - Several acids are listed here with their...Ch. 16 - Which of the following ions or compounds has the...Ch. 16 - Which of the following compounds or ions has the...Ch. 16 - Which of the following compounds or ions has the...Ch. 16 - Which of the following compounds or ion has the...Ch. 16 - Dissolving K2CO3 in water gives a basic solution....Ch. 16 - Dissolving ammonium bromide in water gives an...Ch. 16 - If each of the salts listed here were dissolved in...Ch. 16 - Which of the following common food additives gives...Ch. 16 - Prob. 25PSCh. 16 - Prob. 26PSCh. 16 - Prob. 27PSCh. 16 - An organic acid has pKa = 8.95. What is its Ka...Ch. 16 - Prob. 29PSCh. 16 - Which is the stronger of the following two acids?...Ch. 16 - Chloroacetic acid (ClCH2CO2H) has Ka = 1.41 103....Ch. 16 - A weak base has Kb = 1.5 109. What is the value...Ch. 16 - The trimethylammonium ion, (CH3)3NH+, is the...Ch. 16 - The chromium(III) ion in water, [Cr(H2O)6]3+. Is a...Ch. 16 - Acetic acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate, NaHCO3,...Ch. 16 - Ammonium chloride and sodium dihydrogen phosphate,...Ch. 16 - For each of the following reactions, predict...Ch. 16 - For each of the following reactions, predict...Ch. 16 - Equal molar quantities of sodium hydroxide and...Ch. 16 - Equal molar quantities of hydrochloric acid and...Ch. 16 - Equal molar quantities of acetic acid and sodium...Ch. 16 - Equal molar quantities of ammonia and sodium...Ch. 16 - A 0.015 M solution of hydrogen cyanate, HOCN, has...Ch. 16 - A 0.10 M solution of chloroacetic acid, CICH2CO2H,...Ch. 16 - A 0.025 M solution of hydroxyl amine has a pH of...Ch. 16 - Methylamine, CH3NH2, is a weak base. CH3NH2(aq) +...Ch. 16 - A 2.5 103 M solution of an unknown acid has a pH...Ch. 16 - A 0.015M solution of a base has a pH of 10.09 a)...Ch. 16 - What are the equilibrium concentrations of...Ch. 16 - The ionizations constant of a very weak acid, HA...Ch. 16 - What are the equilibrium concentration of H3O+, CN...Ch. 16 - Phenol (C6H5OH) commonly called carbolic acid is a...Ch. 16 - What are the equilibrium concentrations of...Ch. 16 - A hypothetical weak base has Kb=5.0104.Calculate...Ch. 16 - The weak base methylamine, CH3NH2, has Kb=4.2104....Ch. 16 - Calculate the pH of a 0.12 M aqueous solution of...Ch. 16 - Calculate the pH of a 0.0010 M aqueous solution of...Ch. 16 - A solution of hydrofluoric acid, HF, has a pH of...Ch. 16 - Calculate the hydronium ion concentration and pH...Ch. 16 - Calculate the hydronium ion concentration and pH...Ch. 16 - Sodium cyanide is the salt of the weak acid HCN....Ch. 16 - The sodium salt of propionic acid, NaCH3CH2CO2 is...Ch. 16 - Calculate the hydronium ion concentration and pH...Ch. 16 - Calculate the hydronium ion concentration and the...Ch. 16 - For each of the following cases, decide whether...Ch. 16 - For each of the following cases, decide whether...Ch. 16 - Oxalic acid, H2C2O4, is a diprotic acid. Write a...Ch. 16 - Sodium carbonate is a diprotic base. Write a...Ch. 16 - Prove that Ka1 Kb2 = Kw for oxalic acid H2C2O4,...Ch. 16 - Prove that Ka3 Kb1 = Kw for phosphoric acid,...Ch. 16 - Sulphurous acid, H2SO3, is a weak acid capable of...Ch. 16 - Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, C6H8O6) is a diprotic...Ch. 16 - Hydrazine, N2H4, can interact with water in two...Ch. 16 - Ethylene diamine, H2NCH2CH2NH2, can interact with...Ch. 16 - Which should be stronger acid, HOCN or HCN?...Ch. 16 - Prob. 76PSCh. 16 - Explain why benzene sulfonic acid is a Brnsted...Ch. 16 - The structure of ethylene diamine is illustrated...Ch. 16 - Decide whether each of the following substances...Ch. 16 - Decide whether each of the following substances...Ch. 16 - Carbon monoxide forms complexes with low-valent...Ch. 16 - Trimethylamine, (CH3)3N, is a common reagent. It...Ch. 16 - About this time, you may be wishing you had an...Ch. 16 - Consider the following ions: NH4+, CO32, Br, S2,...Ch. 16 - A 2.50 g sample of a solid that could be Ba(OH)2...Ch. 16 - In a particular solution, acetic acid is 11%...Ch. 16 - Hydrogen, H2S, and sodium acetate, NaCH3CO2 are...Ch. 16 - For each of the following reactions predict...Ch. 16 - A monoprotic acid HX has Ka = 1.3 103. Calculate...Ch. 16 - Arrange the following 0.10M solutions in order of...Ch. 16 - m-Nitrophenol, a weak acid, can be used as a pH...Ch. 16 - The butylammonium ion, C4H9NH3+, has a Ka of 2.3 ...Ch. 16 - The local anaesthetic novocaine is the hydrogen...Ch. 16 - Pyridine is weak organic base and readily forms a...Ch. 16 - The base ethylamine (CH3CH2NH2) has a Kb of. A...Ch. 16 - Chloroacetic acid, ClCH2CO2H, is a moderately weak...Ch. 16 - Saccharin (HC7H4NO3S) is a weak acid with pKa =...Ch. 16 - Given the following solutions: (a) 0.1 M NH3 (b)...Ch. 16 - For each of the following salts, predict whether a...Ch. 16 - Nicotine, C10H14N2, has two basic nitrogen atoms...Ch. 16 - Prob. 101GQCh. 16 - The equilibrium constant for the reaction of...Ch. 16 - The equilibrium constant for the reaction of...Ch. 16 - Calculate the pH of the solution that results from...Ch. 16 - To what volume should 1.00 102 mL of any weak...Ch. 16 - The hydrogen phthalate ion, C8HsO4, is a weak acid...Ch. 16 - Prob. 107GQCh. 16 - Prob. 108GQCh. 16 - Prob. 109ILCh. 16 - Prob. 110ILCh. 16 - Prob. 111ILCh. 16 - A hydrogen atom in the organic base pyridine,...Ch. 16 - Nicotinic acid, C6H5NO2, is found in minute...Ch. 16 - Prob. 114ILCh. 16 - Sulfanilic acid, which is used in making dyes, is...Ch. 16 - Amino acids are an important group of compounds....Ch. 16 - How can water be both a Brnsied base and a Lewis...Ch. 16 - The nickel(II) ion exists as [Ni(H2O)4]2+ in...Ch. 16 - The halogens form three stable, weak acids, HOX....Ch. 16 - The acidity of the oxoacids was described in...Ch. 16 - Perchloric acid behaves as an acid, even when it...Ch. 16 - You purchase a bottle of water. On checking its...Ch. 16 - Prob. 123SCQCh. 16 - Prob. 124SCQCh. 16 - Prob. 125SCQCh. 16 - Consider a salt of a weak base and a weak acid...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forwardWhat characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forward
- For a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forwardDescribe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
- State two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardIn a photochemical reaction, how is the rate of the process related to its quantum yield?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Balancing Redox Reactions in Acidic and Basic Conditions; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N6ivvu6xlog;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY