
(a)
Interpretation: The number of triple points in the given phase diagram of sulfur needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The conversion of
The heating -cooling curve is the curve of temperature v/s time that interpret the change in the states of matter with increase in temperature.
The phase diagram represents the change in the physical state of given substance with temperature and pressure.
(a)
Answer to Problem 104E
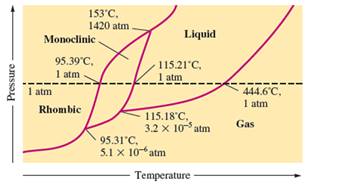
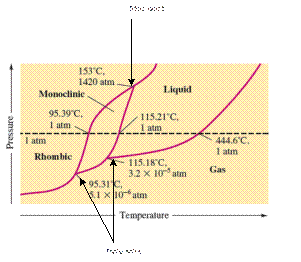
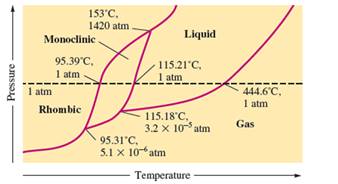
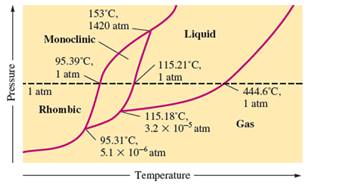
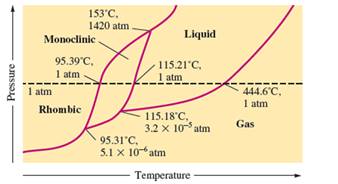
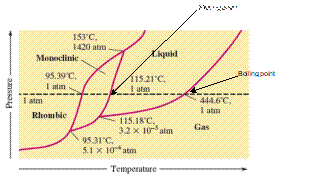
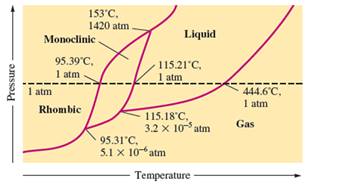
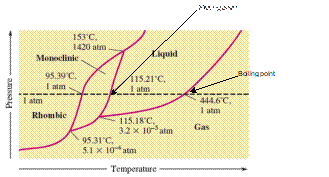
There are three triple points in the given phase diagram of sulfur.
Explanation of Solution
A triple point is the point in the phase diagram at which all the three phases will join together. It indicates the point (temperature and pressure) at which all three states remain in equilibrium.
(b)
Interpretation: The phases at the triple points in the given phase diagram of sulfur needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The conversion of solid to liquid and gas involves the change in temperature that can display in heat curve.
The heating -cooling curve is the curve of temperature v/s time that interpret the change in the states of matter with increase in temperature.
The phase diagram represents the change in the physical state of given substance with temperature and pressure.
(b)
Answer to Problem 104E
- At 95.31°C: rhombic, monoclinic, gas
- At 115.18°C: monoclinic, liquid, gas
- At 153°C: rhombic, monoclinic, and liquid
Explanation of Solution
A triple point is the point in the phase diagram at which all the three phases will join together. It indicates the point (temperature and pressure) at which all three states remain in equilibrium.
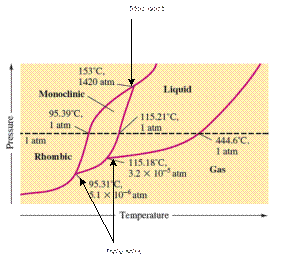
At 95.31°C, the rhombic, monoclinic and gaseous state of sulfur are in equilibrium whereas at 115.18°C monoclinic, liquid and gaseous state of sulfur. The 3rd triple point is at 153°C at which rhombic, monoclinic, and liquid state of sulfur.
(c)
Interpretation: The phases which are stable at room temperature and 1.0 atm pressure in the given phase diagram of sulfur needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The conversion of solid to liquid and gas involves the change in temperature that can display in heat curve.
The heating -cooling curve is the curve of temperature v/s time that interpret the change in the states of matter with increase in temperature.
The phase diagram represents the change in the physical state of given substance with temperature and pressure.
(c)
Answer to Problem 104E
At room temperature and 1.0 atm pressure,the rhombic phase of sulfur is stable. The temperature is approximately ˜ 20°C and pressure is 1.0 atm.
Explanation of Solution
In the given phase diagram, there are four states of sulfur; monoclinic, rhombic, liquid and gaseous state of sulfur.
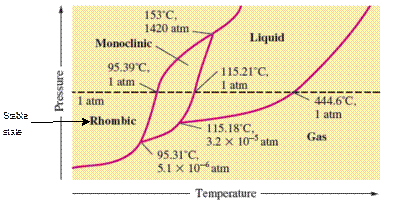
At room temperature and 1.0 atm pressure, the rhombic phase of sulfur is stable. The temperature is approximately ˜ 20°C and pressure is 1.0 atm.
(d)
Interpretation: The possibility of existence of monoclinic sulfur in equilibrium with sulfur vapor needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The conversion of solid to liquid and gas involves the change in temperature that can display in heat curve.
The heating -cooling curve is the curve of temperature v/s time that interpret the change in the states of matter with increase in temperature.
The phase diagram represents the change in the physical state of given substance with temperature and pressure.
(d)
Answer to Problem 104E
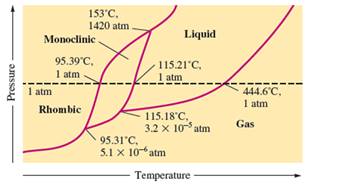
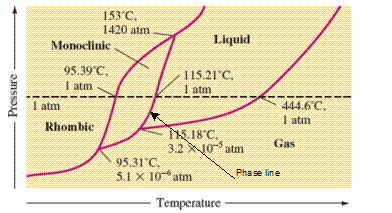
The monoclinic sulfur and vapor or gaseous state of matter share the phase line therefore they can be in equilibrium in the phase diagram.
Explanation of Solution
In the given phase diagram, there are four states of sulfur; monoclinic, rhombic, liquid and gaseous state of sulfur. The monoclinic sulfur and vapor or gaseous state of matter share the phase line therefore they can be in equilibrium in the phase diagram.
(e)
Interpretation: The normal boiling point and normal melting point of sulfur according to given phase diagram needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The conversion of solid to liquid and gas involves the change in temperature that can display in heat curve.
The heating -cooling curve is the curve of temperature v/s time that interpret the change in the states of matter with increase in temperature.
The phase diagram represents the change in the physical state of given substance with temperature and pressure.
(e)
Answer to Problem 104E
Normal melting point = 115.21°C
Normal boiling point = 444.6°C
Explanation of Solution
In the given phase diagram, there are four states of sulfur; monoclinic, rhombic, liquid and gaseous state of sulfur. Boiling point is the temperature at which liquid and gaseous state remain in equilibrium at 1 atm pressure. According to given phase diagram, the normal boiling point of sulfur must be 444.6°C. The melting point of substance is the temperature at which solid melts to liquid state which is 115.21 °C for sulfur.
(f)
Interpretation: The denser phase out of solid, monoclinic or rhombic sulfur according to given phase diagram needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The conversion of solid to liquid and gas involves the change in temperature that can display in heat curve.
The heating -cooling curve is the curve of temperature v/s time that interpret the change in the states of matter with increase in temperature.
The phase diagram represents the change in the physical state of given substance with temperature and pressure.
(f)
Answer to Problem 104E
Rhombic sulfur is the densest phase of sulfur.
Explanation of Solution
In the given phase diagram, there are four states of sulfur; monoclinic, rhombic, liquid and gaseous state of sulfur. The Rhombic phase of sulfur is most dense phase of it compare to monoclinic and solid. This is because the rhombic-monoclinic equilibrium line has a positive slope therefore with increase in the temperature, the rhombic phase changes to monoclinic.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





