
Concept explainers
Repeat Prob. 14-60, but with the pipe diameter increased by a factor of 2 (all else being equal). Does the volume flow rate at which cavitation occurs in the pump increase or decrease with the larger pipe? Discuss.
Whether the volume flow rate at which cavitations occurs in the pump increase or decrease of the larger pipe.
Answer to Problem 62P
The diameter of the pipe is doubled then the flow rate increase by
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The pipe diameter is increased by the factor two.
Write the expression for the net positive suction head.
Here, the net positive suction head is
Write the expression for the total head loss.
Here, the friction factor is
Write the expression for the average speed.
Here, the diameter of the pipe is
Write the expression for the Reynolds number.
Here, the Reynolds number is
Write the expression for the friction factor.
Substitute
Write the expression for the required net positive suction head.
Here, the required net positive head is
Write the expression for the percentage increase.
Here, the percentage increase is
Calculation:
Refer the Table B-1, "The physical properties of saturated liquid" to obtain the value of the density is
Refer the Table B-1, "The physical properties of saturated liquid" to obtain the value of the kinematic viscosity is
Refer the Table B-1, "The physical properties of saturated liquid" to obtain the value of the vapor pressure is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The following table represents the net positive suction head, the required net positive suction head, and discharge.
| | |
Plot the graph by using tabulated values.
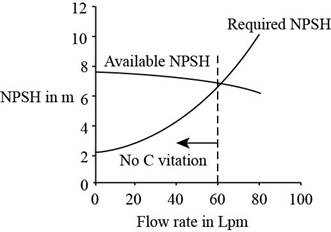
Figure-(1)
From Figure-(1), the cavitations occurs at the flow rate
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The following table represents the net positive suction head, the required net positive suction head, and discharge.
| | |
Plot the graph by using tabulated values.
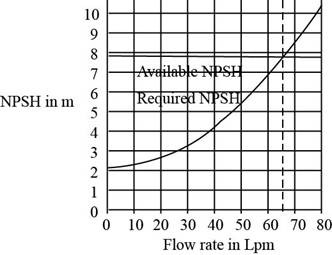
Figure-(2)
From Figure-(2), the cavitations occurs at the flow rate
Substitute
The diameter of the pipe is doubled then the flow rate increase by
Conclusion:
The diameter of the pipe is doubled then the flow rate increase by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- Please answer with the sketches.arrow_forwardThe beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic material. Determine the shape factor for the cross section of the beam (Figure Q3). [Take σy = 250 MPa, yNA = 110.94 mm, I = 78.08 x 106 mm²] y 25 mm 75 mm I 25 mm 200 mm 25 mm 125 Figure Q3arrow_forwardA beam of the cross section shown in Figure Q3 is made of a steel that is assumed to be elastic- perfectectly plastic material with E = 200 GPa and σy = 240 MPa. Determine: i. The shape factor of the cross section ii. The bending moment at which the plastic zones at the top and bottom of the bar are 30 mm thick. 15 mm 30 mm 15 mm 30 mm 30 mm 30 mmarrow_forward
- A torque of magnitude T = 12 kNm is applied to the end of a tank containing compressed air under a pressure of 8 MPa (Figure Q1). The tank has a 180 mm inner diameter and a 12 mm wall thickness. As a result of several tensile tests, it has been found that tensile yeild strength is σy = 250 MPa for thr grade of steel used. Determine the factor of safety with respect to yeild, using: (a) The maximum shearing stress theory (b) The maximum distortion energy theory T Figure Q1arrow_forwardAn external pressure of 12 MPa is applied to a closed-end thick cylinder of internal diameter 150 mm and external diameter 300 mm. If the maximum hoop stress on the inner surface of the cylinder is limited to 30 MPa: (a) What maximum internal pressure can be applied to the cylinder? (b) Sketch the variation of hoop and radial stresses across the cylinder wall. (c) What will be the change in the outside diameter when the above pressure is applied? [Take E = 207 GPa and v = 0.29]arrow_forwardso A 4 I need a detailed drawing with explanation し i need drawing in solution motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the か ---2-125 750 x2.01 98Parrow_forward
- Figure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A 45 B Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C Darrow_forwardI need a detailed drawing with explanation so Solle 4 يكا Pax Pu + 96** motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the 55 ---20125 750 X 2.01 1989arrow_forwardAshaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNM 20,000 10,000 0 90 270 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 720arrow_forward
- chanism shown in figure below, the crank OA rotates at 60 RPM counterclockwise. The velocity diagram is also drawn to scale (take dimensions from space diagram). Knowing that QCD is rigid plate, determine: a. Linear acceleration of slider at B, b. Angular acceleration of the links AC, plate CQD, and BD. D Space Diagram Scale 1:10 A ES a o,p,g b Velocity Diagram Scale 50 mm/(m/s) darrow_forwardA thick closed cylinder, 100 mm inner diameter and 200 mm outer diameter is subjected to an internal pressure of 230 MPa and outer pressure of 70 MPa. Modulus of elasticity, E=200 GPa. and Poisson's ratio is 0.3, determine: i) The maximum hoop stress ii) The maximum shear stress iii) The new dimension of the outer diameter due to these inner and outer pressures.arrow_forwardA ә レ shaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180 degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to 20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter. Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of 500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel. 35,000 TNm 20,000 10,000 495 Crank angle 8 degrees 270 0 90 か ---20125 750 X 2.01 44 720 sarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





