
Concept explainers
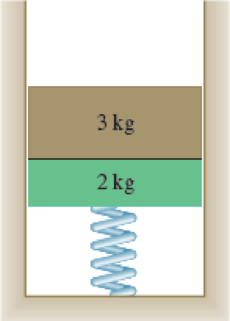
A 3-kg block rests on top of a 2-kg block supported by, but not attached to, a spring of constant 40 N/m. The upper block is suddenly removed. Determine (a) the maximum speed reached by the 2-kg block, (b) the maximum height reached by the 2-kg block.
Fig. P13.26
(a)
Find the maximum speed
Answer to Problem 13.26P
The maximum speed
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the block A
The mass of the block B
The spring constant (k) is
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Consider the position 1, the block B has been removed.
Calculate the spring stretch
Here,
Substitute
Substitute
Take the position 2 be later position while the spring still in contact with block A.
Calculate the work of the force exerted
Integrate the above equation with respect to ‘x’.
Substitute,
Calculate the work of the gravitational force
Substitute,
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
Here, the initial kinetic energy
Calculate the kinetic energy
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Write the expression for the principle of work and energy:
Substitute 0 for
At the maximum speed, differentiate the velocity equation with respect to ‘x’.
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum speed
(b)
Find the maximum height (h) reached by the
Answer to Problem 13.26P
The maximum height (h) reached by the
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the block A
The mass of the block B
The spring constant (k) is
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Consider the position 3, the block A reached the maximum height and assume that the block has separated from the spring so the spring is zero at the separation.
Calculate the work of the force exerted
Integrate the above equation with respect to ‘x’.
Substitute,
Calculate the work of the gravitational force
Substitute
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
At the maximum height, the velocity
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the maximum height (h) reached by the
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the maximum height (h) reached by the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- I keep getting the wrong answer i have gotten 6519.87 and 319.71arrow_forwardthank you for previous answer I apologize if the acceleration was unclear it is underlined now along with values in tablesarrow_forward११११११११ TABLE Much 160,000kg Croll 0,005 CD Ap Par ng При nchs 0.15 5m² 1.2kg/m³ 0.98 0.9 0,98 0,9 0,88 IF 20 10 to add The train is going to make several stops along its journey. It will be important for the train to accelerate quickdy to get back up to speed. In order to get Tesla Model S motors until we get the combined The Forque and power needed we are goins bined power and forque needed to accelerate from 0 to 324 km/hr in less than 5 Minutes. Tesla Prated 270 kW Tesla Trated Twheel ng Jaxle 440 NM 20 8.5kgm² 0.45M a) What is the minimum whole number of Tesla Motors required to achieve accelerate the train from 0 to 324 km/hr in less than 5 Nnutes? Seperate the acceleration into constant torque and constant power 0. b) How long does it take the train to accelerate from 0 to 324 km/hr with the number of Tesla motors from part a? c) Using Matlab plot the relocity profile as a function of time, Is this a constant acceleration profile? Barrow_forward
- Example find f(t)? -4s F(s)= (s² + 4)²arrow_forwarddraw a kinematic diagramarrow_forwardRigid bodies ENG2016. Full complete solutions need okk don't use guidelines but solve full accurate steps by steps don't use chat gpt or any other ai okkk just solve complete solutions okkk take your time but solve complete solutionsarrow_forward
- Question 6 I need to show all work step by step dynamicsarrow_forwardQu. 3 The automobile is originally at rest s = 0. If it then starts to increase its speed at i = (0.05t2)ft/s?, where t is in seconds, determine the magnitudes of its velocity and acceleration at s = 550 ft. please show all work from dynamics step by step formulaarrow_forwardquestion 5 and 6 from dynamics I need to show all work step by step problemsarrow_forward
- Study Area Document Sharing User Settings Access Pearson mylabmastering.pearson.com P Pearson MyLab and Mastering The crash cushion for a highway barrier consists of a nest of barrels filled with an impact-absorbing material. The barrier stopping force is measured versus the vehicle penetration into the barrier. (Figure 1) Part A P Course Home b My Questions | bartleby Review Determine the distance a car having a weight of 4000 lb will penetrate the barrier if it is originally traveling at 55 ft/s when it strikes the first barrel. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 1 of 1 36 μΑ S = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? Next >arrow_forwardWater is the working fluid in an ideal Rankine cycle. Saturated vapor enters the turbine at 12 MPa, and the condenser pressure is 8 kPa. The mass flow rate of steam entering the turbine is 50 kg/s. Determine: (a) the net power developed, in kW. (b) the rate of heat transfer to the steam passing through the boiler, in kW. (c) the percent thermal efficiency. (d) the mass flow rate of condenser cooling water, in kg/s, if the cooling water undergoes a temperature increase of 18°C with negligible pressure change in passing through the condenser.arrow_forward4. The figure below shows a bent pipe with the external loading FA 228 lb, and M₁ = M₂ = 1 kip-ft. The force Fernal loading FA = 300 lb, FB: parallel to the y-axis, and and yc = 60°. = 125 lb, Fc = acts parallel to the x-z plane, the force FB acts Cartesian resultan Coordinate direction angles of Fc are ac = 120°, ẞc = 45°, a. Compute the resultant force vector of the given external loading and express it in EST form. b. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the origin, O, and express it in Cartesian vector form. Use the vector method while computing the moments of forces. c. Compute the resultant moment vector of the given external loading about the line OA and express it in Cartesian vector form. :00 PM EST k ghoufran@buffaternal du 2 ft M₁ A 40° FA M2 C 18 in 1 ft Fc 25 houfran@bald.edu - Feb 19, 3 ft FBarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





