
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.1, Problem 13.14P
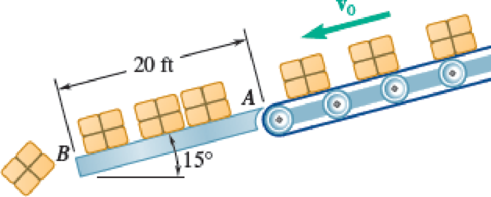
Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a velocity v0 to a fixed incline at A where they slide and eventually fall off at B. Knowing that μk = 0.40, determine the velocity of the conveyor belt if the boxes are to have zero velocity at B.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.
The tensile 0.2 percent offset yield strength of AISI 1137 cold-drawn steel bars up to 1 inch in diameter from 2 mills and 25 heats is
reported as follows:
Sy 93
95
101
f
97 99
107 109 111
19 25 38 17 12 10 5 4
103
105
4
2
where Sy is the class midpoint in kpsi and fis the number in each class.
Presuming the distribution is normal, determine the yield strength exceeded by 99.0% of the population.
The yield strength exceeded by 99.0% of the population is
kpsi.
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 13.1 - Block A is traveling with a speed v0 on a smooth...Ch. 13.1 - A 400-kg satellite is placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.2PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.3PCh. 13.1 - A 500-kg communications satellite is in a circular...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.5PCh. 13.1 - 13.6 In an ore-mixing operation, a bucket full of...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.7PCh. 13.1 - A 2000-kg automobile starts from rest at point A...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.9P
Ch. 13.1 - A 1.4-kg model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 13.1 - Packages are thrown down an incline at A with a...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.12PCh. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - A 1200-kg trailer is hitched to a 1400-kg car. The...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.16PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.17PCh. 13.1 - The subway train shown is traveling at a speed of...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.19PCh. 13.1 - The system shown is at rest when a constant 30-lb...Ch. 13.1 - Car B is towing car A at a constant speed of 10...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.22PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.23PCh. 13.1 - Two blocks A and B, of mass 4 kg and 5 kg,...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.25PCh. 13.1 - A 3-kg block rests on top of a 2-kg block...Ch. 13.1 - Solve Prob. 13.26, assuming that the 2-kg block is...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.28PCh. 13.1 - A 7.5-lb collar is released from rest in the...Ch. 13.1 - A 10-kg block is attached to spring A and...Ch. 13.1 - A 5-kg collar A is at rest on top of, but not...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.32PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.33PCh. 13.1 - Two types of energy-absorbing fenders designed to...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.35PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.36PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.37PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.38PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.39PCh. 13.1 - The sphere at A is given a downward velocity v0...Ch. 13.1 - A bag is gently pushed off the top of a wall at A...Ch. 13.1 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.1 - In Prob. 13.42, determine the range of values of h...Ch. 13.1 - A small block slides at a speed v on a horizontal...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.45PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.46PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.47PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.48PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.49PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.50PCh. 13.1 - A 1400-kg automobile starts from rest and travels...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.52PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.53PCh. 13.1 - The elevator E has a weight of 6600 lb when fully...Ch. 13.2 - Two small balls A and B with masses 2m and m,...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.3CQCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.55PCh. 13.2 - A loaded railroad car of mass m is rolling at a...Ch. 13.2 - A 750-g collar can slide along the horizontal rod...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.58PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.59PCh. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction on the...Ch. 13.2 - For the adapted shuffleboard device in Prob 13.28,...Ch. 13.2 - An elastic cable is to be designed for bungee...Ch. 13.2 - It is shown in mechanics of materials that the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.64PCh. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction along...Ch. 13.2 - A thin circular rod is supported in a vertical...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.67PCh. 13.2 - A spring is used to stop a 50-kg package that is...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.69PCh. 13.2 - 13.70 A section of track for a roller coaster...Ch. 13.2 - 13.71 A section of track for a roller coaster...Ch. 13.2 - A 1-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - A 10-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.74PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.75PCh. 13.2 - A small package of weight W is projected into a...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.77PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.78PCh. 13.2 - Prove that a force F(x, y, z) is conservative if,...Ch. 13.2 - The force F = (yzi + zxj + xyk)/xyz acts on the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.81PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.82PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.83PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.84PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.85PCh. 13.2 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit of minimum...Ch. 13.2 - While describing a circular orbit 200 mi above the...Ch. 13.2 - How much energy per pound should be imparted to a...Ch. 13.2 - Knowing that the velocity of an experimental space...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.90PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.91PCh. 13.2 - (a) Show that, by setting r = R + y in the...Ch. 13.2 - Collar A has a mass of 3 kg and is attached to a...Ch. 13.2 - Collar A has a mass of 3 kg and is attached to a...Ch. 13.2 - A governor is designed so that the valve of...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.5-lb ball that can slide on a horizontal...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.5-lb ball that can slide on a horizontal...Ch. 13.2 - Using the principles of conservation of energy and...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.99PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft is describing an elliptic orbit of...Ch. 13.2 - While describing a circular orbit, 185 mi above...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.102PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.103PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.104PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.105PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.106PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.107PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.108PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.109PCh. 13.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit at an...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.111PCh. 13.2 - Show that the values vA and vP of the speed of an...Ch. 13.2 - Show that the total energy E of an earth satellite...Ch. 13.2 - A space probe describes a circular orbit of radius...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.115PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft of mass m describes a circular orbit...Ch. 13.2 - Using the answers obtained in Prob. 13.108, show...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.118PCh. 13.3 - A large insect impacts the front windshield of a...Ch. 13.3 - The expected damages associated with two types of...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.1IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.2IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.3IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.4IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.5IMDCh. 13.3 - A 35 000-Mg ocean liner has an initial velocity of...Ch. 13.3 - A 2500-lb automobile is moving at a speed of 60...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.121PCh. 13.3 - A truck is hauling a 300-kg log out of a ditch...Ch. 13.3 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 13.3 - Steep safety ramps are built beside mountain...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.125PCh. 13.3 - The 18 000-kg F-35B uses thrust vectoring to allow...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.127PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.128PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.129PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.130PCh. 13.3 - A tractor-trailer rig with a 2000-kg tractor, a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.132PCh. 13.3 - An 8-kg cylinder C rests on a 4-kg platform A...Ch. 13.3 - An estimate of the expected load on...Ch. 13.3 - A 60-g model rocket is fired vertically. The...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.136PCh. 13.3 - A crash test is performed between an SUV A and a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.138PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.139PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.140PCh. 13.3 - The triple jump is a track-and-field event in...Ch. 13.3 - The last segment of the triple jump...Ch. 13.3 - The design for a new cementless hip implant is to...Ch. 13.3 - A 28-g steel-jacketed bullet is fired with a...Ch. 13.3 - 13.145 A 25-ton railroad car moving at 2.5 mi/h is...Ch. 13.3 - At an intersection, car B was traveling south and...Ch. 13.3 - The 650-kg hammer of a drop-hammer pile driver...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.148PCh. 13.3 - Bullet B weighs 0.5 oz and blocks A and C both...Ch. 13.3 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand at opposite...Ch. 13.3 - A 75-g ball is projected from a height of 1.6 m...Ch. 13.3 - A ballistic pendulum is used to measure the speed...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.153PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.154PCh. 13.4 - A 5-kg ball A strikes a 1-kg ball B that is...Ch. 13.4 - A sphere with a speed v0 rebounds after striking a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.7IMDCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.8IMDCh. 13.4 - A 10-kg ball A moving horizontally at 12 m/s...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.10IMDCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.155PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.156PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.157PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.158PCh. 13.4 - To apply shock loading to an artillery shell, a...Ch. 13.4 - Packages in an automobile parts supply house are...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.161PCh. 13.4 - At an amusement park, there are 200-kg bumper cars...Ch. 13.4 - At an amusement park there are 200-kg bumper cars...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.164PCh. 13.4 - 13.165 Two identical pool balls with a 2.37-in....Ch. 13.4 - A 600-g ball A is moving with a velocity of...Ch. 13.4 - Two identical hockey pucks are moving on a hockey...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.168PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.169PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.170PCh. 13.4 - A girl throws a ball at an inclined wall from a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.172PCh. 13.4 - From experimental tests, smaller boulders tend to...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.174PCh. 13.4 - A 1-kg block B is moving with a velocity v0 of...Ch. 13.4 - A 0.25-lb ball thrown with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 13.4 - After having been pushed by an airline employee,...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.178PCh. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y = 2 m...Ch. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y = 3 m...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.181PCh. 13.4 - Block A is released from rest and slides down the...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.183PCh. 13.4 - A test machine that kicks soccer balls has a 5-lb...Ch. 13.4 - Ball B is hanging from an inextensible cord. An...Ch. 13.4 - A 70-g ball B dropped from a height h0 = 1.5 m...Ch. 13.4 - A 2-kg sphere moving to the right with a velocity...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of = 30, the 1-lb...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of = 30, the 1-kg...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.190RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.191RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.192RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.193RPCh. 13 - 13.194 A 50-lb sphere A with a radius of 4.5 in....Ch. 13 - A 300-g block is released from rest after a spring...Ch. 13 - A kicking-simulation attachment goes on the front...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.197RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.198RPCh. 13 - A 2-kg ball B is traveling horizontally at 10 m/s...Ch. 13 - A 2-kg block A is pushed up against a spring...Ch. 13 - The 2-lb ball at A is suspended by an inextensible...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I tried to go through this problem but I don't know what I'm doing wrong can you help me?arrow_forwardGenerate the kinematic diagram of the following mechanisms using the given symbols. Then, draw their graphs and calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. !!!arrow_forwardCreate a schematic representation of the following mechanisms using the given symbols and draw their graphs. Then, calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7.arrow_forward
- how the kinematic diagram of the following mechanisms would be represented using the given symbols? PUNTO 0. PUNTO 1. °arrow_forwardCreate a schematic representation of the following mechanisms using the given symbols and draw their graphs. Then, calculate their degrees of freedom (DOF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 4. PUNTO 5. (0) Groundarrow_forwardDraw the graph of ALL the mechanisms and calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 0. PUNTO 1.arrow_forward
- An adjustable support. Construction designed to carry vertical load and is adjusted by moving the blue attachment vertically. The link is articulated at both ends (free to rotate) and can therefore only transmit power axially. Analytically calculate the force to which the link is subjected? Calculate analytically rated voltage in the middle of the link.? F=20kN Alpha 30 deg Rel 225 Mpans:5arrow_forwardA swivel crane where the load is moved axially along the beam through the wagon to which the hook is attached. Round bar with a diameter of ∅30 mm. The support beam is articulated at both ends (free to rotate) and can therefore only transmit force axially. Calculate reaction force in the x-direction at point A? Calculate analytical reaction force in the y-direction of point A? Calculate nominal stress in the middle of the support beam?Lengt 5 mAlfa 25 degX=1.5mIPE300-steelmass:1000 kgarrow_forwardgot wrong answers help pleasearrow_forward
- A crate weighs 530 lb and is hung by three ropes attached to a steel ring at A such that the top surface is parallel to the xy plane. Point A is located at a height of h = 42 in above the top of the crate directly over the geometric center of the top surface. Use the dimensions given in the table below to determine the tension in each of the three ropes. 2013 Michael Swanbom cc00 BY NC SA ↑ Z C b B У a D Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 30 in b 43 in 4.5 in The tension in rope AB is 383 x lb The tension in rope AC is 156 x lb The tension in rope AD is 156 x lbarrow_forwardA block of mass m hangs from the end of bar AB that is 7.2 meters long and connected to the wall in the xz plane. The bar is supported at A by a ball joint such that it carries only a compressive force along its axis. The bar is supported at end B by cables BD and BC that connect to the xz plane at points C and D respectively with coordinates given in the figure. Cable BD is elastic and can be modeled as a linear spring with a spring constant k = 400 N/m and unstretched length of 6.34 meters. Determine the mass m, the compressive force in beam AB and the tension force in cable BC. Z C D (c, 0, d) (a, 0, b) A B y f m cc 10 BY NC SA 2016 Eric Davishahl x Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 8.1 m b 3.3 m с 2.7 m d 3.9 m e 2 m f 5.4 m The mass of the block is 68.8 The compressive force in bar AB is 364 × kg. × N. The tension in cable BC is 393 × N.arrow_forwardThe airplane weighs 144100 lbs and flies at constant speed and trajectory given by 0 on the figure. The plane experiences a drag force of 73620 lbs. 0 a.) If 11.3°, determine the thrust and lift forces = required to maintain this speed and trajectory. b.) Next consider the case where is unknown, but it is known that the lift force is equal to 7.8 times the quantity (Fthrust Fdrag). Compute the resulting trajectory angle and the lift force in this case. Use the same values for the weight and drag forces as you used for part a. 20. YAAY' Farag Ө Fthrust CC + BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbom Flift Fweight The lift force acts in the y' direction. The weight acts in the negative y direction. The thrust and drag forces act in the positive and negative x' directions respectively. Part (a) The thrust force is equal to 101,855 ☑ lbs. The lift force is equal to 141,282 ☑ lbs. Part (b) The trajectory angle 0 is equal to 7.31 ✓ deg. The lift force is equal to 143,005 ☑ lbs.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY