
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13.4, Problem 13.6IMD
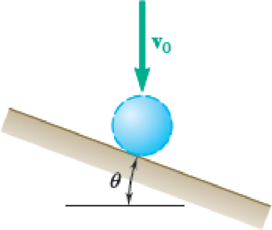
A sphere with a speed v0 rebounds after striking a frictionless inclined plane as shown. Draw the impulse–momentum diagram that can be used to find the velocity of the sphere after the impact.
Fig. P13.F6
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
My answers are incorrect
Picture
What is the weight of a 5-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s², kgf, Ibm-ft/s², and lbf?
The weight of a 5-kg substance in N is 49.05
N.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kN is
KN.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kg·m/s² is 49.05
kg-m/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kgf is 5.0 kgf.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in Ibm-ft/s² is 11.02 lbm-ft/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in lbf is 11.023
lbf.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 13.1 - Block A is traveling with a speed v0 on a smooth...Ch. 13.1 - A 400-kg satellite is placed in a circular orbit...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.2PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.3PCh. 13.1 - A 500-kg communications satellite is in a circular...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.5PCh. 13.1 - 13.6 In an ore-mixing operation, a bucket full of...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.7PCh. 13.1 - A 2000-kg automobile starts from rest at point A...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.9P
Ch. 13.1 - A 1.4-kg model rocket is launched vertically from...Ch. 13.1 - Packages are thrown down an incline at A with a...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.12PCh. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - Boxes are transported by a conveyor belt with a...Ch. 13.1 - A 1200-kg trailer is hitched to a 1400-kg car. The...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.16PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.17PCh. 13.1 - The subway train shown is traveling at a speed of...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.19PCh. 13.1 - The system shown is at rest when a constant 30-lb...Ch. 13.1 - Car B is towing car A at a constant speed of 10...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.22PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.23PCh. 13.1 - Two blocks A and B, of mass 4 kg and 5 kg,...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.25PCh. 13.1 - A 3-kg block rests on top of a 2-kg block...Ch. 13.1 - Solve Prob. 13.26, assuming that the 2-kg block is...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.28PCh. 13.1 - A 7.5-lb collar is released from rest in the...Ch. 13.1 - A 10-kg block is attached to spring A and...Ch. 13.1 - A 5-kg collar A is at rest on top of, but not...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.32PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.33PCh. 13.1 - Two types of energy-absorbing fenders designed to...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.35PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.36PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.37PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.38PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.39PCh. 13.1 - The sphere at A is given a downward velocity v0...Ch. 13.1 - A bag is gently pushed off the top of a wall at A...Ch. 13.1 - A roller coaster starts from rest at A, rolls down...Ch. 13.1 - In Prob. 13.42, determine the range of values of h...Ch. 13.1 - A small block slides at a speed v on a horizontal...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.45PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.46PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.47PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.48PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.49PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.50PCh. 13.1 - A 1400-kg automobile starts from rest and travels...Ch. 13.1 - Prob. 13.52PCh. 13.1 - Prob. 13.53PCh. 13.1 - The elevator E has a weight of 6600 lb when fully...Ch. 13.2 - Two small balls A and B with masses 2m and m,...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.3CQCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.55PCh. 13.2 - A loaded railroad car of mass m is rolling at a...Ch. 13.2 - A 750-g collar can slide along the horizontal rod...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.58PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.59PCh. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction on the...Ch. 13.2 - For the adapted shuffleboard device in Prob 13.28,...Ch. 13.2 - An elastic cable is to be designed for bungee...Ch. 13.2 - It is shown in mechanics of materials that the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.64PCh. 13.2 - A 500-g collar can slide without friction along...Ch. 13.2 - A thin circular rod is supported in a vertical...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.67PCh. 13.2 - A spring is used to stop a 50-kg package that is...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.69PCh. 13.2 - 13.70 A section of track for a roller coaster...Ch. 13.2 - 13.71 A section of track for a roller coaster...Ch. 13.2 - A 1-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - A 10-lb collar is attached to a spring and slides...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.74PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.75PCh. 13.2 - A small package of weight W is projected into a...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.77PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.78PCh. 13.2 - Prove that a force F(x, y, z) is conservative if,...Ch. 13.2 - The force F = (yzi + zxj + xyk)/xyz acts on the...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.81PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.82PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.83PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.84PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.85PCh. 13.2 - A satellite describes an elliptic orbit of minimum...Ch. 13.2 - While describing a circular orbit 200 mi above the...Ch. 13.2 - How much energy per pound should be imparted to a...Ch. 13.2 - Knowing that the velocity of an experimental space...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.90PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.91PCh. 13.2 - (a) Show that, by setting r = R + y in the...Ch. 13.2 - Collar A has a mass of 3 kg and is attached to a...Ch. 13.2 - Collar A has a mass of 3 kg and is attached to a...Ch. 13.2 - A governor is designed so that the valve of...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.5-lb ball that can slide on a horizontal...Ch. 13.2 - A 1.5-lb ball that can slide on a horizontal...Ch. 13.2 - Using the principles of conservation of energy and...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.99PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft is describing an elliptic orbit of...Ch. 13.2 - While describing a circular orbit, 185 mi above...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.102PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.103PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.104PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.105PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.106PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.107PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.108PCh. 13.2 - Prob. 13.109PCh. 13.2 - A space vehicle is in a circular orbit at an...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.111PCh. 13.2 - Show that the values vA and vP of the speed of an...Ch. 13.2 - Show that the total energy E of an earth satellite...Ch. 13.2 - A space probe describes a circular orbit of radius...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.115PCh. 13.2 - A spacecraft of mass m describes a circular orbit...Ch. 13.2 - Using the answers obtained in Prob. 13.108, show...Ch. 13.2 - Prob. 13.118PCh. 13.3 - A large insect impacts the front windshield of a...Ch. 13.3 - The expected damages associated with two types of...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.1IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.2IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.3IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.4IMDCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.5IMDCh. 13.3 - A 35 000-Mg ocean liner has an initial velocity of...Ch. 13.3 - A 2500-lb automobile is moving at a speed of 60...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.121PCh. 13.3 - A truck is hauling a 300-kg log out of a ditch...Ch. 13.3 - The coefficients of friction between the load and...Ch. 13.3 - Steep safety ramps are built beside mountain...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.125PCh. 13.3 - The 18 000-kg F-35B uses thrust vectoring to allow...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.127PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.128PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.129PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.130PCh. 13.3 - A tractor-trailer rig with a 2000-kg tractor, a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.132PCh. 13.3 - An 8-kg cylinder C rests on a 4-kg platform A...Ch. 13.3 - An estimate of the expected load on...Ch. 13.3 - A 60-g model rocket is fired vertically. The...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.136PCh. 13.3 - A crash test is performed between an SUV A and a...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.138PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.139PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.140PCh. 13.3 - The triple jump is a track-and-field event in...Ch. 13.3 - The last segment of the triple jump...Ch. 13.3 - The design for a new cementless hip implant is to...Ch. 13.3 - A 28-g steel-jacketed bullet is fired with a...Ch. 13.3 - 13.145 A 25-ton railroad car moving at 2.5 mi/h is...Ch. 13.3 - At an intersection, car B was traveling south and...Ch. 13.3 - The 650-kg hammer of a drop-hammer pile driver...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.148PCh. 13.3 - Bullet B weighs 0.5 oz and blocks A and C both...Ch. 13.3 - A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand at opposite...Ch. 13.3 - A 75-g ball is projected from a height of 1.6 m...Ch. 13.3 - A ballistic pendulum is used to measure the speed...Ch. 13.3 - Prob. 13.153PCh. 13.3 - Prob. 13.154PCh. 13.4 - A 5-kg ball A strikes a 1-kg ball B that is...Ch. 13.4 - A sphere with a speed v0 rebounds after striking a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.7IMDCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.8IMDCh. 13.4 - A 10-kg ball A moving horizontally at 12 m/s...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.10IMDCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.155PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.156PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.157PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.158PCh. 13.4 - To apply shock loading to an artillery shell, a...Ch. 13.4 - Packages in an automobile parts supply house are...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.161PCh. 13.4 - At an amusement park, there are 200-kg bumper cars...Ch. 13.4 - At an amusement park there are 200-kg bumper cars...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.164PCh. 13.4 - 13.165 Two identical pool balls with a 2.37-in....Ch. 13.4 - A 600-g ball A is moving with a velocity of...Ch. 13.4 - Two identical hockey pucks are moving on a hockey...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.168PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.169PCh. 13.4 - Prob. 13.170PCh. 13.4 - A girl throws a ball at an inclined wall from a...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.172PCh. 13.4 - From experimental tests, smaller boulders tend to...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.174PCh. 13.4 - A 1-kg block B is moving with a velocity v0 of...Ch. 13.4 - A 0.25-lb ball thrown with a horizontal velocity...Ch. 13.4 - After having been pushed by an airline employee,...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.178PCh. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y = 2 m...Ch. 13.4 - A 5-kg sphere is dropped from a height of y = 3 m...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.181PCh. 13.4 - Block A is released from rest and slides down the...Ch. 13.4 - Prob. 13.183PCh. 13.4 - A test machine that kicks soccer balls has a 5-lb...Ch. 13.4 - Ball B is hanging from an inextensible cord. An...Ch. 13.4 - A 70-g ball B dropped from a height h0 = 1.5 m...Ch. 13.4 - A 2-kg sphere moving to the right with a velocity...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of = 30, the 1-lb...Ch. 13.4 - When the rope is at an angle of = 30, the 1-kg...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.190RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.191RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.192RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.193RPCh. 13 - 13.194 A 50-lb sphere A with a radius of 4.5 in....Ch. 13 - A 300-g block is released from rest after a spring...Ch. 13 - A kicking-simulation attachment goes on the front...Ch. 13 - Prob. 13.197RPCh. 13 - Prob. 13.198RPCh. 13 - A 2-kg ball B is traveling horizontally at 10 m/s...Ch. 13 - A 2-kg block A is pushed up against a spring...Ch. 13 - The 2-lb ball at A is suspended by an inextensible...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mych CD 36280 kg. 0.36 givens Tesla truck frailer 2017 Model Vven 96154kph ronge 804,5km Cr Powertrain Across PHVAC rwheel 0.006 0.88 9M² 2 2kW 0.55M ng Zg Prated Trated Pair 20 0.95 1080 kW 1760 Nm 1,2 determine the battery energy required to meet the range when fully loaded determine the approximate time for the fully-loaded truck-trailor to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph while Ignoring vehicle load forcesarrow_forward12-217. The block B is sus- pended from a cable that is at- tached to the block at E, wraps around three pulleys, and is tied to the back of a truck. If the truck starts from rest when ID is zero, and moves forward with a constant acceleration of ap = 0.5 m/s², determine the speed of the block at D the instant x = 2 m. Neglect the size of the pulleys in the calcu- lation. When xƊ = 0, yc = 5 m, so that points C and D are at the Prob. 12-217 5 m yc =2M Xparrow_forwardsolve both and show matlab code auto controlsarrow_forward
- 12-82. The roller coaster car trav- els down the helical path at con- stant speed such that the paramet- ric equations that define its posi- tion are x = c sin kt, y = c cos kt, z = h - bt, where c, h, and b are constants. Determine the mag- nitudes of its velocity and accelera- tion. Prob. 12-82 Narrow_forwardGiven: = refueling Powertran SOURCE EMISSIONS vehide eff eff gasoline 266g co₂/kwh- HEV 0.90 0.285 FLgrid 411ilg Co₂/kWh 41111gCo₂/kWh EV 0.85 0.80 Production 11x10% og CO₂ 13.7 x 10°g CO₂ A) Calculate the breakeven pont (in km driven) for a EV against on HEV in Florida of 0.1kWh/kM Use a drive cycle conversion 5) How efficient would the powertrain of the HEV in this example have to be to break even with an EV in Florida after 150,000 Miles of service (240,000) km Is it plausible to achieve the answer from pert b Consideans the HaXINERY theoretical efficiency of the Carnot cycle is 5020 and there are additional losses of the transMISSION :- 90% efficiency ? c A what do you conclude is the leading factor in why EVs are less emissive than ICE,arrow_forwardsolve autocontrolsarrow_forward
- Problem 3.21P: Air at 100F(38C) db,65F(18C) wb, and sea-level pressure is humidified adiabatically with steam. The steam supplied contains 20 percent moisture(quality of 0.80) at 14.7psia(101.3kpa). The air is humidified to 60 percent relative humidity. Find the dry bulb temperature of the humidified air using (a)chart 1a or 1b and (b) the program PSYCH.arrow_forwardPUNTO 4. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 5. Groundarrow_forwardPUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. III IAarrow_forward
- calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7. (Ctrl)arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.given that: summation of K gate valve = 0.25check valve=390 degree elbow= 0.75foot valve= 0.78arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY