
Concept explainers
A 7.5-lb collar is released from rest in the position shown, slides down the inclined rod, and compresses the spring. The direction of motion is reversed and the collar slides up the rod. Knowing that the maximum deflection of the spring is 5 in., determine (a) the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and the rod, (b) the maximum speed of the collar.
Fig. P13.29
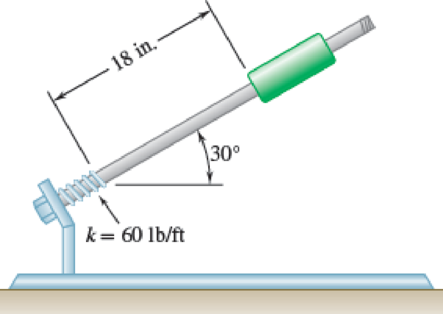
(a)
Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
Answer to Problem 13.29P
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the collar
The maximum deflection of the spring (x) is
The distance between the spring and collar (d) is
The spring constant (k) is
The angle of the inclined rod
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the inclined rod with the forces acting as in Figure (1).
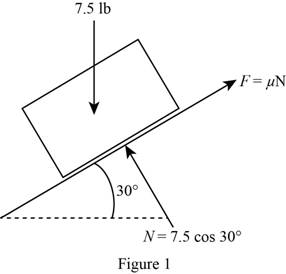
Here, the initial kinetic energy
Calculate the work done
Here, F is the frictional force.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Substitute
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the coefficient of kinetic friction between the collar and rod
(b)
Find the maximum speed
Answer to Problem 13.29P
The maximum speed
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The weight of the collar
The maximum deflection of the spring (x) is
The distance between the spring and collar (d) is
The spring constant (k) is
The angle of the inclined rod
Assume the acceleration due to gravity (g) is
Calculation:
Calculate the kinetic energy
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Here, F is the frictional force.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Calculate the work done
Substitute
Calculate the total work done
Substitute
Substitute 0.159 for
Use work and energy principle which states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Find the maximum speed
Substitute 0 for
Therefore, the maximum speed
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Steam enters a nozzle at 400°C and 800 kPa with a velocity of 10 m/s and leaves at 375°C and 400 kPa while losing heat at a rate of 26.5 kW. For an inlet area of 800 cm2, determine the velocity and the volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit. Use steam tables. At the left side of the lines, 800 kilo Pascal, 400 degree Centigrade, 10 meters per second are shown. At the right side of the lines, 400 kilo Pascal, 375 degree Centigrade are shown. The velocity of the steam at the nozzle exit is m/s. The volume flow rate of the steam at the nozzle exit is m3/s.arrow_forwardA saturated liquid–vapor mixture of water, called wet steam, in a steam line at 1450 kPa is throttled to 50 kPa and 100°C. What is the quality in the steam line? Use data from the steam tables. Above the right side of the tube, 50 kilos 100 degree Centigrade indicated. The quality in the steam line is .arrow_forwardI tried this problems a couple of ways but I don't know what I'm doing wrong can you help me please?arrow_forward
- Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor at 180 kPa as a saturated vapor with a flow rate of 0.35 m3/min and leaves at 900 kPa. The power supplied to the refrigerant during the compression process is 2.35 kW. What is the temperature of R-134a at the exit of the compressor? The temperature of R-134a at the exit of the compressor is °C.arrow_forwardAir enters the compressor of a gas-turbine plant at ambient conditions of 100 kPa and 25°C with a low velocity and exits at 1 MPa and 347°C with a velocity of 90 m/s. The compressor is cooled at a rate of 1500 kJ/min, and the power input to the compressor is 250 kW. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the compressor. The inlet and exit enthalpies of air are 298.2 kJ/kg and 628.07 kJ/kg. The mass flow rate of air is kg/s.arrow_forwardConsider a 1000-W iron whose base plate is made of 0.5-cm-thick aluminum alloy 2024-T6 (ρ = 2770 kg/m3 and cp = 875 J/kg·°C). The base plate has a surface area of 0.03 m2. Initially, the iron is in thermal equilibrium with the ambient air at 22°C. Assuming 90 percent of the heat generated in the resistance wires is transferred to the plate, determine the minimum time needed for the plate temperature to reach 240°C. The minimum time needed for the plate temperature to reach 240°C is s.arrow_forward
- A desktop computer is to be cooled by a fan whose flow rate is 0.34 m3/min. Determine the mass flow rate of air through the fan at an elevation of 3400 m where the air density is 0.7 kg/m3. Also, if the average velocity of air is not to exceed 123 m/min, determine the diameter of the casing of the fan. The mass flow rate of air through the fan is kg/min. The diameter of the casing of the fan is cm.arrow_forwardThe diffuser in a jet engine is designed to decrease the kinetic energy of the air entering the engine compressor without any work or heat interactions. Calculate the velocity at the exit of a diffuser when air at 100 kPa and 30°C enters it with a velocity of 359 m/s and the exit state is 200 kPa and 90°C. The specific heat of air at the average temperature of 60°C = 333 K is cp = 1.007 kJ/kg·K. The velocity at the exit is m/sarrow_forwardA piston–cylinder device contains 3 kg of nitrogen initially at 100 kPa and 25°C. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly in a polytropic process during which PV1.3 = constant until the volume is reduced by one-half. Determine the work done and the heat transfer for this process. The gas constant of N2 is R = 0.2968 kPa·m3/kg·K. The cv value of N2 at the anticipated average temperature of 350 K is 0.744 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2b). The work done for this process is kJ. The heat transfer for this process is kJ.arrow_forward
- A 4-m × 5-m × 6-m room is to be heated by a baseboard resistance heater. It is desired that the resistance heater be able to raise the air temperature in the room from 5 to 25°C within 10 min. Assuming no heat losses from the room and an atmospheric pressure of 100 kPa, determine the required power of the resistance heater. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. The properties of air are R = 0.287 kJ/kg·K and cv = 0.718 kJ/kg·K (Table A-2a). The required power of the resistance heater is kW.arrow_forwardI need solve without AI and chatgptarrow_forwardAn ordinary egg can be approximated as a 5.5-cm-diameter sphere. The egg is initially at a uniform temperature of 8°C and is dropped into boiling water at 97°C. Taking the properties of the egg to be ρ = 1020 kg/m3 and cp = 3.32 kJ/kg·°C, determine how much heat is transferred to the egg by the time the average temperature of the egg rises to 82°C. The heat transferred to the egg in this case is kJ.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





