
Concept explainers
13-25 Answer true or false.
(a) Phenols and alcohols have in common the presence of an —OH group.
Phenols are weak acids and react with strong bases to give water-soluble salts.
- The pK„ of phenol is smaller than that of acetic acid.
(f, A characteristic of a chain initiation step is conversion of a nonradical to a radical.
(a)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: Phenols and alcohols have in common the presence of an −OH group,is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
Phenols and alcohols have in common the presence of an −OH group. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The alcohols are represented by a general formula: R-OH. In alcohols, the r is an alkyl group. The phenols are represented by a general formula: R-OH In phenol, the r is an aromatic benzene ring. An example of alcohol is methanol compared to phenol, as shown in the figure below:
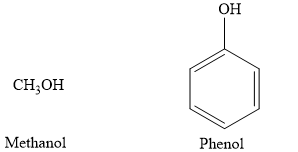
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(b)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: Phenols are weak acids and react with strong bases to give water-soluble salts, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
Phenols are weak acids and react with strong bases to give water-soluble salts. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Phenol is a weak acid. When it reacts with a strong base like sodium hydroxide NaOH, it forms water-soluble salt, or sodium phenoxide. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(c)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: The
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
The
Explanation of Solution
The strength of an acid is measured by the acid dissociation constant Ka.
Consider this reaction.
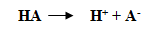
The acid dissociation constant is given by the formula.
The pKa is the logarithmic measurement of the acid dissociation constant. We know that the pKa value for phenol is 10 and for acetic acid is 4.7. Hence, the pKa value of phenol is much greater than the pKa value of acetic acid. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(d)
Interpretation:
To analyse whether the given statement: Autoxidation converts an R-H group to an R-OH group, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
Autoxidation converts an R-H group to an R-OOH group.Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. In auto-oxidation, the r — H group changes to an ROOH group and not to an ROH group. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(e)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement: A carbon radical has only seven electrons in the valence shell of one of its carbons, and this carbon bears a positive charge, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
A carbon radical has only seven electrons in the valence shell of one of its carbons, and this carbon may bear a positive charge or negative charge of no charge.Thus, the statement is false.
Explanation of Solution
Radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons or untilled electrons in their valence shells. A radical may have a positive charge, a negative charge, or no charge. A carbon radical does not carry any charge on it. Therefore, the given statement is false.
(f)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -A characteristic of a chain initiation step is conversion of a nonradical to a radical, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
A characteristic of a chain initiation step is conversion of a nonradical to a radical. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
The characteristic of any chain initiation is the conversion of any non-radical to a radical. In a chain initiation process, hydrogen is converted to a hydrogen radical and carbon is converted to a carbon radical. For Example,
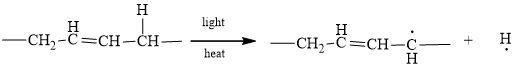
Therefore, the given statement is true.
(g)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -Autoxidation is a radical-chain reaction, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
Autoxidation is a radical-chain reaction. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a diradical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(h)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -A characteristic of the chain propagation step is reaction of a radical and a molecule to form a new radical and a new molecule, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Phenols act as antioxidants. Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants. It takes place in molecules containing carbon-carbon double bonds. Auto oxidation is a radical chain process. It takes place in different steps. In the first step, a non-radical compound changes to a radical form. For example, an oxygen atom is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical. This new radical reacts with another molecule to form a new auto-oxidation product and a carbon radical compound.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
A characteristic of the chain propagation step is reaction of a radical and a molecule to form a new radical and a new molecule. Thus, the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
A chain propagation step takes place in different steps. Autoxidation is an example of a chain propagation reaction. In the first step, a nonradical compound is changed to a radical form. Oxygen is a di-radical. A radical reacts with oxygen to form a new radical, which reacts with another radical and forms a carbon radical and a chain radical. Therefore, the given statement is true.
(i)
Interpretation:
To analyze whether the given statement -Vitamin E and other natural antioxidants function by interrupting the cycle of chain propagation steps that occurs in autoxidation, is true or not.
Concept Introduction:
Phenols are the compounds which have a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to a benzene ring. Phenol is a weak acid and pKa value for phenol is 10. Phenols are oxidized to quinone which is in turn easily reduced to hydroquinone.
Autoxidation is an oxidation reaction that requires only oxygen and no other reactants whereas the substance which inhibits oxidation is known as antioxidant.
Answer to Problem 13.25P
Vitamin E and other natural antioxidants function by interrupting the cycle of chain propagation steps that occurs in autoxidation. Thus the statement is true.
Explanation of Solution
Vitamin E is a stable radical. It breaks the chain propagation steps in auto-oxidation and prevents the formation of destructive hydro peroxides. Therefore, the given statement is true.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Pt + H₂ Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds), Atoms, and Advanced Templ 9 2 0 © 120arrow_forwardComplete boxes in the flow chart. Draw the structure of the organic compound foundin each layer after adding 3M NaOH and extraction. Make sure to include any charges. Provide explanation on answers.arrow_forward== Vid4Q2 Unanswered ☑ Provide IUPAC name of product in the reaction below A 3,4-dimethylcyclohexene B 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane C 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene D 3,4-dimethylcyclohexane H₂ Pdarrow_forward
- 5. Use the MS data to answer the questions on the next page. 14.0 1.4 15.0 8.1 100- MS-IW-5644 26.0 2.8 27.0 6.7 28.0 1.8 29.0 80 4.4 38.0 1.0 39.0 1.5 41.0 1.2 42.0 11.2 43.0 100.0 44.0 4.3 79.0 1.9 80.0 2.6 Relative Intensity 40 81.0 1.9 82.0 2.5 93.0 8.7 20- 95.0 8.2 121.0 2.0 123.0 2.0 136.0 11.8 0 138.0 11.5 20 40 8. 60 a. Br - 0 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 m/z Identify the m/z of the base peak and molecular ion. 2 b. Draw structures for each of the following fragments (include electrons and charges): 43.0, 93.0, 95.0, 136.0, and 138.0 m/z. C. Draw a reasonable a-fragmentation mechanism for the fragmentation of the molecular ion to fragment 43.0 m/z. Be sure to include all electrons and formal charges. 6. Using the values provided in Appendix E of your lab manual, calculate the monoisotopic mass for the pyridinium ion (CsH6N) and show your work.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardStereochemistry: Three possible answers- diastereomers, enantiomers OH CH₂OH I -c=0 21108 1101 41745 HOR CH₂OH IL Но CH₂OH TIL a. Compounds I and III have this relationship with each other: enantiomers b. Compounds II and IV have this relationship with each other: c. Compounds I and II have this relationship with each other: d. *Draw one structure that is a stereoisomer of II, but neither a diastereomer nor an enantiomer. (more than one correct answer)arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

