
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: To identify the number of steps in glycolysis that produce ATP.
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:
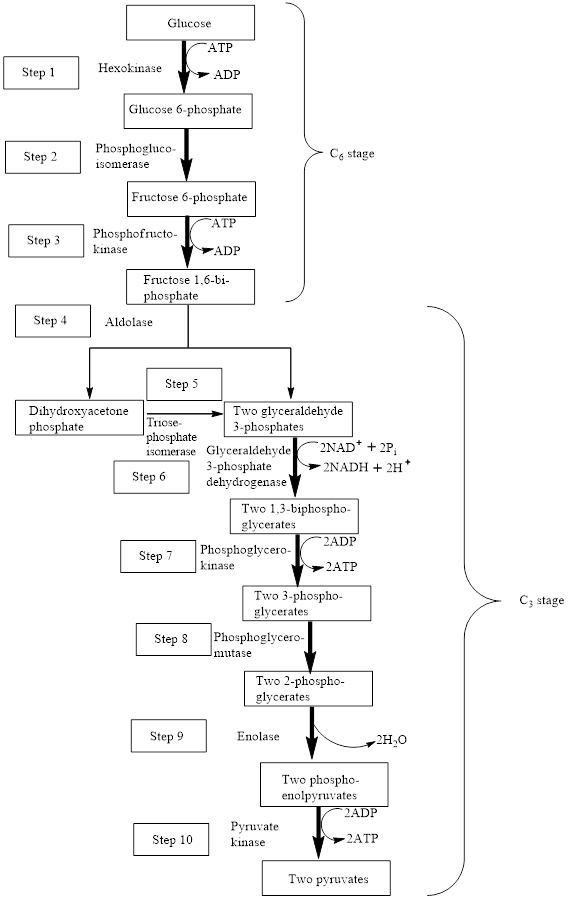
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that is defined as the energy currency of life and provides energy to carry out the metabolic processes in the living cells. It is converted either to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) or to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) after the consumption in the metabolic processes.
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.17EP
In glycolysis, two steps produce ATP.
Explanation of Solution
In step 7 and step 10, two ATP molecules are produced in each step. Hence, in the glycolysis pathway, four ATP molecules are produced is two steps.
(b)
Interpretation: To identify the number of steps in glycolysis that involve phosphorylation.
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:

In the phosphorylation reaction, the molecule is attached to the phosphoryl group. The transfer of a phosphoryl group
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.17EP
Phosphorylation is involved in five steps.
Explanation of Solution
The first step in the glycolysis process is the phosphorylation of glucose using ATP. Glucose is converted to
In the third step,
In step 6,
Therefore, step 6 proceeds through the oxidation and phosphorylation reaction using
The seventh step in the glycolysis process is the phosphorylation of
Step 10 is the final step of the glycolysis process. In step 10, phosphoenolpyruvate is converted to pyruvate using ADP, thus, ADP is converted to ATP. Pyruvate kinase enzymes are involved in this reaction. The type of reaction is phosphorylation. The word equation for the phosphorylation reaction is as follows:
Therefore, step 1, step 2, step 6, step 7 and step 10 involved the phosphorylation reaction.
(c)
Interpretation: To identify the number of steps in glycolysis that involve
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:

A reactant is defined as the substance that is initially present in the
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is associated with the
(c)
Answer to Problem 13.17EP
One step involves
Explanation of Solution
In step 6,
Therefore,
(d)
Interpretation: To identify the number of steps in glycolysis that involve a compound with a high-energy bond as a reactant.
Concept introduction: In the glycolysis metabolic pathway, a glucose molecule breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. Two ATP molecules and NADH coenzymes are produced along with pyruvate.
The block diagram to represent an overview of glycolysis is as follows:

A reactant is defined as the substance that is initially present in the chemical reaction and gets consumed to form a new substance.
High energy compounds are those compounds that release a large amount of energy upon hydrolysis. These compounds consist of highly strained bonds that are responsible for the release of a high amount of energy. The compounds containing a phosphate group are examples of high energy compounds.
A high-energy phosphate group is formed when a phosphate group is attached to a carbon atom participating in carbon-oxygen or carbon-carbon double bond.
(d)
Answer to Problem 13.17EP
Two steps involve a compound with a high-energy bond as a reactant.
Explanation of Solution
The seventh step in the glycolysis process is the phosphorylation of

Here,  denotes the
denotes the
In step 10, phosphoenolpyruvate is converted to pyruvate using ADP, thus, ADP is converted to ATP. Pyruvate kinase enzymes are involved in this reaction. Phosphoenolpyruvate is a compound with a high-energy phosphate group because the phosphate group is attached to that carbon atom which is involved in carbon-carbon double bond. The chemical reaction is as follows:

Therefore, in step 10, a high-energy bond is encountered as a reactant.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Give the organic product: O A O B Ос ○ D -NH–CH3 + CH3 CH3 NEN C ? A CH3 CH3 NH- CH3 B CH3 CH3 N=N- C CH3 CH3 N=NNH CH3 D CH3 N=N CH3 NHCH3 LNH CHOarrow_forwardFinish the reaction- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic products: (benzyne) Br ? CH3 + K* :NH, liq NH3 HINT: Two products are formed. Each is a substituted aniline; they are isomers of each other. NH2 II I H₂N. CH3 CH3 III Select one: ○ A. I and II ○ B. I and III O C. I and IV O D. II and III O E. III and IV H₂N CH3 IV CH₂-NH2arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Erase something Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terarrow_forwardQ14. Fill this chart: (please refer to ppt notes/browser to answer these questions) What alcohol is also called wood alcohol? What is the common name of ethanol? Draw the structure of phenol and thiophene? Are bigger chain alcohol like heptanol and octanol are soluble or insoluble in water and explain it ? Are ethers soluble or insoluble in water? What suffix and prefix are used for alcohol while naming alcohol and ether? What the process called when we add water to any alkene to make alcohol? Q16. Draw the diagram of following aromatic compound (practice from previous module) Aniline Phenol Benzoic acid Methyl benzoate Q17. a. Write the oxidation reactions for the 2 propanol. b. Write the oxidation reaction of the ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 11 of 18 (1 point) Question Attempt: 3 of How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box…arrow_forward
- Organic Chemistry Esterification reactions 1. Write the steps to prepare ester. 2. Write complete reaction of ethanol and acetic acid to make ester. 3. What does ester smell like? What are the uses of ester. 4. What the role of sulfuric acid in the esterification reactionarrow_forward11. Complete the following esterification reaction with names of all the reactants and products under. Hint: Remove the water and end up with ester R-C-OH + ROH R-C-OR + H₂O A carboxylic acid An alcohol An ester Water BYJU'S H-C-C O-H Нин C-C-C-H HAAA H O-C-C-C-H AAA Ethanoic acid Propanol Water Propyl ethanoate By com CH3COOH + CH3CH2CH2CH₂CH₂OH → Practice for alcohols aldehydes and ketones: 12. Draw the structures from the following names mixed of alcohol/aldehyde and ketone: a. 4-methyl cyclohexanone b. 3-methyl-2-pentenal c. 2,3-dimethylcyclohexanone d. 1,3propanediol or Propane 1,3 diol 13. Write systematic names for the following compounds identify functional group: a. b. (CH3)2CH-C OH c) CH(CH₂)-- OH -,-,arrow_forwardmay you please show all steps! i am having a hard time understanding and applying in this format, thank you!arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





