
A hypothetical reaction has the two-step mechanism
The potential-energy curve for the reaction is
- a Write the chemical formulas of the reactants, products, and the reaction intermediate on the potential energy curve.
- b From the mechanism, what is the overall reaction?
- c What is the rate-limiting step for the reaction?
- d Propose a rate law based on the rate-limiting step.
- e Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
(a)
Interpretation:
The explanations for the given set have to be answered.
Concept Introduction:
The rate of reaction is the quantity of formation of product or the quantity of reactant used per unit time. The rate of reaction doesn’t depend on the sum of amount of reaction mixture used.
The raise in molar concentration of product of a reaction per unit time or decrease in molarity of reactant per unit time is called rate of reaction and is expressed in units of
The variation in concentration of reaction or product over a certain interval of time is called average reaction rate.
The equation that relates the reaction rate to the reactants concentrations that is raised to various powers is called as rate law.
Rate law can be determined by the slow step or otherwise called as rate-determining step.
The overall chemical equation is represented by the net result of two elementary reactions in the mechanism. This is obtained by summing up the steps and canceling the species that occur in either side of the reactions.
A catalyst is substance that provides a pathway for the reaction to occur rapidly than in mechanism of an uncatalyzed reaction.
The catalyst gets consumed in the first step of the reaction and it can be regenerated in the later step of the reaction.
A species that is formed during a chemical reaction which does not appear in overall reacts due its presence in the following step in the mechanism is called Reaction intermediate.
To write the chemical formula of the reactants, products and the reaction intermediate
Explanation of Solution
In the potential energy diagram given below, the dotted lines represents the bonds that are formed or broken.
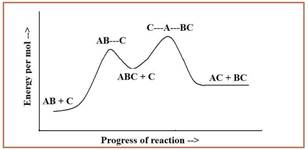
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The explanations for the given set have to be answered.
Concept Introduction:
The rate of reaction is the quantity of formation of product or the quantity of reactant used per unit time. The rate of reaction doesn’t depend on the sum of amount of reaction mixture used.
The raise in molar concentration of product of a reaction per unit time or decrease in molarity of reactant per unit time is called rate of reaction and is expressed in units of
The variation in concentration of reaction or product over a certain interval of time is called average reaction rate.
The equation that relates the reaction rate to the reactants concentrations that is raised to various powers is called as rate law.
Rate law can be determined by the slow step or otherwise called as rate-determining step.
The overall chemical equation is represented by the net result of two elementary reactions in the mechanism. This is obtained by summing up the steps and canceling the species that occur in either side of the reactions.
A catalyst is substance that provides a pathway for the reaction to occur rapidly than in mechanism of an uncatalyzed reaction.
The catalyst gets consumed in the first step of the reaction and it can be regenerated in the later step of the reaction.
A species that is formed during a chemical reaction which does not appear in overall reacts due its presence in the following step in the mechanism is called Reaction intermediate.
To write the overall reaction
Explanation of Solution
The overall reaction is given by addition of two steps of the mechanism and by eliminating intermediate ABC.
The overall reaction is given as,
(c)
Interpretation:
The explanations for the given set have to be answered.
Concept Introduction:
The rate of reaction is the quantity of formation of product or the quantity of reactant used per unit time. The rate of reaction doesn’t depend on the sum of amount of reaction mixture used.
The raise in molar concentration of product of a reaction per unit time or decrease in molarity of reactant per unit time is called rate of reaction and is expressed in units of
The variation in concentration of reaction or product over a certain interval of time is called average reaction rate.
The equation that relates the reaction rate to the reactants concentrations that is raised to various powers is called as rate law.
Rate law can be determined by the slow step or otherwise called as rate-determining step.
The overall chemical equation is represented by the net result of two elementary reactions in the mechanism. This is obtained by summing up the steps and canceling the species that occur in either side of the reactions.
A catalyst is substance that provides a pathway for the reaction to occur rapidly than in mechanism of an uncatalyzed reaction.
The catalyst gets consumed in the first step of the reaction and it can be regenerated in the later step of the reaction.
A species that is formed during a chemical reaction which does not appear in overall reacts due its presence in the following step in the mechanism is called Reaction intermediate.
To identify the rate limiting step
Explanation of Solution
The second step of the reaction is the rate limiting step since it has the highest overall energy of activation.
(d)
Interpretation:
The explanations for the given set have to be answered.
Concept Introduction:
The rate of reaction is the quantity of formation of product or the quantity of reactant used per unit time. The rate of reaction doesn’t depend on the sum of amount of reaction mixture used.
The raise in molar concentration of product of a reaction per unit time or decrease in molarity of reactant per unit time is called rate of reaction and is expressed in units of
The variation in concentration of reaction or product over a certain interval of time is called average reaction rate.
The equation that relates the reaction rate to the reactants concentrations that is raised to various powers is called as rate law.
Rate law can be determined by the slow step or otherwise called as rate-determining step.
The overall chemical equation is represented by the net result of two elementary reactions in the mechanism. This is obtained by summing up the steps and canceling the species that occur in either side of the reactions.
A catalyst is substance that provides a pathway for the reaction to occur rapidly than in mechanism of an uncatalyzed reaction.
The catalyst gets consumed in the first step of the reaction and it can be regenerated in the later step of the reaction.
A species that is formed during a chemical reaction which does not appear in overall reacts due its presence in the following step in the mechanism is called Reaction intermediate.
To propose a rate law based on rate limiting step
Explanation of Solution
The rate is written on the slow step,
The first step reaches the state of equilibrium rapidly and the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse. This is given as,
Rearranging this equation and solve for
Substitute the above in the rate law to eliminate
Rate=
(e)
Interpretation:
The explanations for the given set have to be answered.
Concept Introduction:
The rate of reaction is the quantity of formation of product or the quantity of reactant used per unit time. The rate of reaction doesn’t depend on the sum of amount of reaction mixture used.
The raise in molar concentration of product of a reaction per unit time or decrease in molarity of reactant per unit time is called rate of reaction and is expressed in units of
The variation in concentration of reaction or product over a certain interval of time is called average reaction rate.
The equation that relates the reaction rate to the reactants concentrations that is raised to various powers is called as rate law.
Rate law can be determined by the slow step or otherwise called as rate-determining step.
The overall chemical equation is represented by the net result of two elementary reactions in the mechanism. This is obtained by summing up the steps and canceling the species that occur in either side of the reactions.
A catalyst is substance that provides a pathway for the reaction to occur rapidly than in mechanism of an uncatalyzed reaction.
The catalyst gets consumed in the first step of the reaction and it can be regenerated in the later step of the reaction.
A species that is formed during a chemical reaction which does not appear in overall reacts due its presence in the following step in the mechanism is called Reaction intermediate.
To identify the type of reaction
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is identified as exothermic reaction since the energy per mole of the products is higher than the energy per mole of reactants.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardWhat is the IUPAC name of the following compound? CH₂CH₂ H CI H₂CH₂C H CH₂ Selected Answer: O (35,4R)-4 chloro-3-ethylpentane Correctarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. I I I H Select to Add Arrows HCI, CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and the follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the intermediates and product of the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and the product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardLook at the following pairs of structures carefully to identify them as representing a) completely different compounds, b) compounds that are structural isomers of each other, c) compounds that are geometric isomers of each other, d) conformers of the same compound (part of structure rotated around a single bond) or e) the same structure.arrow_forwardGiven 10.0 g of NaOH, what volume of a 0.100 M solution of H2SO4 would be required to exactly react all the NaOH?arrow_forward
- 3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forward3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forwardConcentration Trial1 Concentration of iodide solution (mA) 255.8 Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mM) 47.0 Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mM) 110.1 Temperature of iodide solution ('C) 25.0 Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL) 10.0 Volume of thiosulfate solution (5:03) used (mL) Volume of DI water used (mL) Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL) 1.0 2.5 7.5 Time (s) 16.9 Dark blue Observations Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mA) Initial Rate (mA's)arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





