
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Correct option must be chosen regarding the formation of diamond.
Concept introduction:
Diamond is one of the allotropes of C which is formed at very high pressure.
Answer to Problem 6STP
Correct answer: Option C is correct.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct option:
The phase diagram is represented as follows:
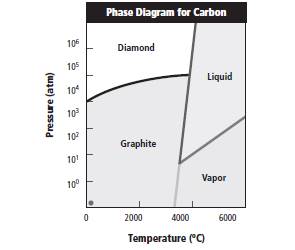
Option C is correct as when temperature is less than 3500 K and pressure is more than 100000 atm, carbon exists as diamond.
Reasons for incorrect options: Option A is incorrect as at temperature more than 5000K and pressure less than 100 atm, carbon can exist in vapor and liquid form.
Option B is incorrect as at temperature greater than 6000 K and pressure less than 25 atm, carbon exists in vapor form.
Option D is incorrect as at temperature less than 4500 K and pressure less than 10 atm, carbon exists as graphite form.
Chapter 12 Solutions
Glencoe Chemistry: Matter and Change, Student Edition
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- One step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardWhy does the following reaction lead to poor yields? Correct the reaction. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardDraw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardI have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





