
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
8th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744127
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 12, Problem 45P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The change in the degree of regioselectivity compared to the ratio of relative rates found in problem 44 has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Chlorine radical forms a tertiary radical five times faster than a primary radical and it forms a secondary radical 3.8 times faster than a primary radical.
Relative rates of alkyl radical formation by a chlorine radical at 125 °C.
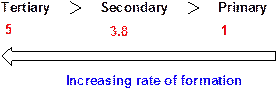
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Provide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.
Identify which compound is more acidic. Justify your choice.
Provide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 12.2 - Prob. 1PCh. 12.2 - Write the steps for formation of...Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 3PCh. 12.4 - How many alkyl chlorides are obtained from...Ch. 12.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 12.5 - Prob. 8PCh. 12.5 - a. Would chlorination or bromination produce a...Ch. 12.5 - Show how the following compounds could be prepared...Ch. 12.6 - Prob. 12PCh. 12.7 - Prob. 13P
Ch. 12.7 - Prob. 14PCh. 12.8 - Prob. 15PCh. 12.8 - Draw the stereoisomers of the major...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 18PCh. 12.9 - How many allylic substituted bromoalkenes are...Ch. 12.9 - a. How many stereoisomers are formed from the...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 21PCh. 12.9 - Prob. 22PCh. 12.10 - Prob. 23PCh. 12.11 - How many atoms share the unpaired electrons in...Ch. 12.11 - Prob. 25PCh. 12 - Prob. 26PCh. 12 - Prob. 27PCh. 12 - Prob. 28PCh. 12 - Prob. 29PCh. 12 - Prob. 30PCh. 12 - Prob. 31PCh. 12 - Prob. 32PCh. 12 - Prob. 33PCh. 12 - Prob. 34PCh. 12 - Prob. 35PCh. 12 - Prob. 36PCh. 12 - Prob. 37PCh. 12 - a. What five-carbon alkene forms the same product...Ch. 12 - Prob. 39PCh. 12 - Starting with cyclohexane, how could the following...Ch. 12 - a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 12 - What stereoisomers are obtained from the following...Ch. 12 - Prob. 43PCh. 12 - Prob. 44PCh. 12 - Prob. 45PCh. 12 - Draw the products of the following reactions,...Ch. 12 - Prob. 47PCh. 12 - Prob. 48PCh. 12 - Prob. 49PCh. 12 - Explain why the rate of bromination of methane...Ch. 12 - Prob. 51PCh. 12 - Prob. 1PCh. 12 - Prob. 2PCh. 12 - Prob. 3PCh. 12 - Prob. 4P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Given the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardk₁ Given the reaction A B, indicate k-1 d[A] (A). the rate law with respect to A: (B). the rate law with respect to B: d[B] dt dtarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning 
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Kinetics: Initial Rates and Integrated Rate Laws; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wYqQCojggyM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY