
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of
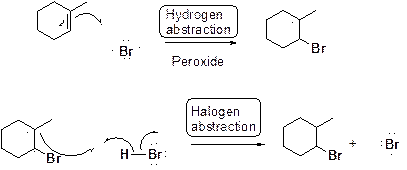
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
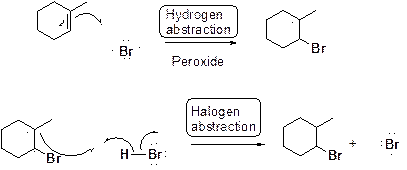
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
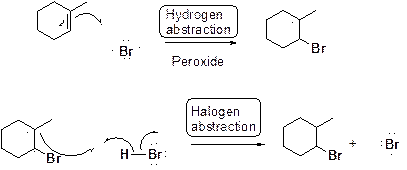
(f)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
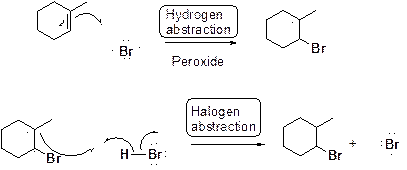
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Name the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward1b. Br LOHarrow_forwardI would like my graphs checked please. Do they look right? Do I have iodine and persulfate on the right axis ?arrow_forward
- Reaction Fill-ins Part 2! Predict the product(s) OR starting material of the following reactions. Remember, Hydride shifts are possible if/when a more stable carbocation can exist (depending on reaction mechanism)! Put your answers in the indicated boxes d. d. ง HCIarrow_forwardA cylinder contains 12 L of water vapour at 150˚C and 5 atm. The temperature of the water vapour is raised to 175˚C, and the volume of the cylinder is reduced to 8.5 L. What is the final pressure of the gas in atmospheres? assume that the gas is idealarrow_forwardOn the next page is an LC separation of the parabens found in baby wash. Parabens are suspected in a link to breast cancer therefore an accurate way to quantitate them is desired. a. In the chromatogram, estimate k' for ethyl paraben. Clearly indicate what values you used for all the terms in your calculation. b. Is this a "good" value for a capacity factor? Explain. c. What is the resolution between n-Propyl paraben and n-Butyl paraben? Again, indicate clearly what values you used in your calculation. MAU | Methyl paraben 40 20 0 -2 Ethyl paraben n-Propyl paraben n-Butyl paraben App ID 22925 6 8 minarrow_forward
- d. In Figure 4, each stationary phase shows some negative correlation between plate count and retention factor. In other words, as k' increases, N decreases. Explain this relationship between k' and N. Plate Count (N) 4000 3500 2500 2000 1500 1000 Figure 4. Column efficiency (N) vs retention factor (k') for 22 nonionizable solutes on FMS (red), PGC (black), and COZ (green). 3000 Eluent compositions (acetonitrile/water, A/W) were adjusted to obtain k' less than 15, which was achieved for most solutes as follows: FMS (30/70 A/W), PGC (60/40), COZ (80/20). Slightly different compositions were used for the most highly retained solutes. All columns were 50 mm × 4.6 mm id and packed with 5 um particles, except for COZ, which was packed with 3 um particles. All other chromatographic conditions were constant: column length 5 cm, column j.§. 4.6 mm, flow rate 2 mL/min, column temperature 40 °C, and injection volume 0.5 μL Log(k'x/K'ethylbenzene) FMS 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 ཐྭ ཋ ཤྩ བྷྲ ; 500 0 5 10…arrow_forwardf. Predict how the van Deemter curve in Figure 7 would change if the temperature were raised from 40 °C to 55 °C. Figure 7. van Desmter curves in reduced coordinates for four nitroalkane homologues (nitropropane, black; nitrobutane, red; nitropentane, blue; and nitrohexane, green) separated on the FMS phase. Chromatographic conditions: column dimensions 50 mm × 4.6 mm id, eluent 30/70 ACN/water, flow rates 0.2-5.0 mL/min, injection volume 0.5 and column temperature 40 °C. No corrections to the plate heights have been made to account for extracolumn dispersion. Reduced Plate Height (h) ° 20 40 60 Reduced Velocity (v) 8. (2) A water sample is analyzed for traces of benzene using headspace analysis. The sample and standard are spiked with a fixed amount of toluene as an internal standard. The following data are obtained: Ppb benzene Peak area benzene Peak area toluene 10.0 252 376 Sample 533 368 What is the concentration of benzene in the sample?arrow_forwardLiquid chromatography has been used to track the concentration of remdesivir (a broad-spectrum antiviral drug, structure shown at right) in COVID patients undergoing experimental treatments. Intensity The authors provide the following details regarding standard solutions preparation: HN CN HO OH NH2 Remdesivir (RDV) stock solution (5000 µg/mL) was prepared by dissolving RDV drug powder using the mixture of DMSO: MeOH (30:70 v/v). The RDV working standard solutions for calibration and quality controls were prepared using methanol in concentrations of 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 µg/mL. 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100, 250, 500, 1000, and 5000 ng/mL sample solutions were prepared freshly by spiking calibration standard solutions into the blank human plasma samples for method calibration. a) What type of calibration method is being described? Why do you think the authors chose this method as opposed to another? b) Based on the details provided in part a, describe an appropriate method blank…arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


