
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of chlorination product obtained from radical chlorination of methylcyclohexane has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
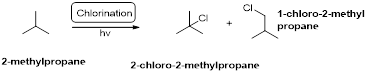
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in greater yield should be given and explained.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
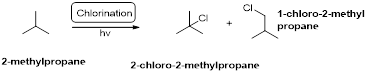
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of monochlorination products obtained by considering all stereoisomers should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
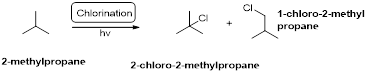
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Tartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forwardCan I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forward
- Ordene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
- Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction. For the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) · 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 -> NO2 + NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 →> N2O5 (k-1) → NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Give the expression for the acceptable rate. (A). d[N₂O] dt = -1 2k,k₂[N205] k₁+k₂ d[N₂O5] (B). dt =-k₁[N₂O₂] + k₁[NO2][NO3] - k₂[NO2]³ (C). d[N₂O] dt =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[N205] - K3 [NO] [N205] (D). d[N2O5] =-k₁[NO] - K3[NO] [N₂05] dtarrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 20.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFor the decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 NO2 + NO3 (K1) | NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) | NO2 + NO3 NO2 + O2 + NO (k2) | NO + N2O51 NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) → Give the expression for the acceptable rate. → → (A). d[N205] dt == 2k,k₂[N₂O₂] k₁+k₁₂ (B). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k₁[NO₂] [NO3] - k₂[NO₂]³ dt (C). d[N2O5] =-k₁[N₂O] + k [NO] - k₂[NO] [NO] d[N2O5] (D). = dt = -k₁[N2O5] - k¸[NO][N₂05] dt Do not apply the calculations, based on the approximation of the stationary state, to make them perform correctly. Basta discard the 3 responses that you encounter that are obviously erroneous if you apply the formula to determine the speed of a reaction.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

